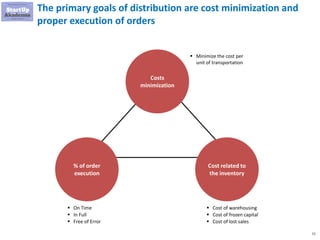
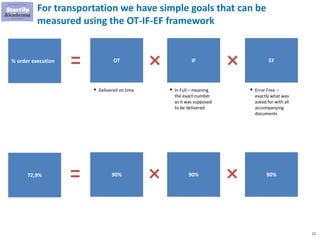
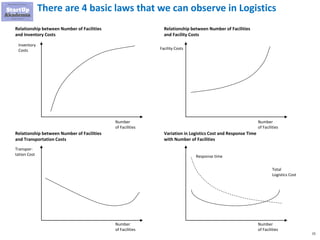
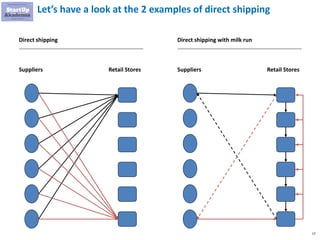
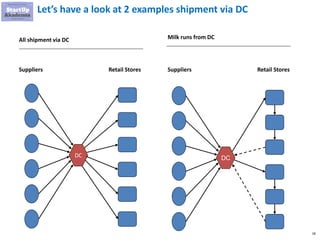
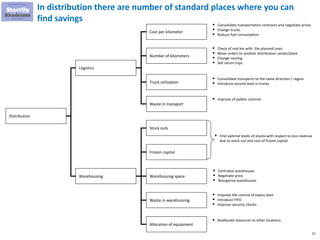
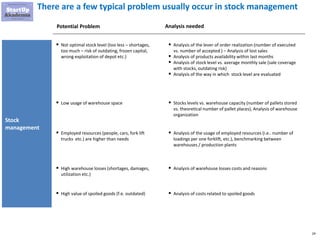
The document discusses key aspects of distribution and logistics for management consultants, emphasizing the complexity of supply chains and the importance of analytical and innovative approaches to find savings and improvements. It outlines the goals of the distribution model, basic laws of distribution, and typical problems encountered, providing strategies for cost minimization and optimization in logistics. Additionally, it offers links to courses and presentations for further learning on supply chain management and consulting techniques.