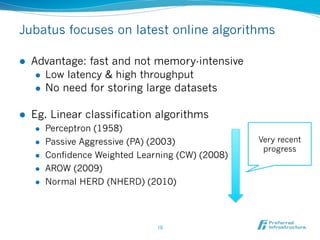
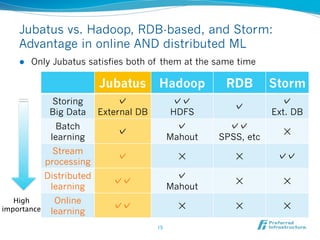
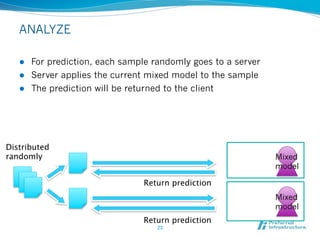
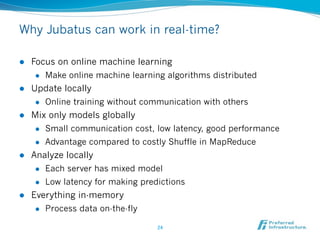
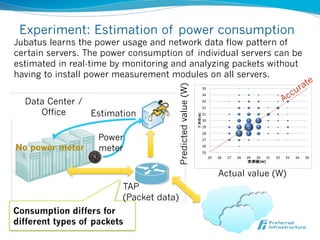
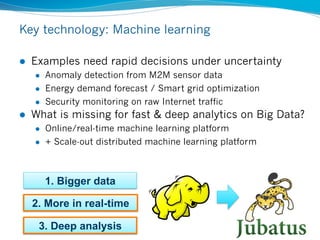
Jubatus is an open-source online machine learning platform designed for big data analytics, allowing for real-time and deep analysis without the need for storage or data sharing. It offers unique features like online learning and a loose model-sharing system, differentiating it from existing frameworks like Hadoop and Mahout. The platform supports various machine learning functions, including classification and anomaly detection, and has demonstrated high efficiency in applications such as Twitter data classification and real-time power consumption estimation.


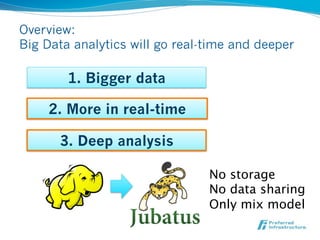
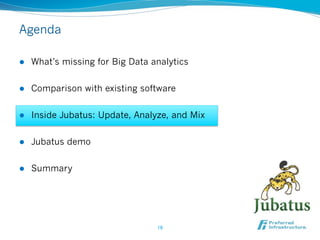
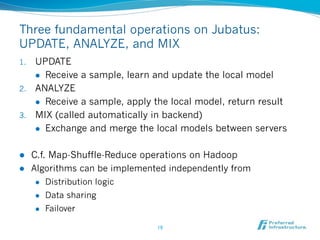
![Increasing demand in Big Data applications:
Real-time deeper analysis
l Current focus: aggregation and rule processing on bigger data
l CEP (Complex Event Processing) for real-time processing
l Hadoop/MapReduce for distributed computation
l Future: deeper analysis for rapid decisions and actions
l Ex. 1: Defect detection on NY power grid [Rubin+,TPAMI2012]
l Ex. 2: Proactive algorithmic trading [ComputerWorldUK, 2011]
Data size
What will
Hadoop come?
CEP
Deep
Reference:http://web.mit.edu/rudin/www/TPAMIPreprint.pdf
5
analysis
http://www.computerworlduk.com/news/networking/3302464/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jubatusxldbasia-120814192725-phpapp02/85/Distributed-Online-Machine-Learning-Framework-for-Big-Data-5-320.jpg)
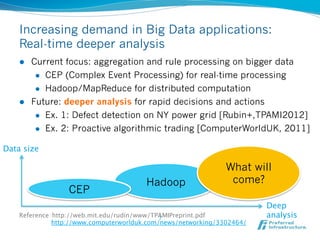
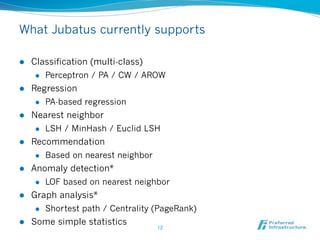
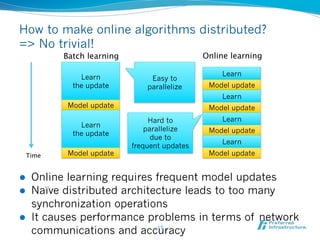
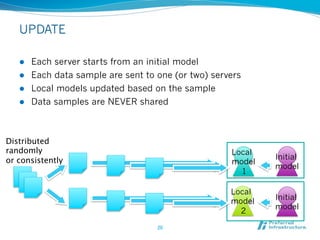
![Online learning or distributed learning:
No unified solution has been available
l Jubatus combines them into a unified computation framework
Real-time/
Online
Online ML alg.: Jubatus
PA [2003] 2011-
CW[2008]
Large scale
Small scale &
Stand-alone Distributed/
Parallel
WEKA Mahout computing
1993- 2006-
SPSS
1988-
Batch
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jubatusxldbasia-120814192725-phpapp02/85/Distributed-Online-Machine-Learning-Framework-for-Big-Data-9-320.jpg)