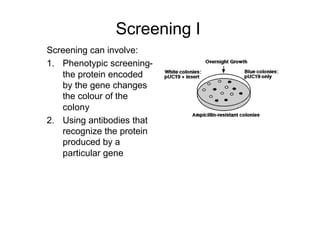
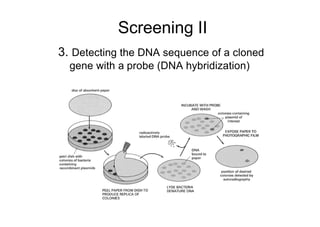
This document discusses gene cloning and summarizes key steps in the process:
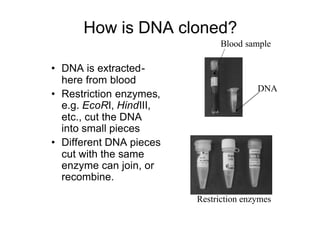
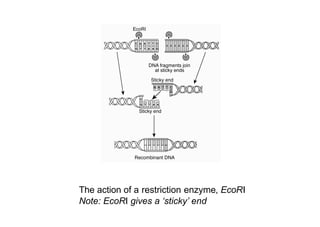
1. DNA is extracted from a sample and cut into fragments using restriction enzymes.
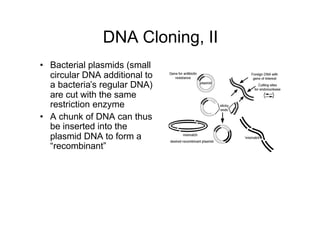
2. Bacterial plasmids are also cut with the same restriction enzymes.
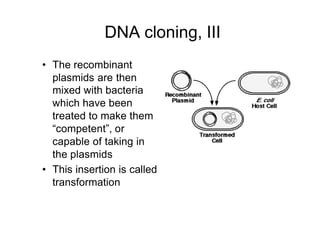
3. DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmids through recombination, creating recombinant plasmids.
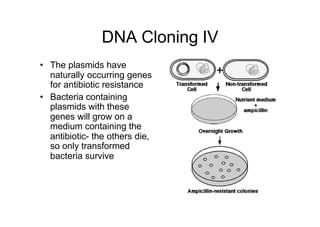
4. The recombinant plasmids are introduced into bacteria through transformation. Transformed bacteria are selected by their ability to grow in antibiotic-containing media, as the plasmids contain antibiotic resistance genes.






![Expression of the Lipase Encoded by
Expression of the Lipase Encoded by
ORF1
ORF1
kD M 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
In its native form: [using ORF1]
97
66
45
31
22
14
97
66
45
31
22
14
kD M 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
F Expression was
observed in all
fractions:
supernatant,
periplasm, soluble
cytoplasm and
insoluble
cytoplasm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnacloning-230725111448-a1c59d38/85/dna-cloning-pdf-19-320.jpg)
![Characterization of the Lipase:
Characterization of the Lipase:
Effect of T and pH on the Activity
Effect of T and pH on the Activity
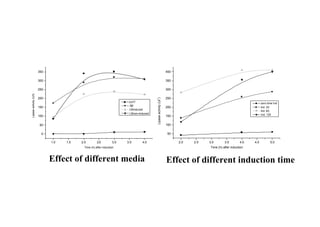
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
Temperature °C
Residual
activity
[%]
Optimum
temperature
Thermostability
(A)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
5 6 7 8 9 10 11
pH
Residual
activity
[%]
(A)
PNP-palmitate, 60°C
PNP-palmitate, T 60°C, pH 7.5
PNP-palmitate, 60°C,pH 7.5
0
50
100
150
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Time (min)
Relative
activity
[%]
pH 5.0
pH 10.5
(B)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Time (min)
Residual
activity
[%]
70 °C
(B)
PNP-palmitate, 60°C, pH 9.5
PNP-palmitate, pH 7.5 PNP-palmitate, T 60°C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnacloning-230725111448-a1c59d38/85/dna-cloning-pdf-20-320.jpg)