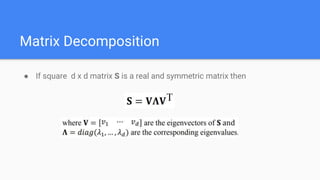
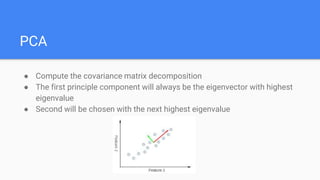
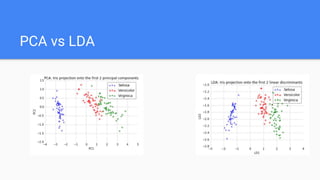
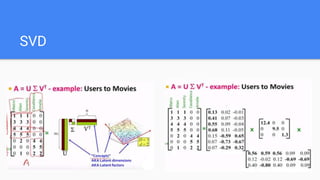
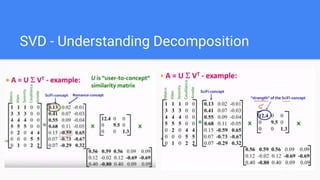
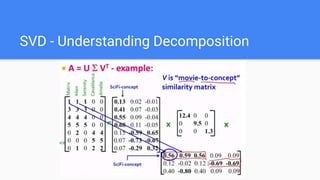
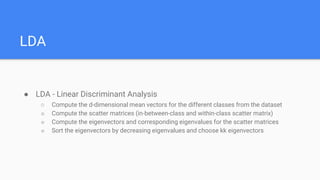
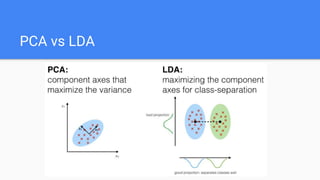
The document provides an overview of dimensionality reduction techniques, including PCA, SVD, and LDA. PCA uses linear projections to reduce dimensions while preserving variance in the data. It computes eigenvectors of the covariance matrix. SVD is similar to PCA but works directly with the data matrix rather than the covariance matrix. LDA aims to maximize class separability during dimensionality reduction for classification tasks. It computes within-class and between-class scatter matrices. While PCA maximizes variance, LDA maximizes class discrimination.