This document discusses various types of display devices used for visual presentation of information. It describes cathode ray tube displays, LED displays, vacuum fluorescent displays, gas discharge displays, plasma display panels, and liquid crystal displays. The key points covered are:
- Display devices include analog cathode ray tubes and various digital displays such as LED, LCD, plasma, and gas discharge displays.
- Flat panel displays like LED, LCD, plasma and OLED are thinner alternatives to bulky cathode ray tubes.
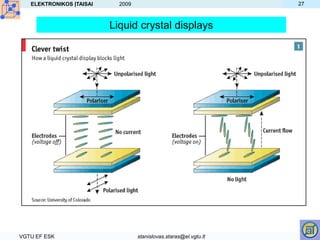
- LCDs use liquid crystals that can be electrically controlled to change the orientation of molecules and thereby manipulate light transmission through a cell.
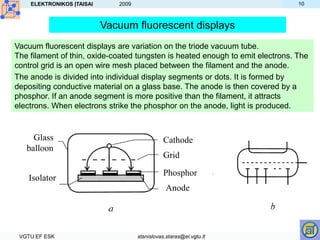
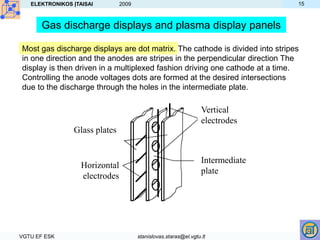
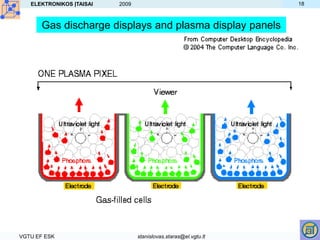
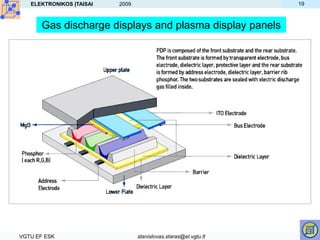
- Other displays like LED, plasma and gas discharge operate by exciting materials with electric