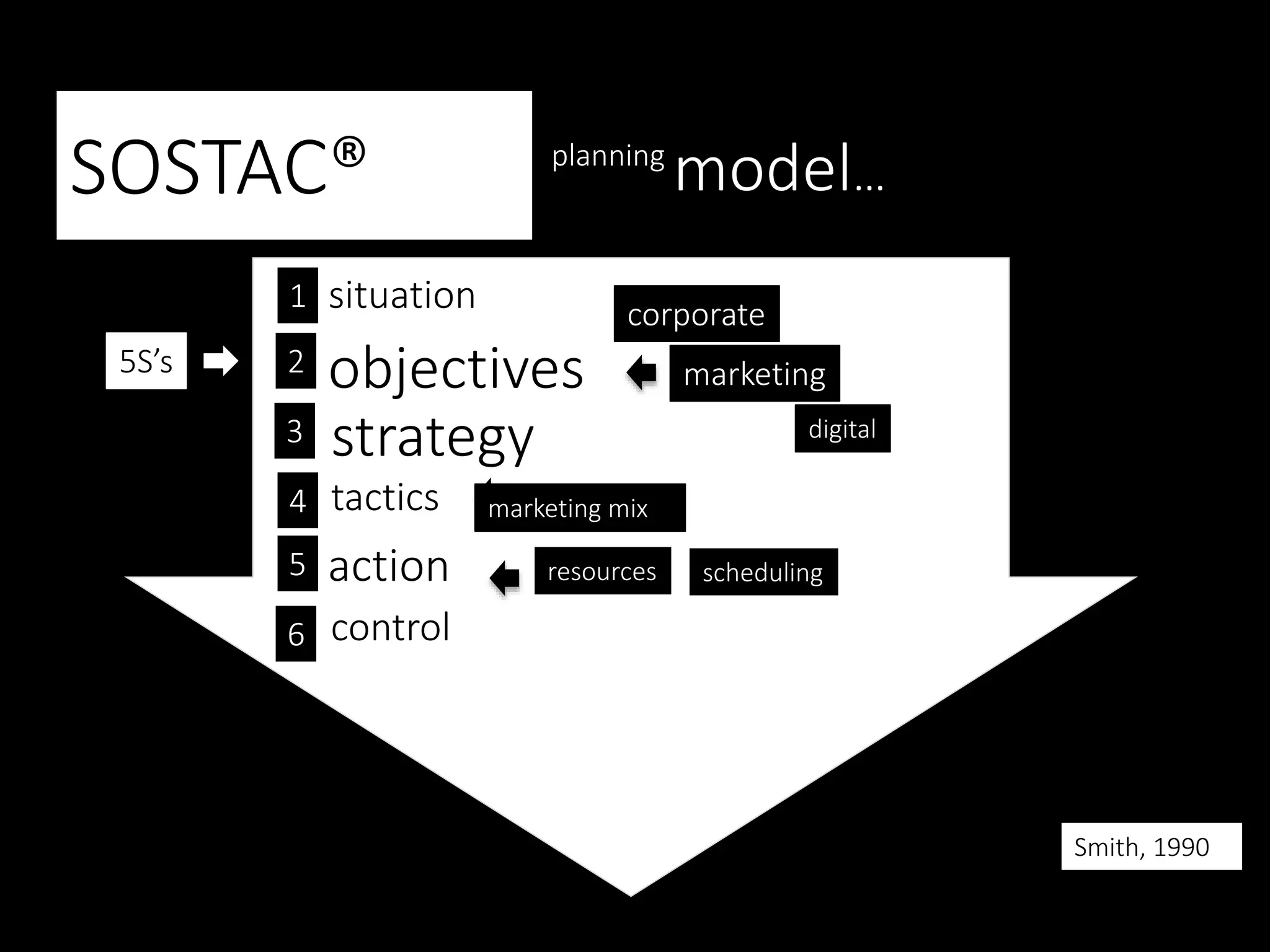
