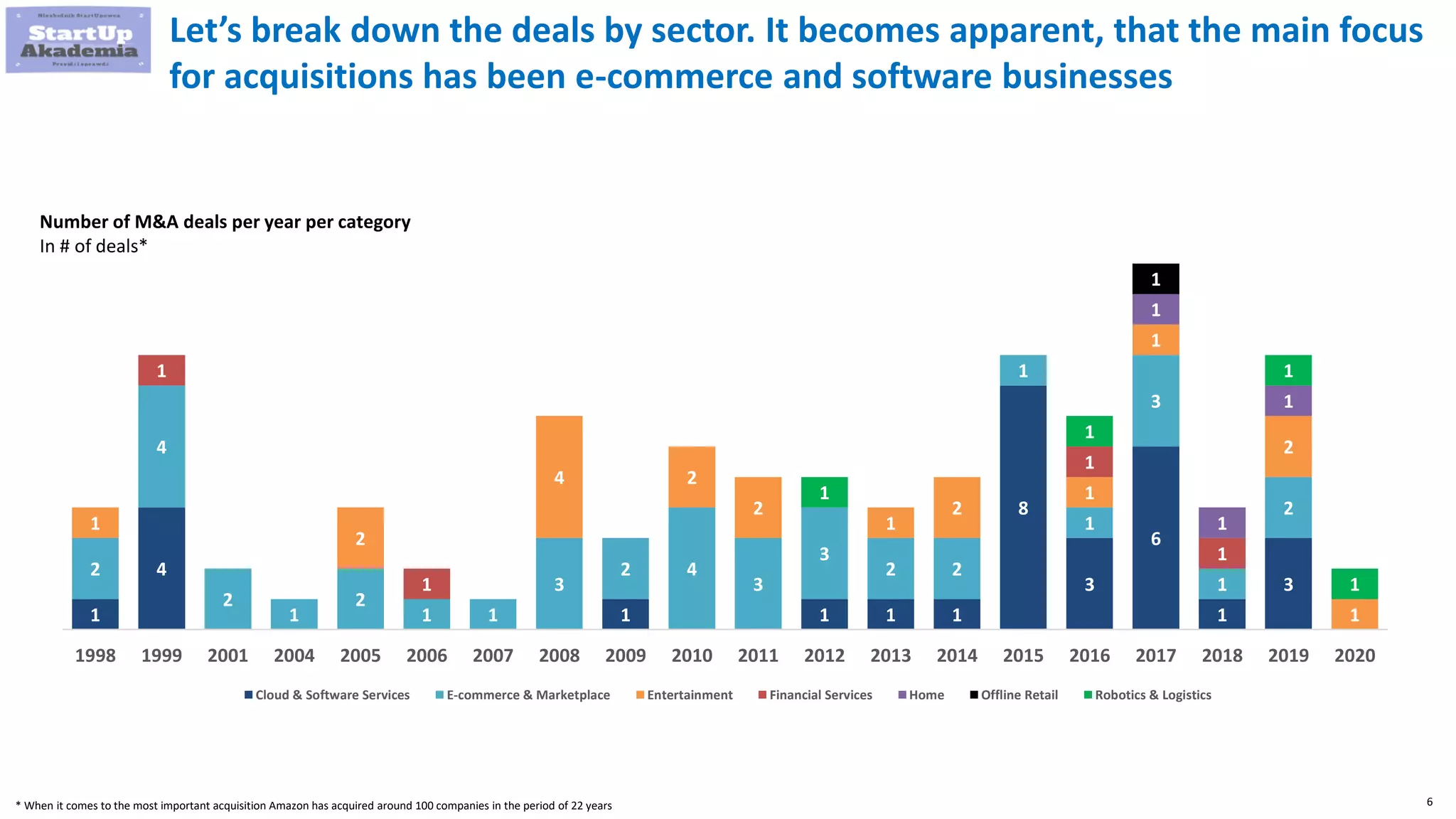
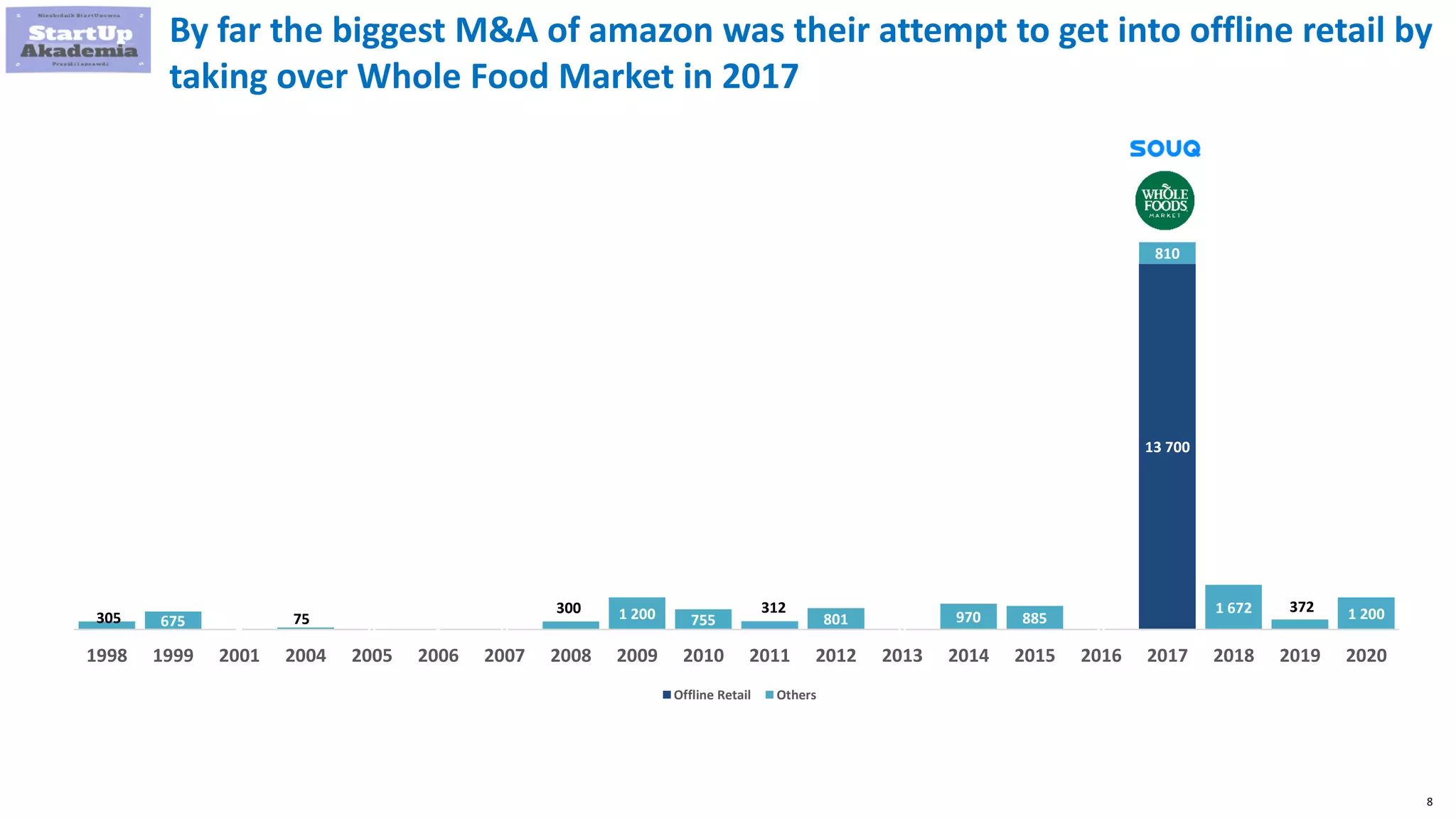
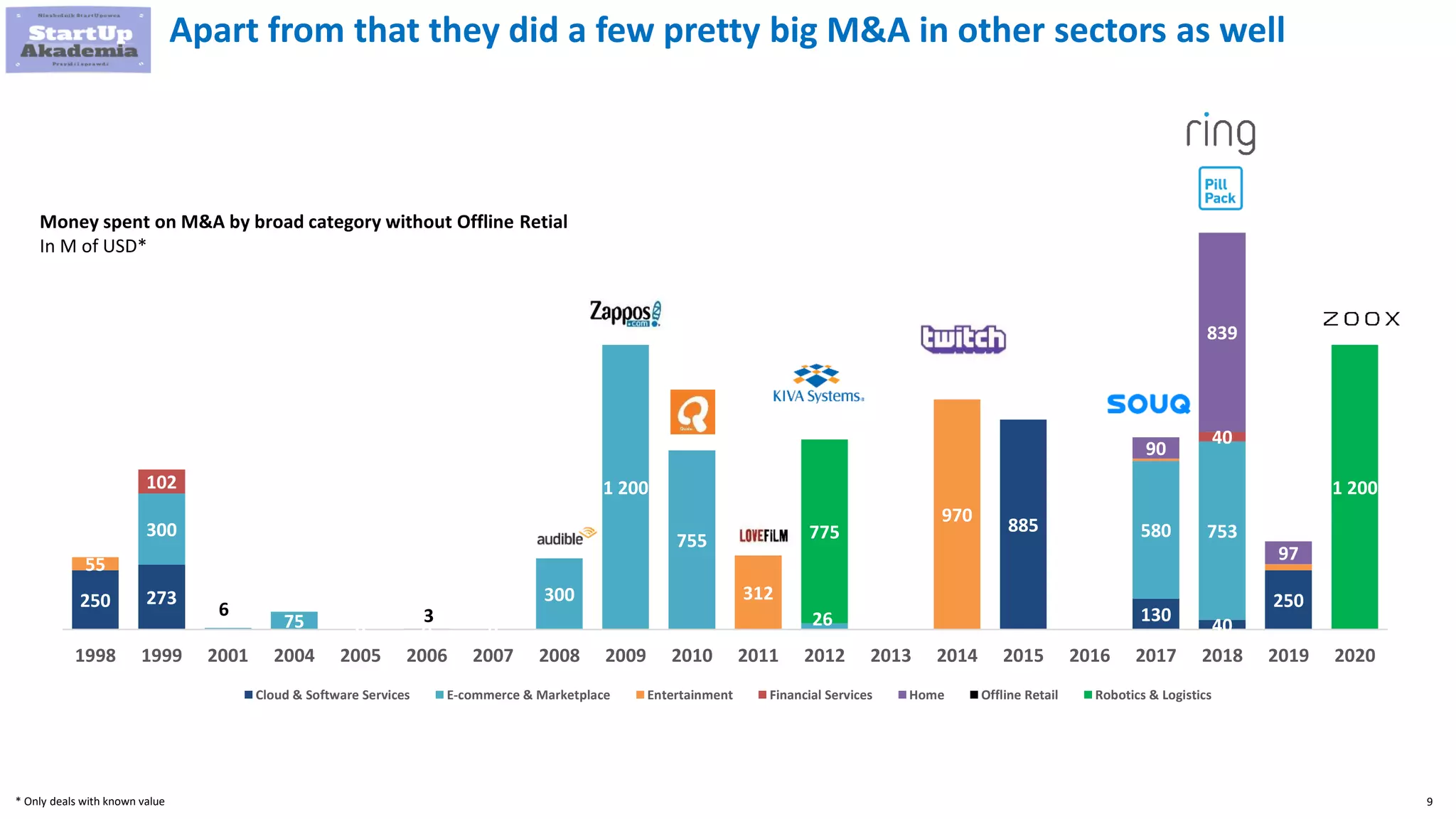
