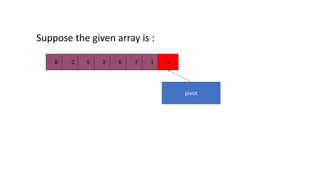
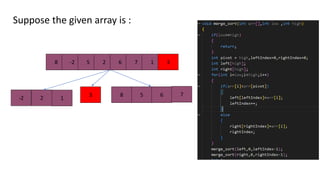
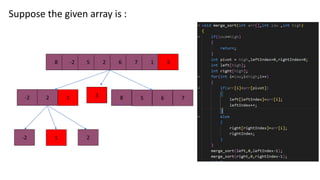
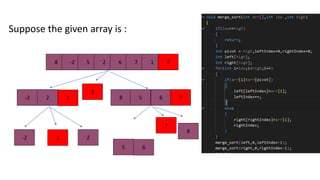
Quick sort is a sorting algorithm that uses divide-and-conquer to partition an array into two sub-arrays based on a pivot element, and then recursively sorts the sub-arrays. It works by picking a pivot element, partitioning the array into elements less than or equal to the pivot and elements greater than the pivot, and then applying quicksort recursively on the two sub-arrays. Quick sort has an average time complexity of O(nlogn) and is often faster in practice than other popular sorting algorithms like merge sort and heap sort.




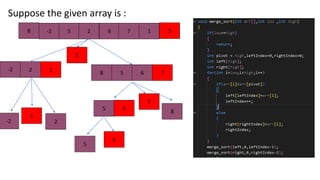
![Working procedure of quick sort
[8, -2, 5, 2, 6, 7, 1, 3]
3
-2,2,1 8,5,6,7
5,6
-2 2
1
7
6
8
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samiul13quicksort-231222124008-dfce620c/85/Quicksort-algorithm-and-implantation-process-5-320.jpg)