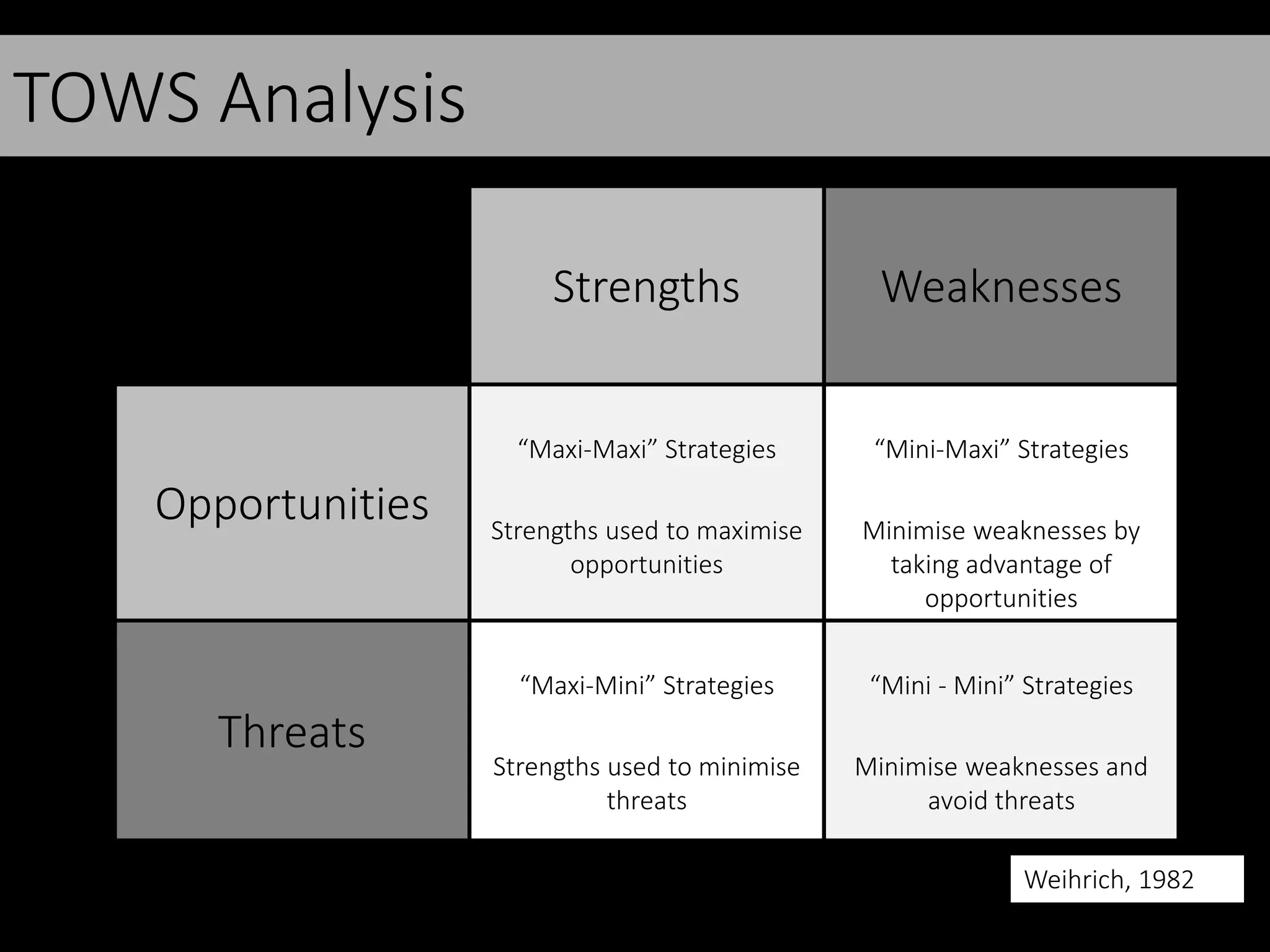
