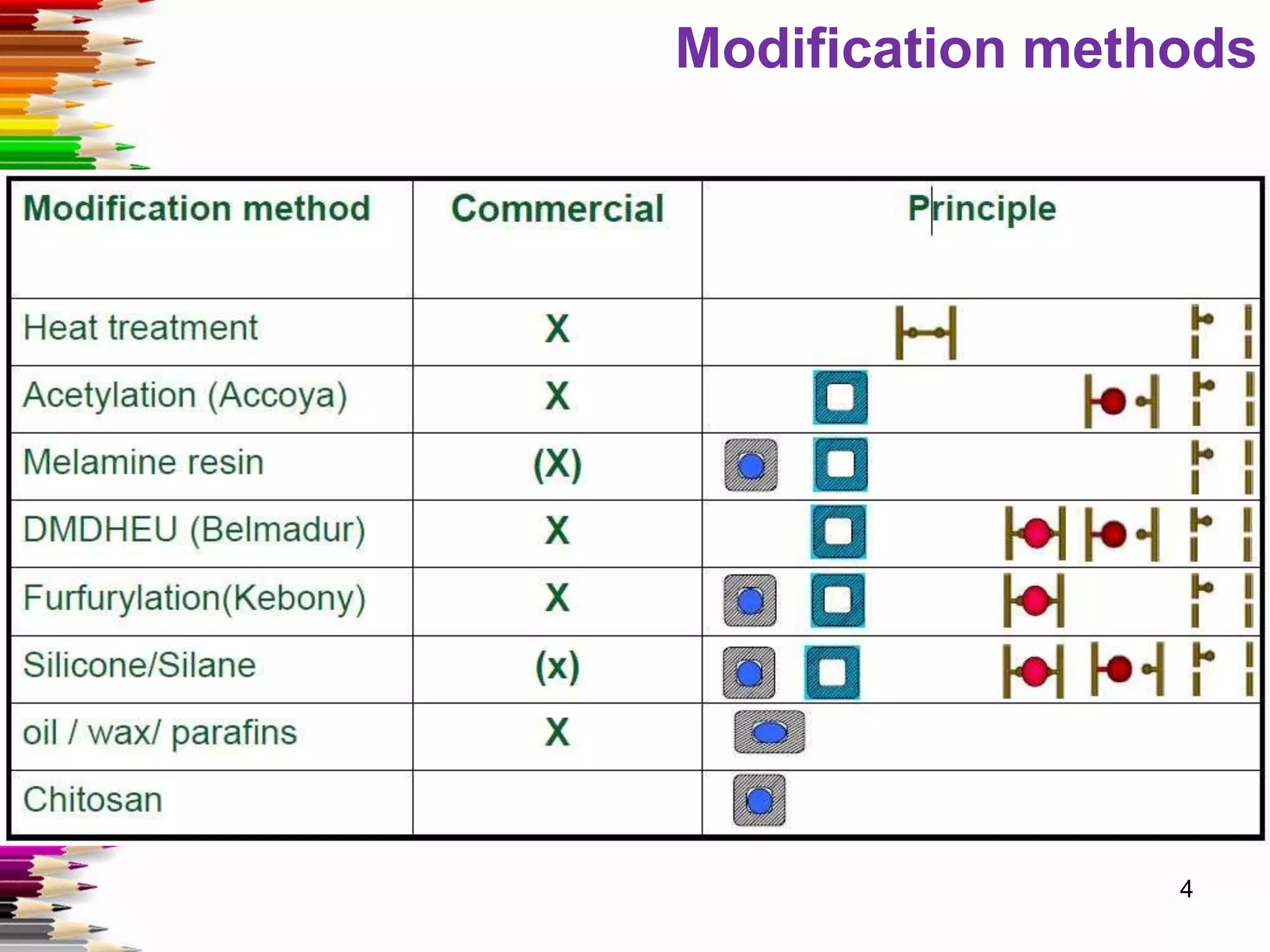
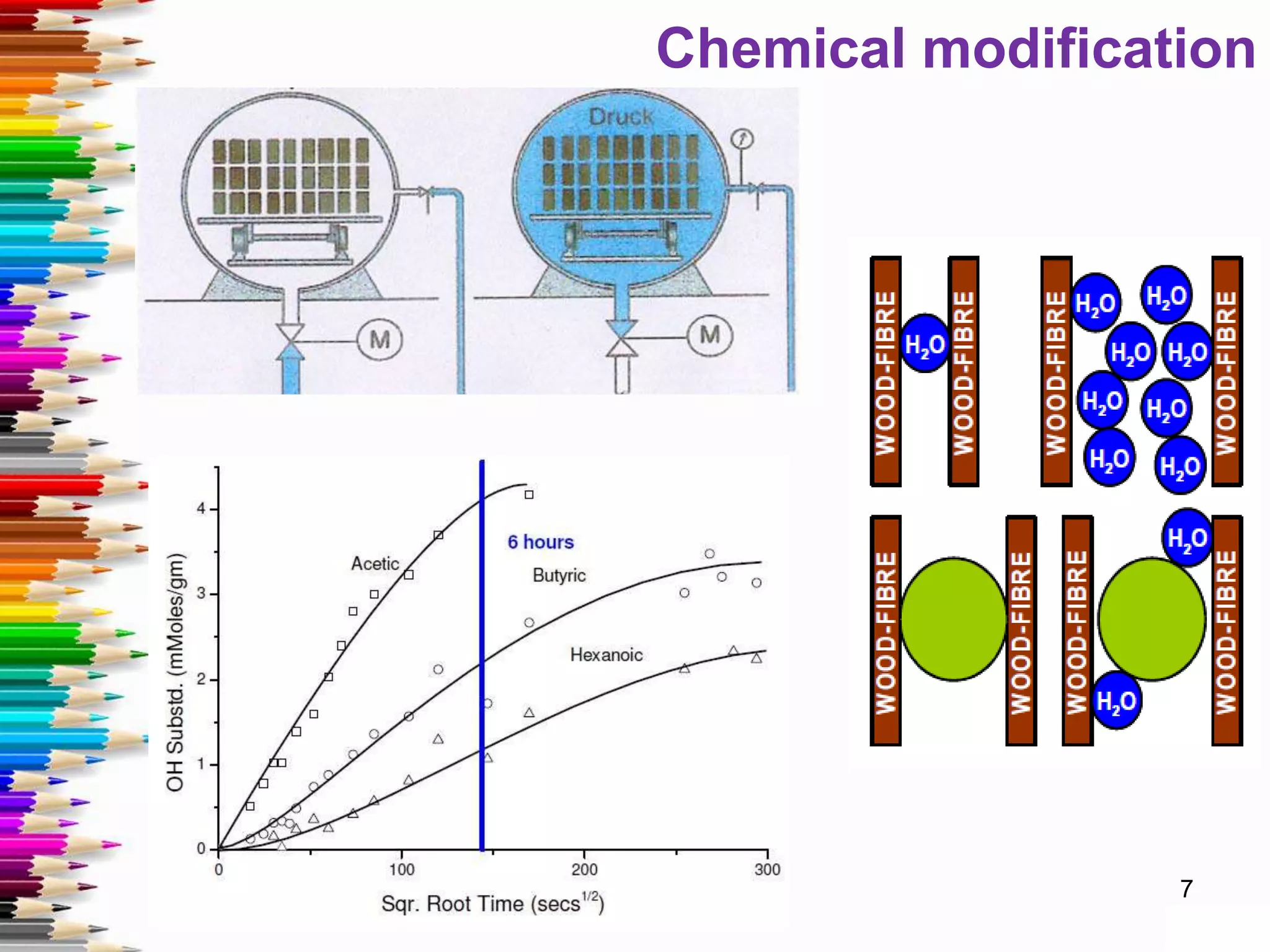
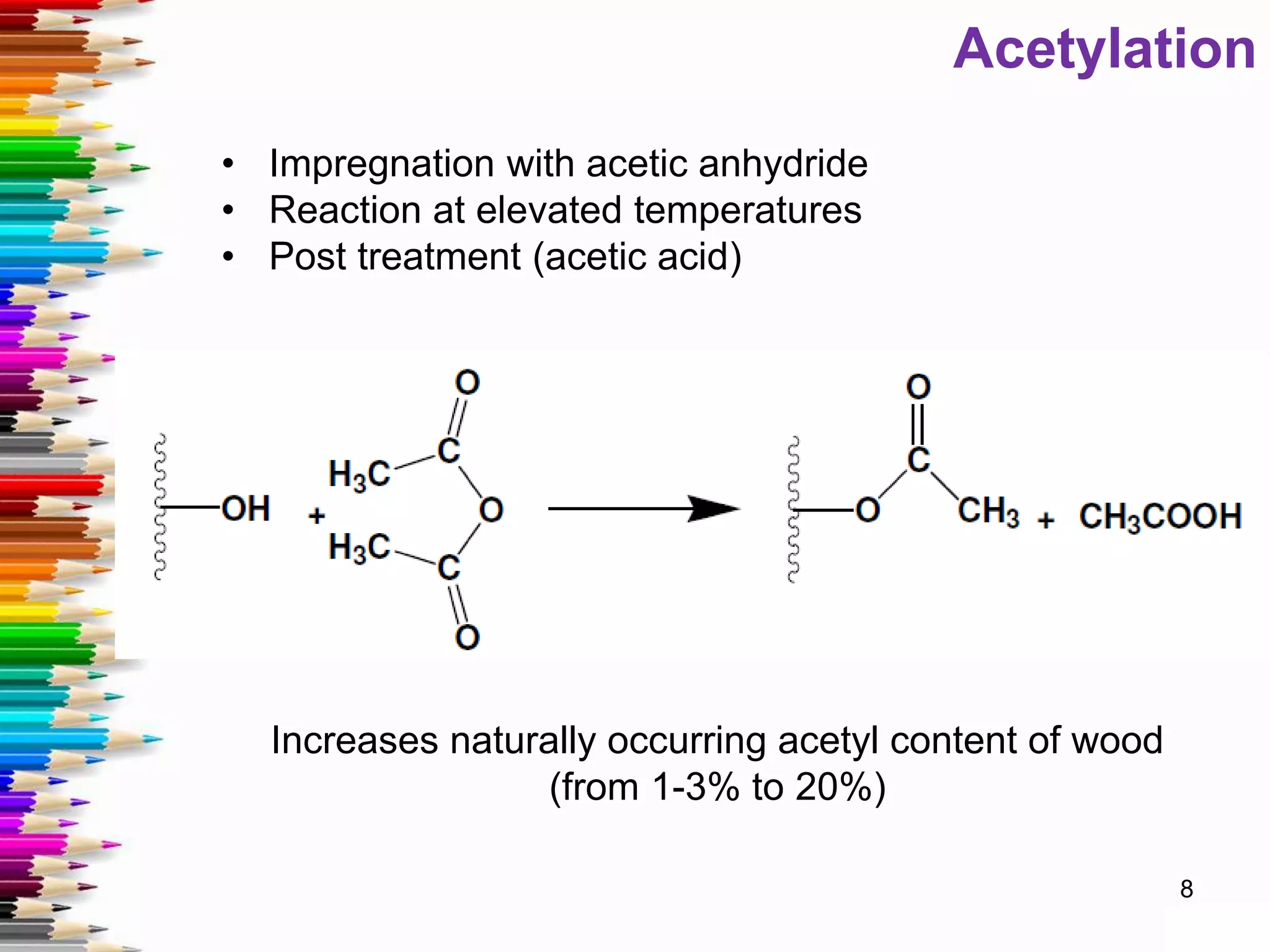
