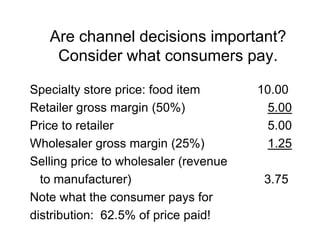
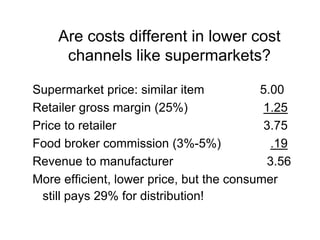
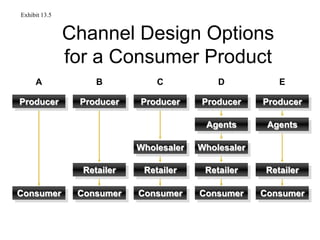
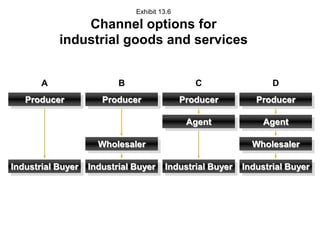
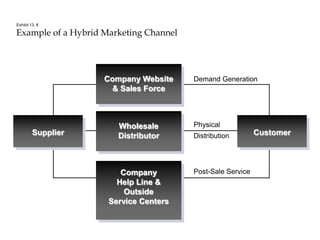
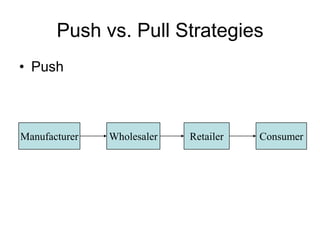
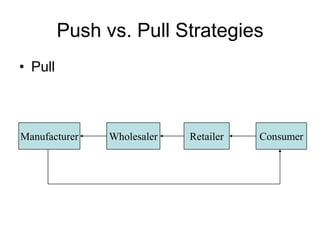
Distribution channels are an important part of the supply chain that focuses on making products available to customers. Channel decisions can significantly impact what consumers pay, with distribution costs sometimes accounting for over 60% of the retail price. While more efficient channels like supermarkets have lower margins, distribution still makes up around 30% of the consumer price. Producers have various channel options to sell directly to consumers or through retailers, agents, wholesalers or a hybrid system. The objectives are to make the right products available to customers at the right time and place cost effectively while meeting service requirements.