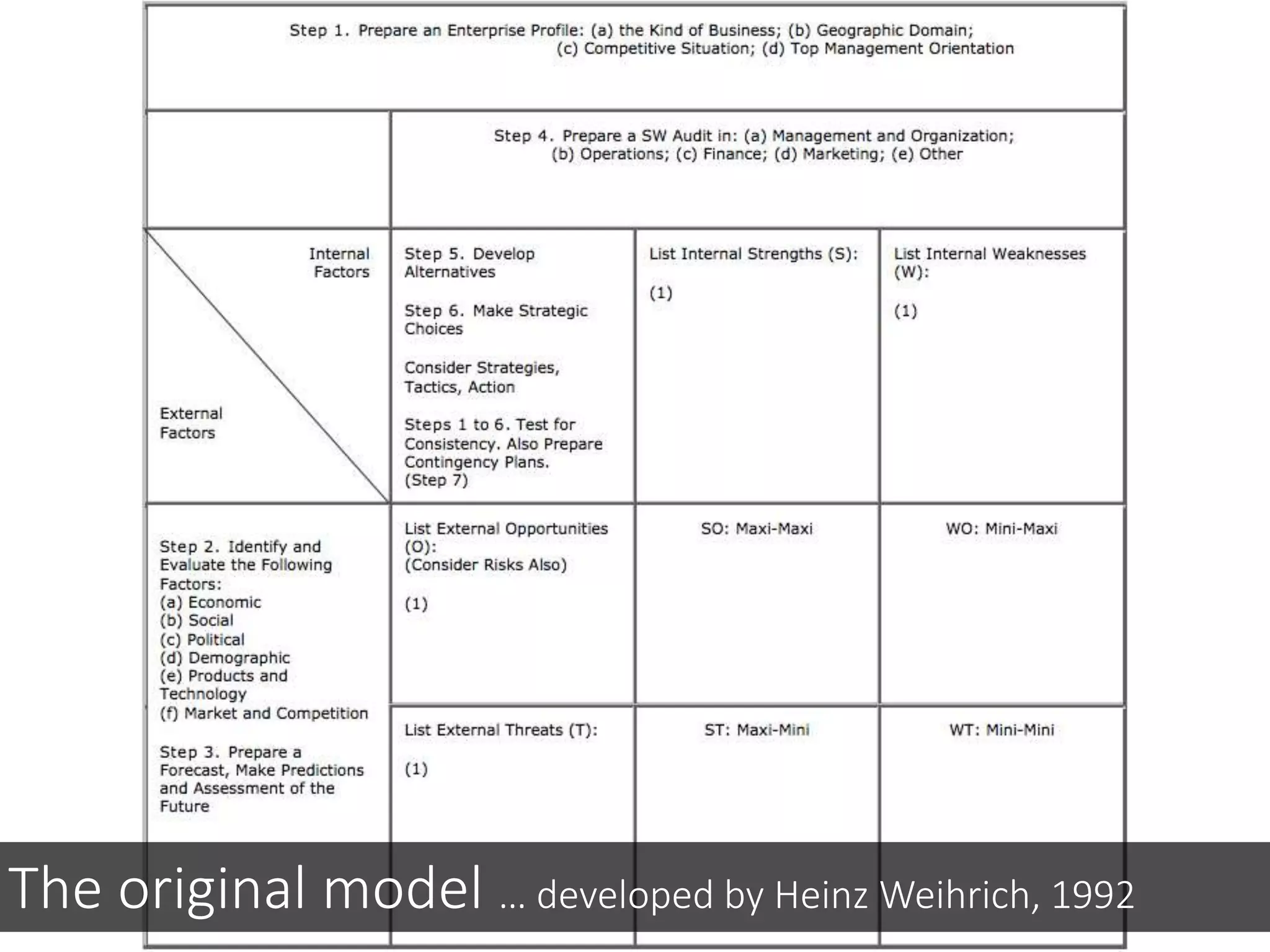