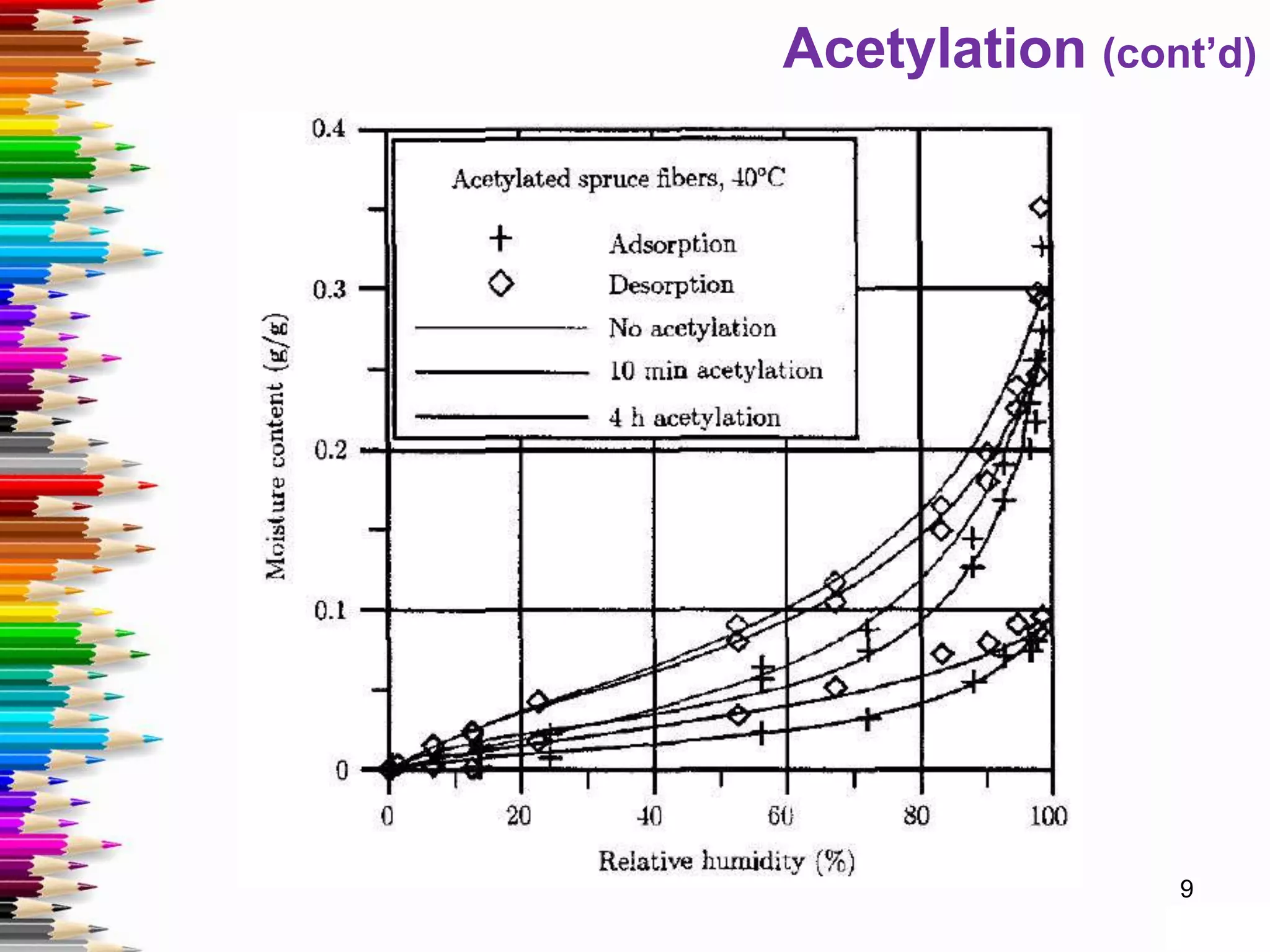
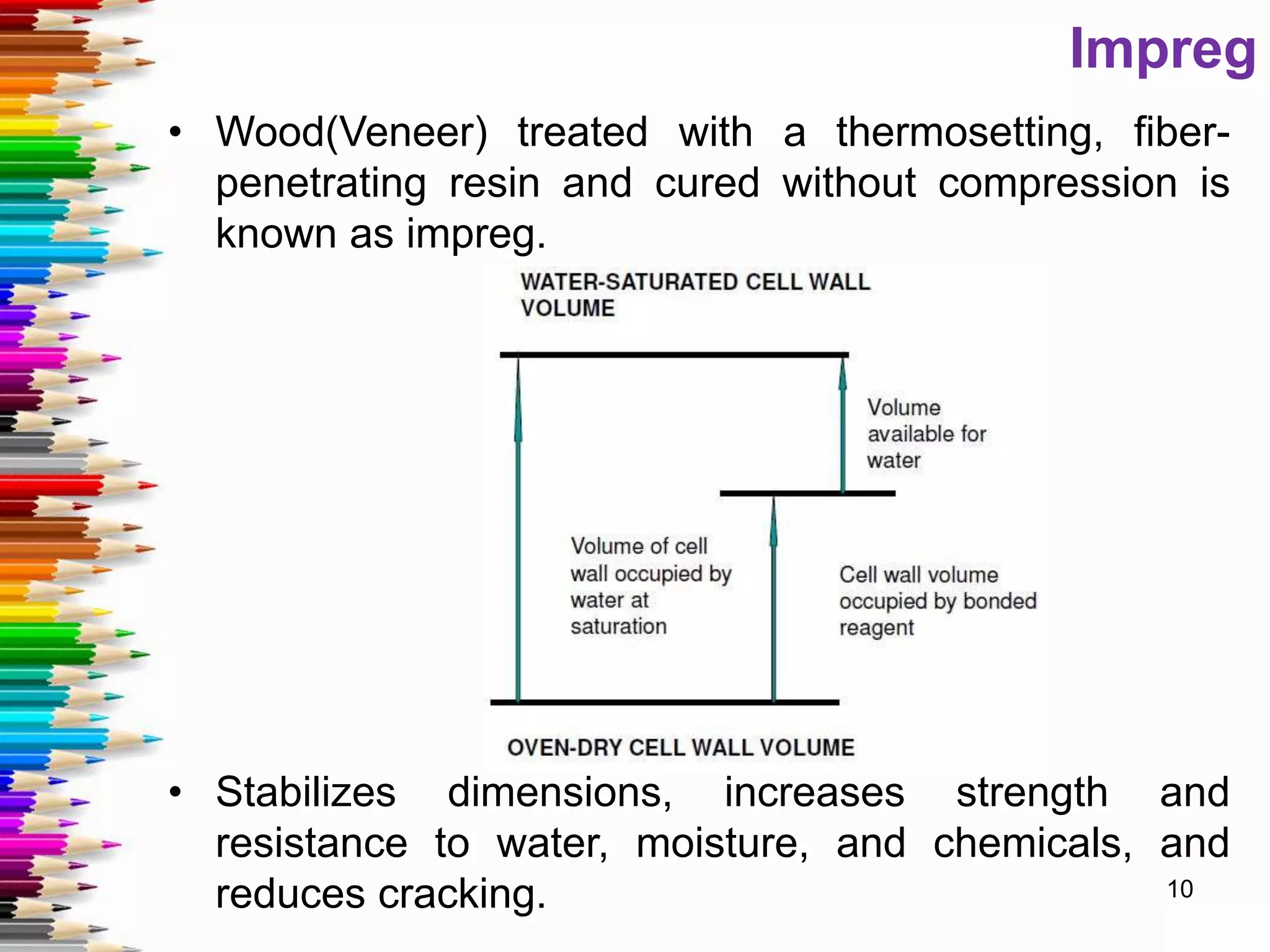
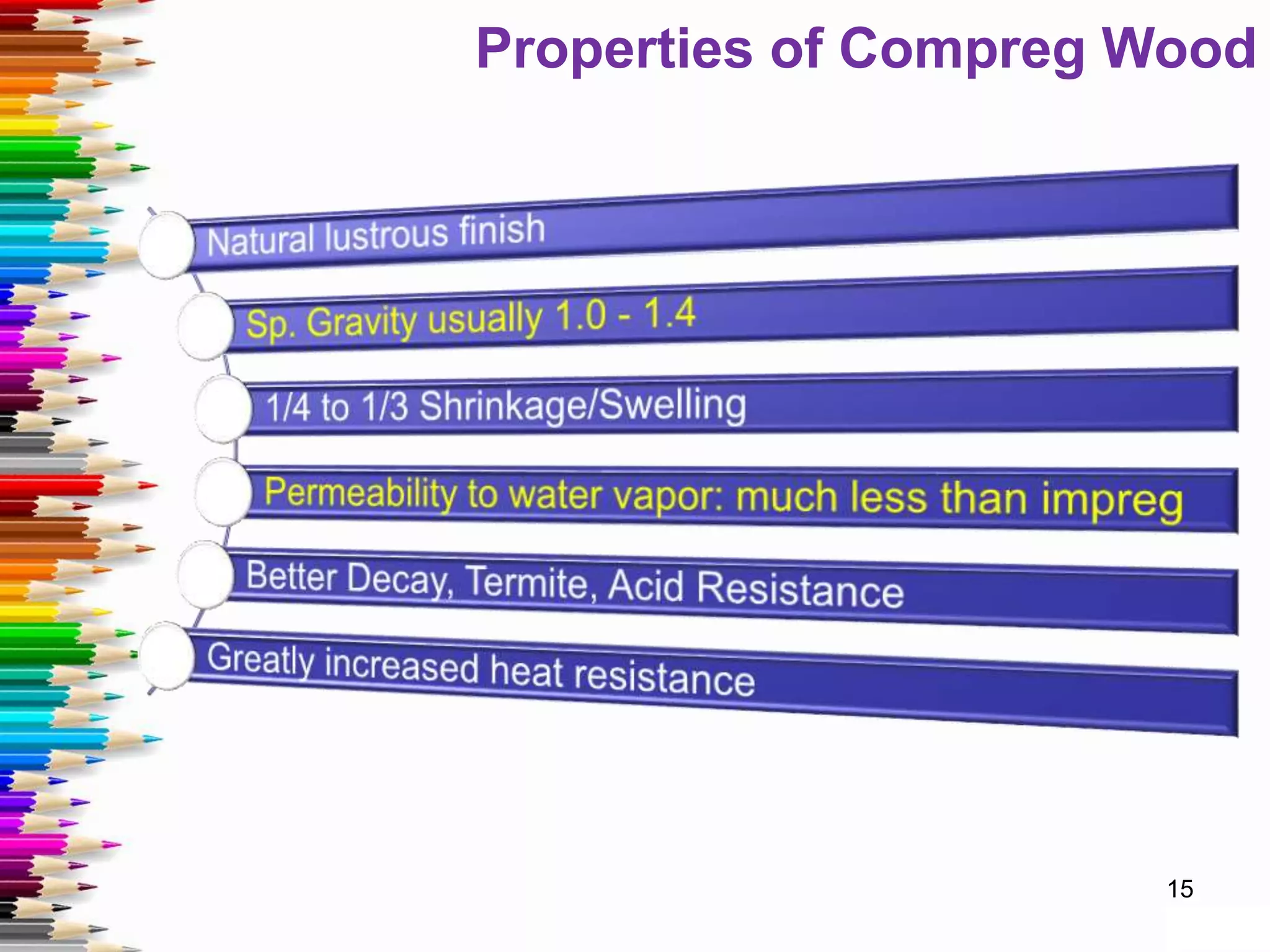
