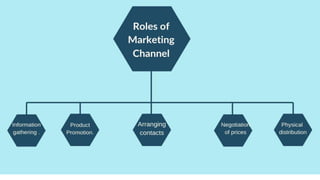
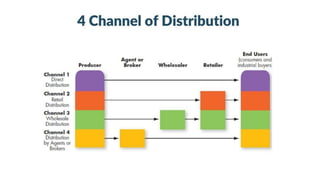
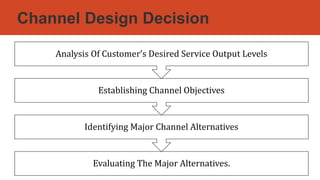
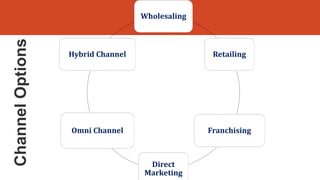
This document discusses key aspects of distribution channels and retail formats. It outlines the functions of distribution channels in buying, carrying inventory, selling, transporting, financing, promoting, negotiating, conducting market research, and servicing. It also discusses channel design considerations like establishing objectives, identifying alternatives, and evaluating options. Finally, it describes various retail formats like convenience stores, department stores, supermarkets, hypermarkets, discount stores, and factory outlets.