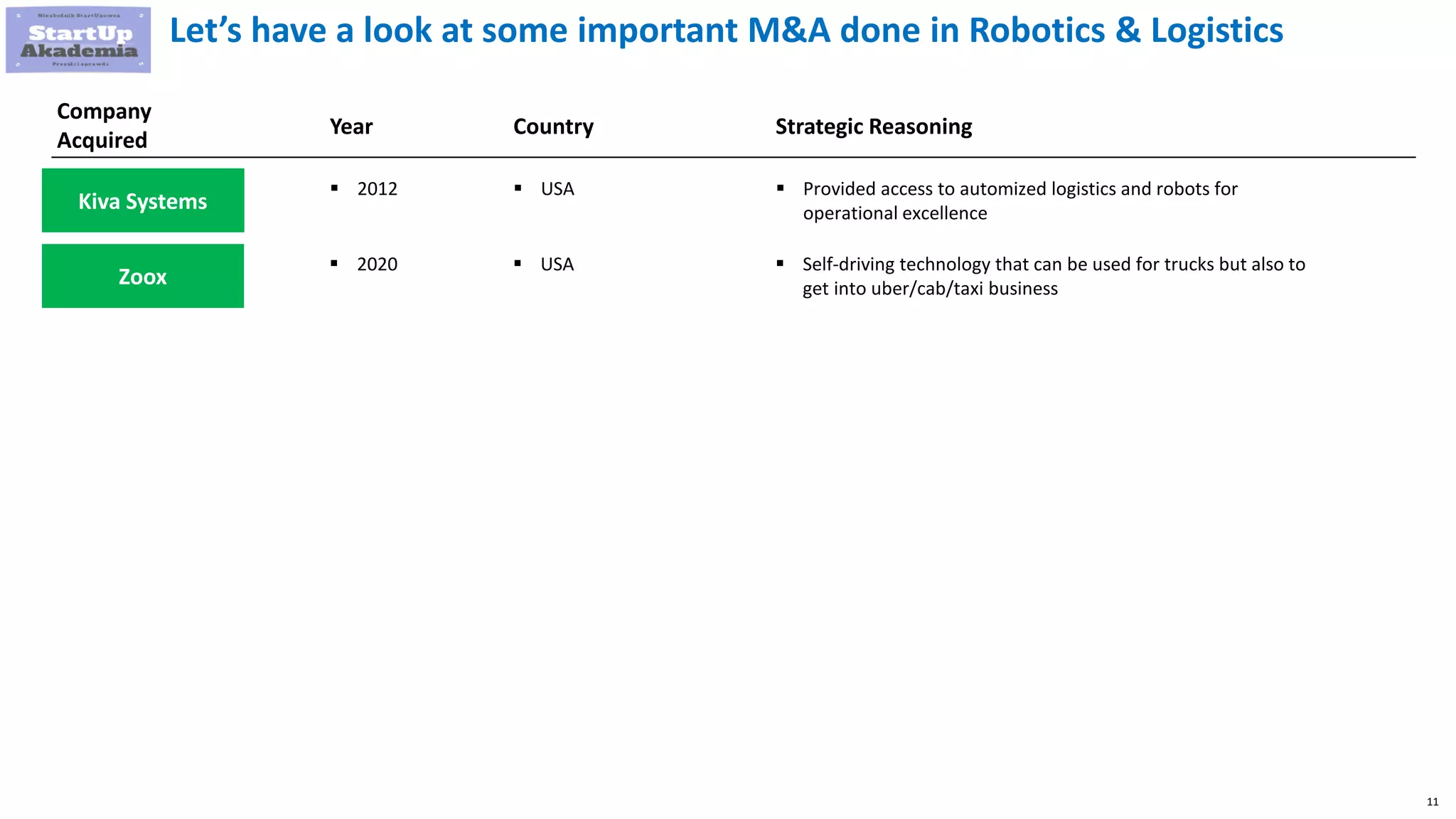
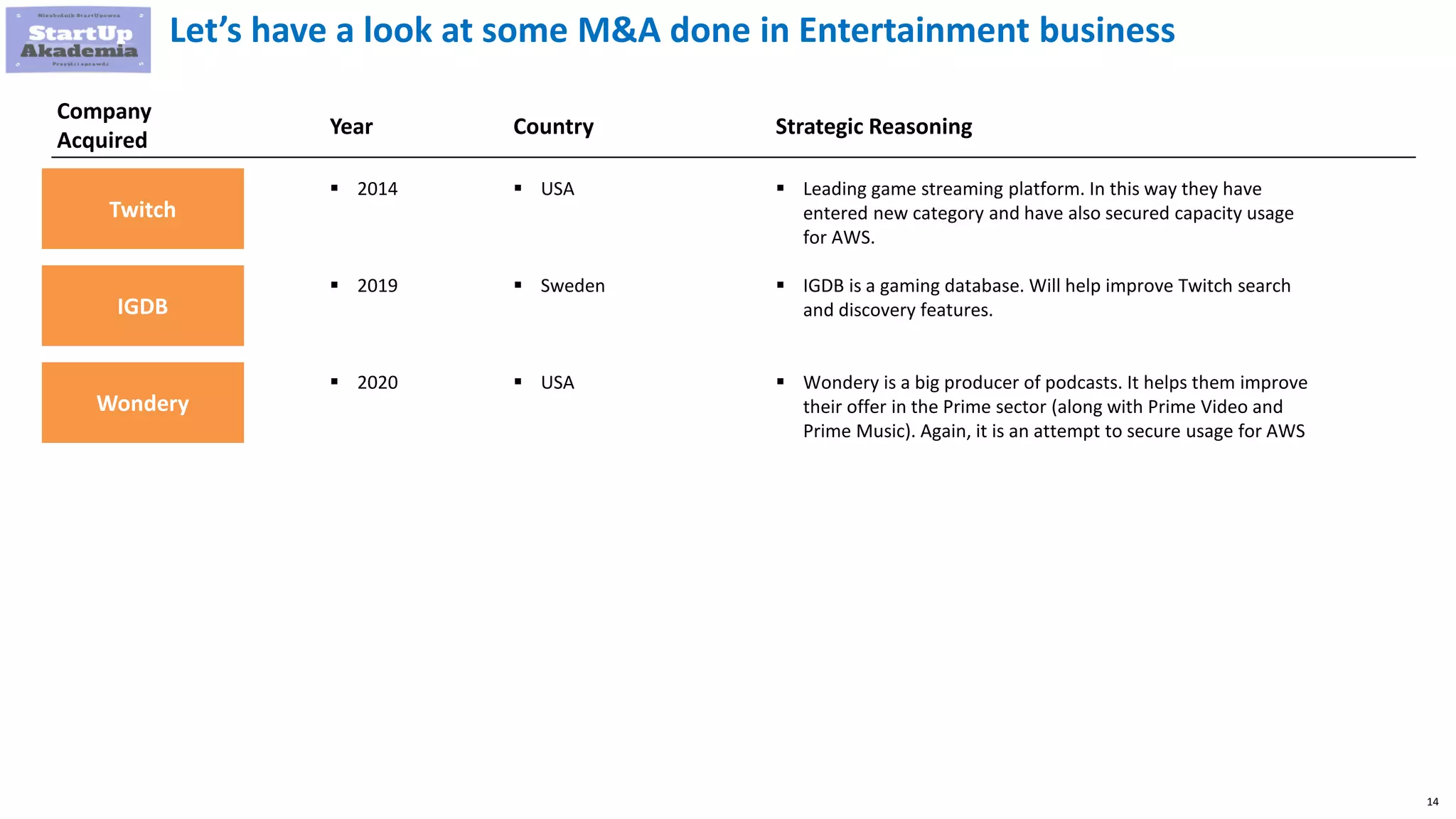
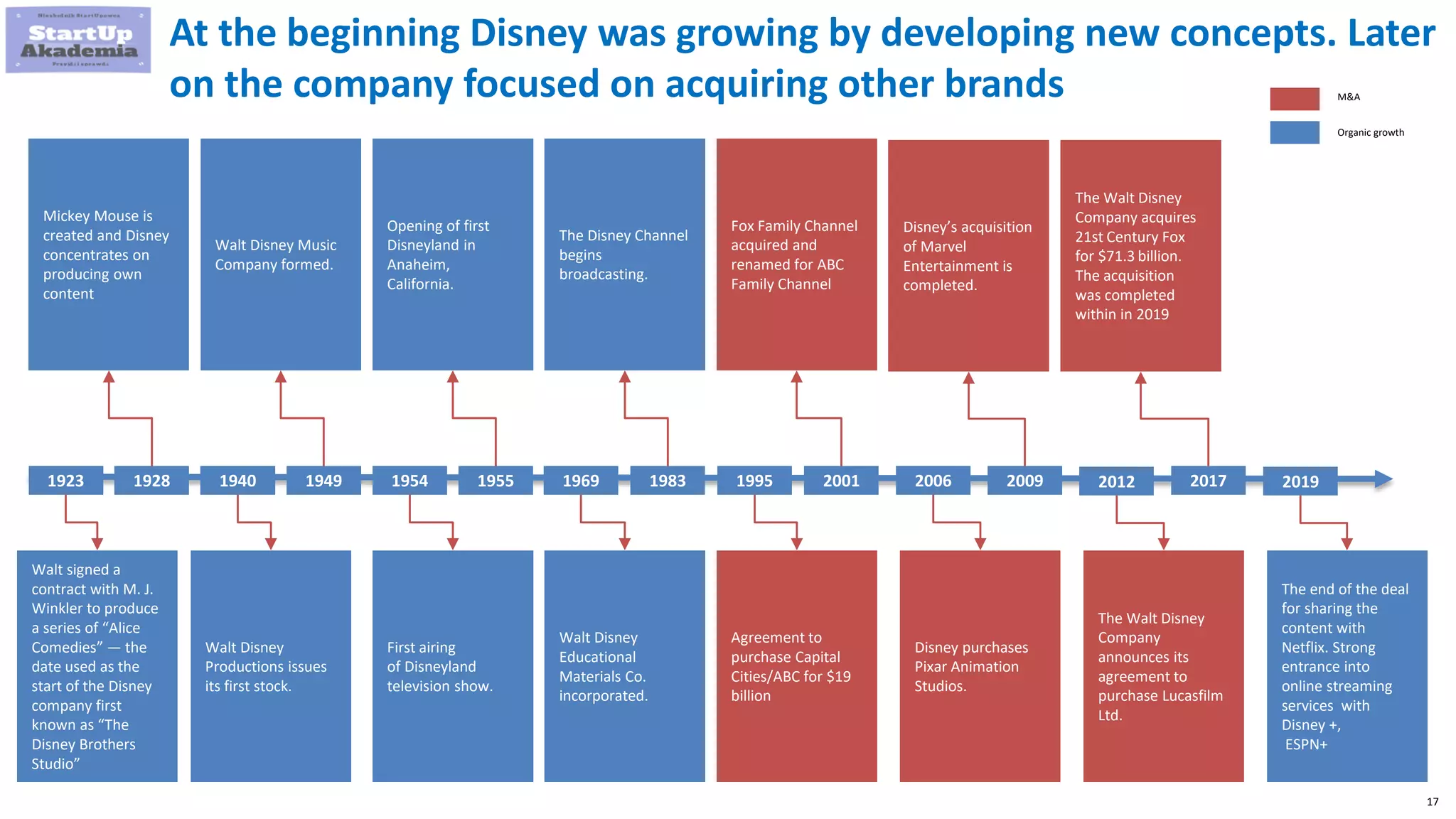