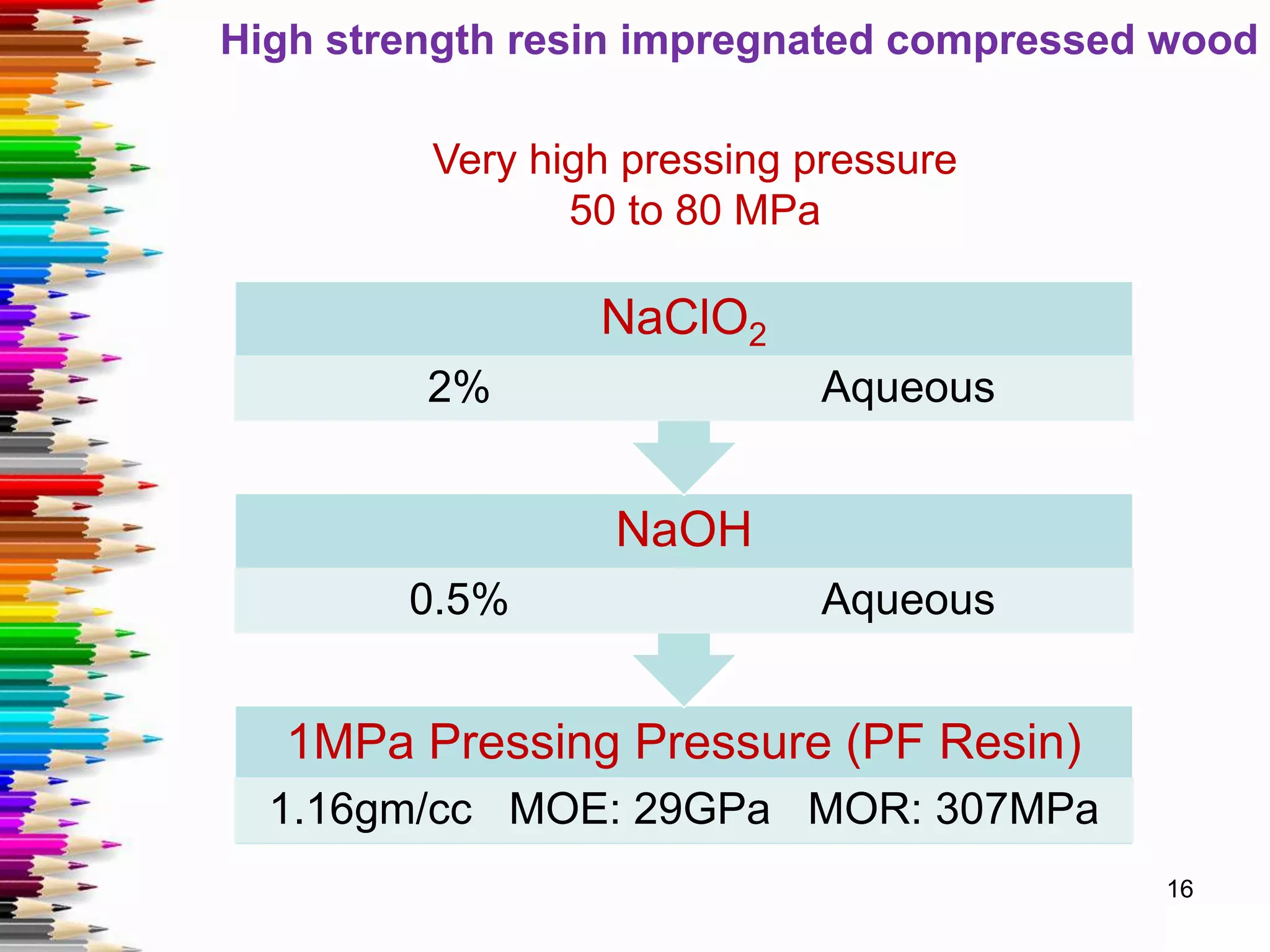
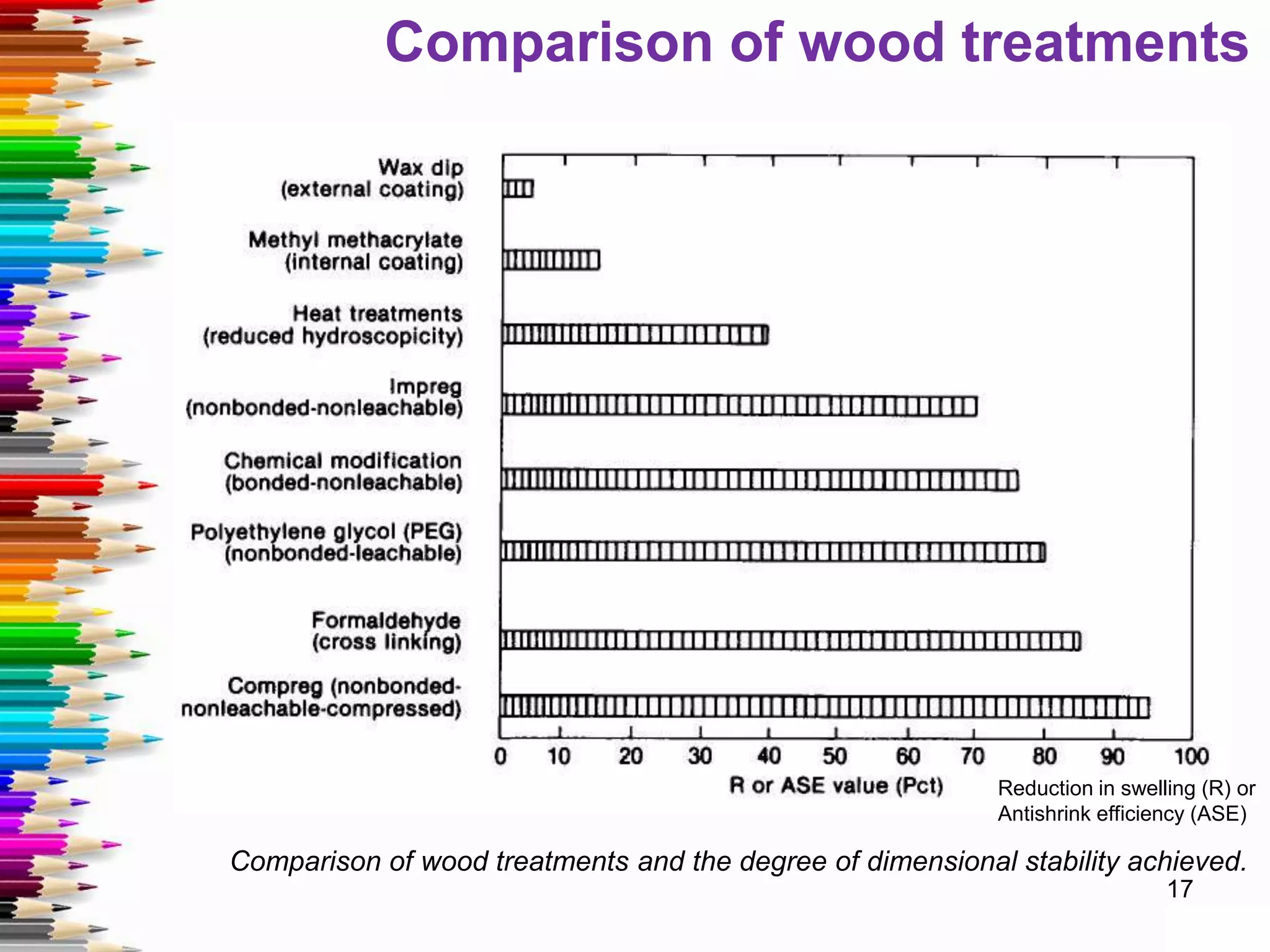
This document discusses various methods for stabilizing the dimensions of wood, including thermal modification, acetylation, impregnation, and compression. Thermal modification processes like Plato and Staypak heat wood to temperatures of 160-190°C to reduce hygroscopicity and increase hardness. Acetylation increases the wood's natural acetyl content through impregnation with acetic anhydride and heat treatment. Impregnation and compression methods soak wood in thermosetting resins then cure it with or without compression to stabilize dimensions, increase strength, and reduce cracking. Comparison charts show the degree of dimensional stability achieved by different wood treatment methods.