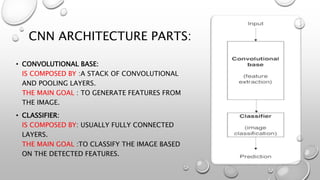
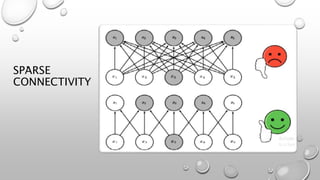
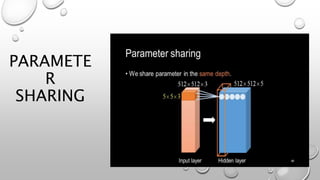
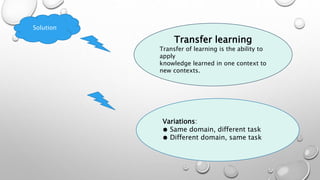
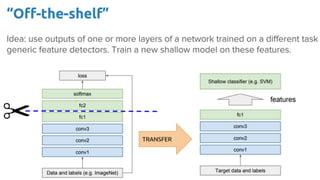
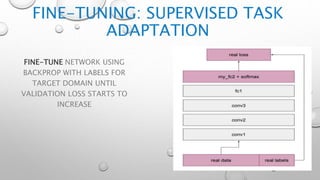
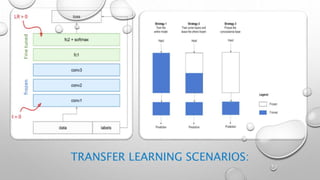
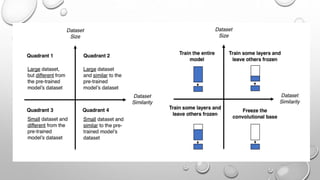
CNNs are a type of neural network that can analyze visual imagery. They use convolutional and pooling layers to automatically extract image features and classify images. CNNs use convolution operations instead of general matrix multiplication, which allows them to identify important characteristics in images. They have sparse connectivity and parameter sharing that make them effective for tasks like computer vision, NLP, and audio analysis. Transfer learning is commonly used with CNNs to repurpose pre-trained models for new problems by retraining only the final layers.