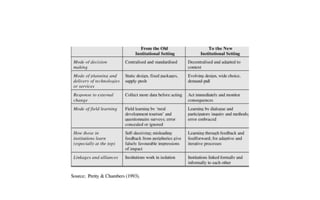
The document discusses different approaches in social sciences, including institutionalism. It describes institutionalism as a subject matter, method, and theory. As a subject matter, it focuses on the study of political institutions. As a method, it is descriptive, inductive, formal-legal, and comparative in examining institutions historically. As a theory, it makes claims about the causes and consequences of institutions and supports democratic values.