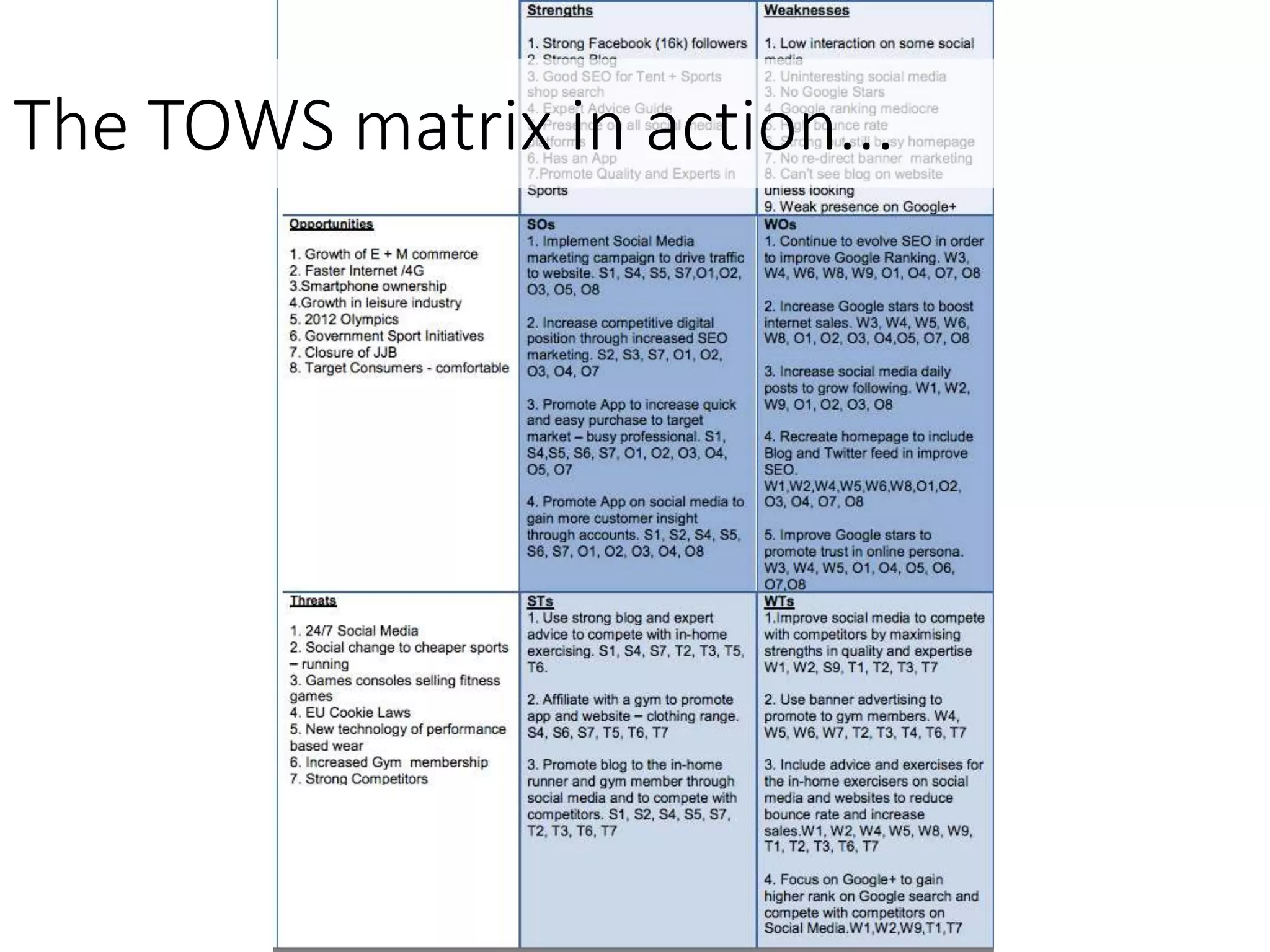
