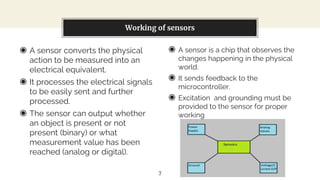
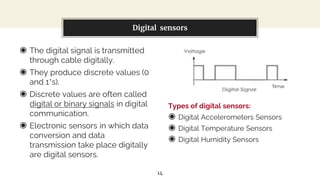
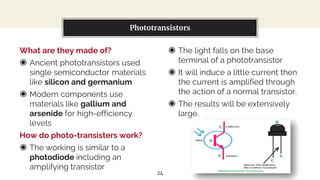
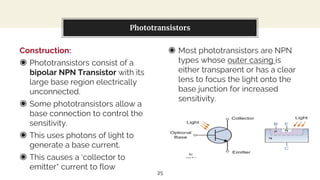
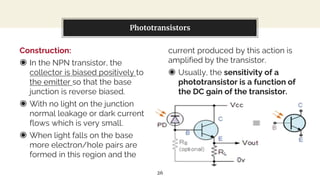
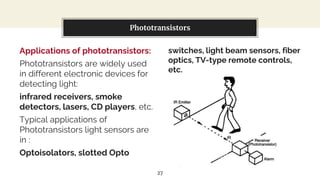
This presentation discusses diode-based sensors. It begins by defining sensors as devices that detect inputs from the environment and output a human-readable signal. It then discusses the basic components and workings of sensors, distinguishing between analog and digital sensors. Regarding analog sensors, it provides examples like temperature, pressure, and light sensors. For digital sensors, it notes they output discrete binary values. The presentation then focuses on applications of diodes in light and temperature sensing. It describes photodiodes, phototransistors, and how they can be used in light sensors. It also explains how peltier diodes and pn-junctions can act as temperature sensors by changing voltage with temperature.