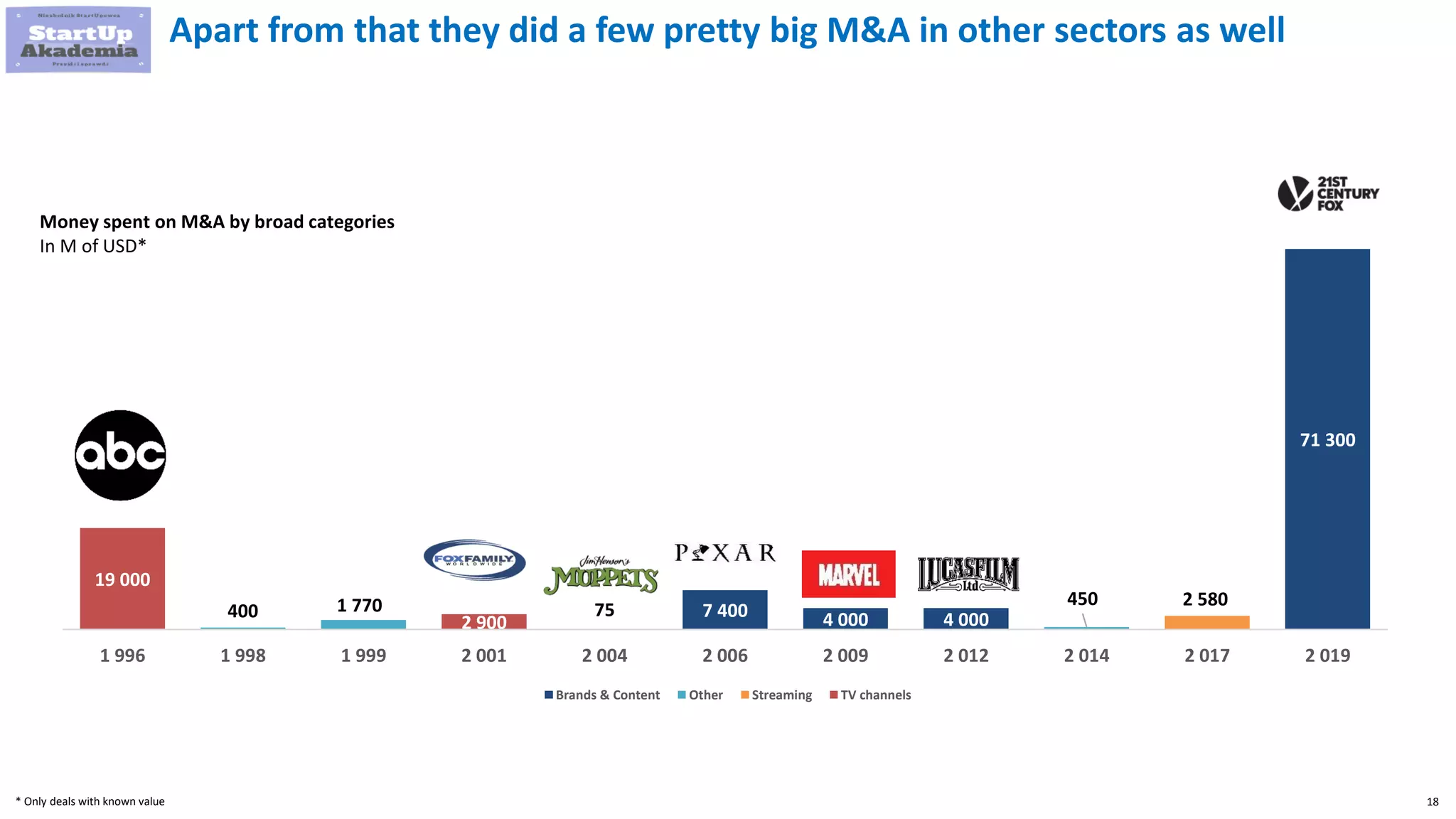
Amazon has pursued mergers and acquisitions (M&A) aggressively since 1998, primarily to expand into new markets, eliminate competition, and acquire technology that provides a competitive edge, with a notable focus on e-commerce and software sectors. Over 22 years, Amazon has completed around 100 acquisitions, with significant deals including Whole Foods Market in 2017 and various technology firms to bolster its logistics and cloud services. In contrast, Disney's M&A strategy has evolved from organic growth to large acquisitions of brands like Pixar, Marvel, and 21st Century Fox, enhancing its portfolio and streaming capabilities.