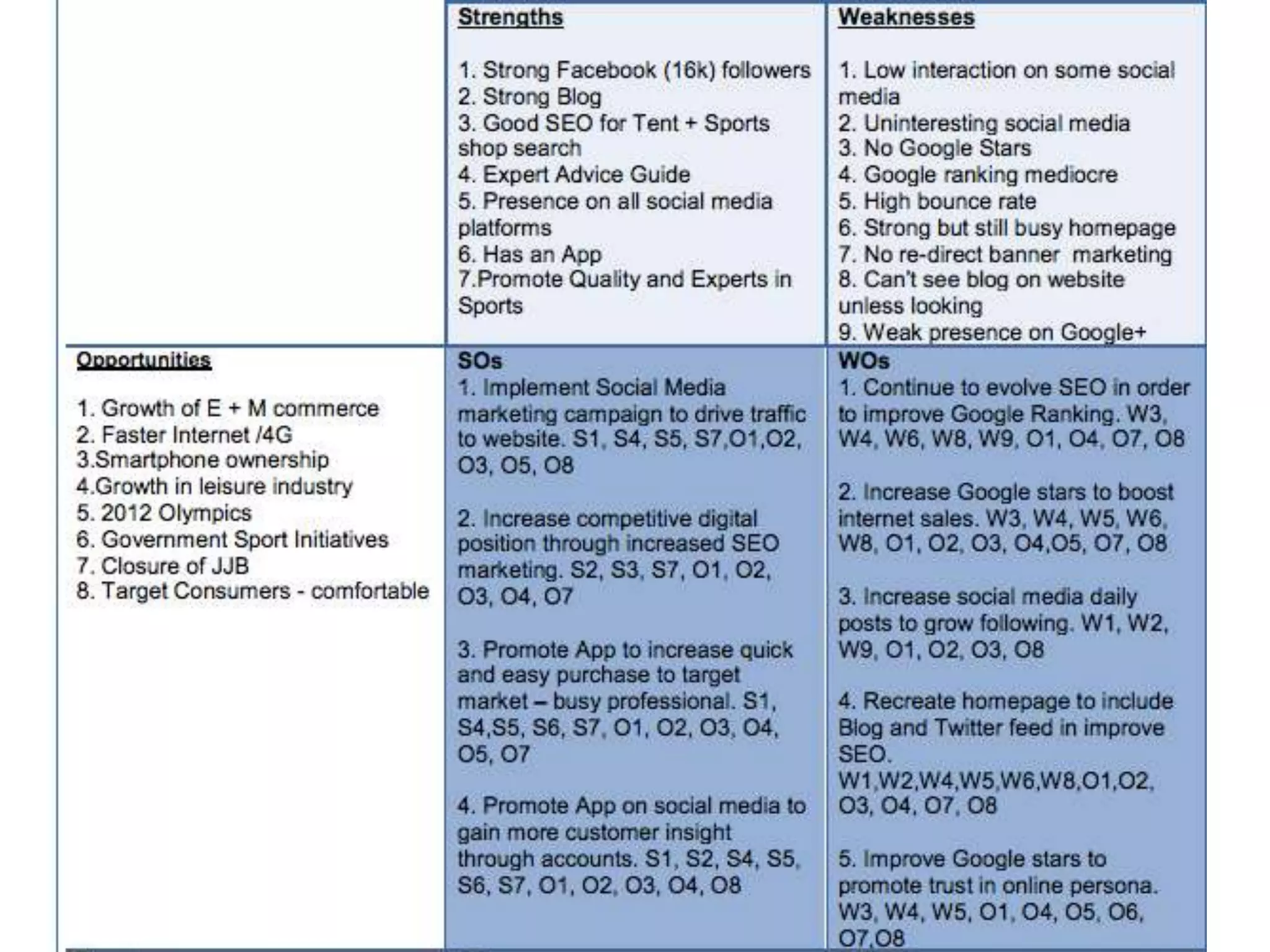
