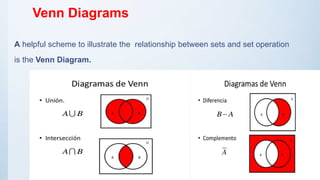
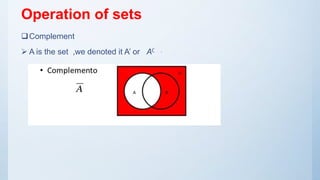
The document defines sets and describes their key characteristics and operations. It defines a set as a collection of distinct objects, and outlines different types of sets including empty, finite, infinite, subset, disjoint, equal, union, and intersection sets. It also explains Venn diagrams and common set operations such as union, intersection, and complement. Finally, it lists several laws of sets including commutative, associative, idempotent, distributive, and De Morgan's laws.