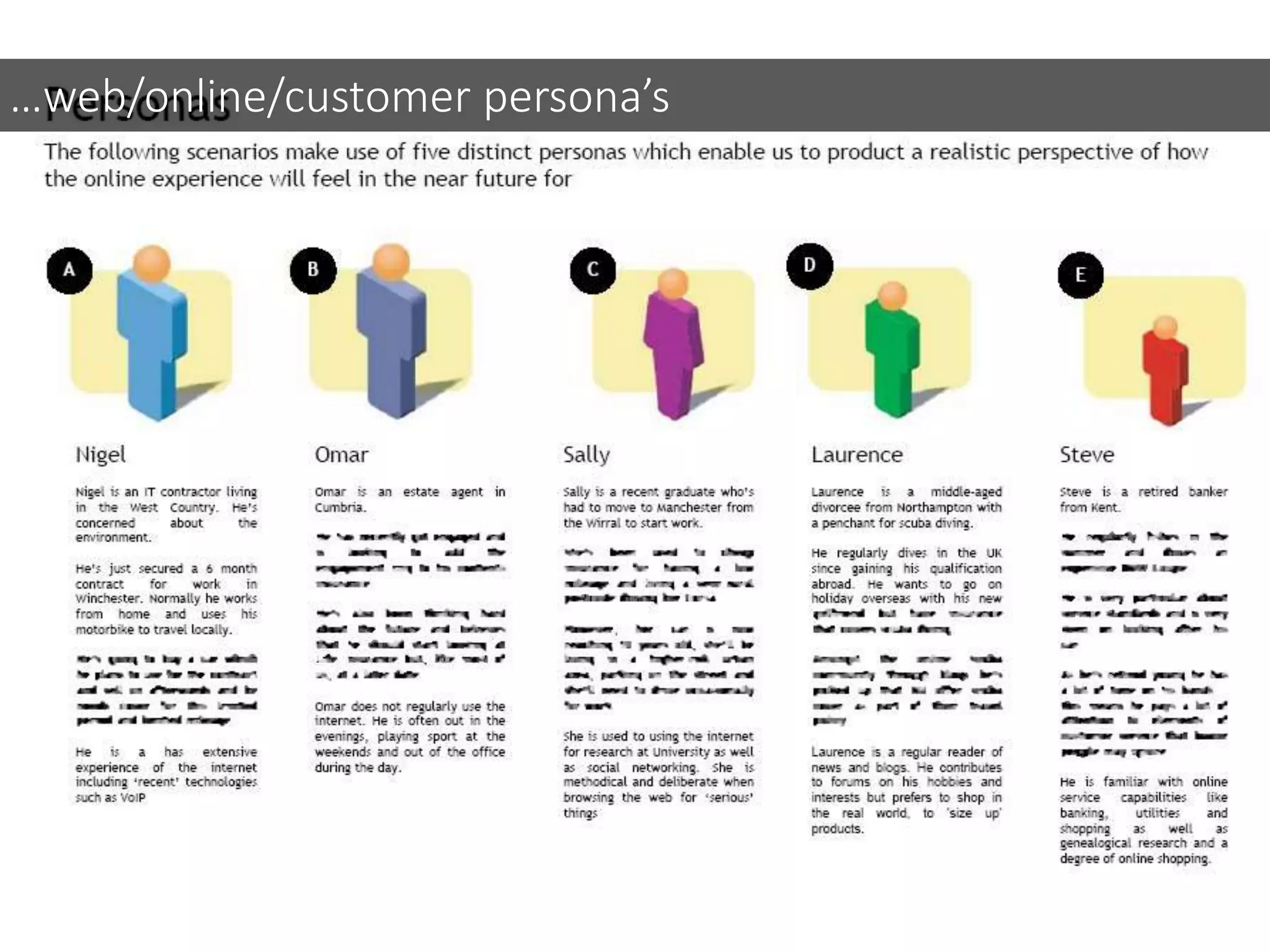
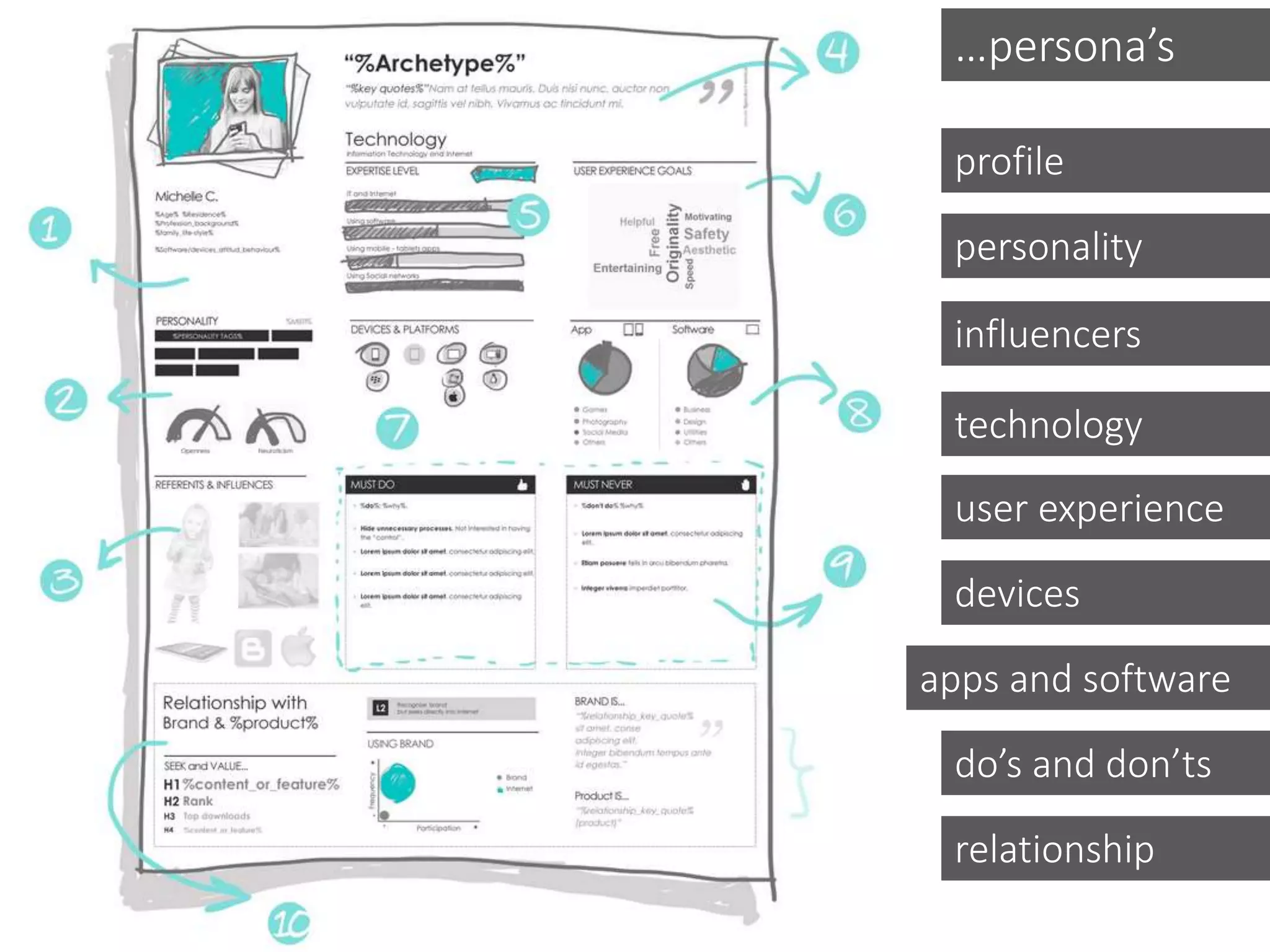
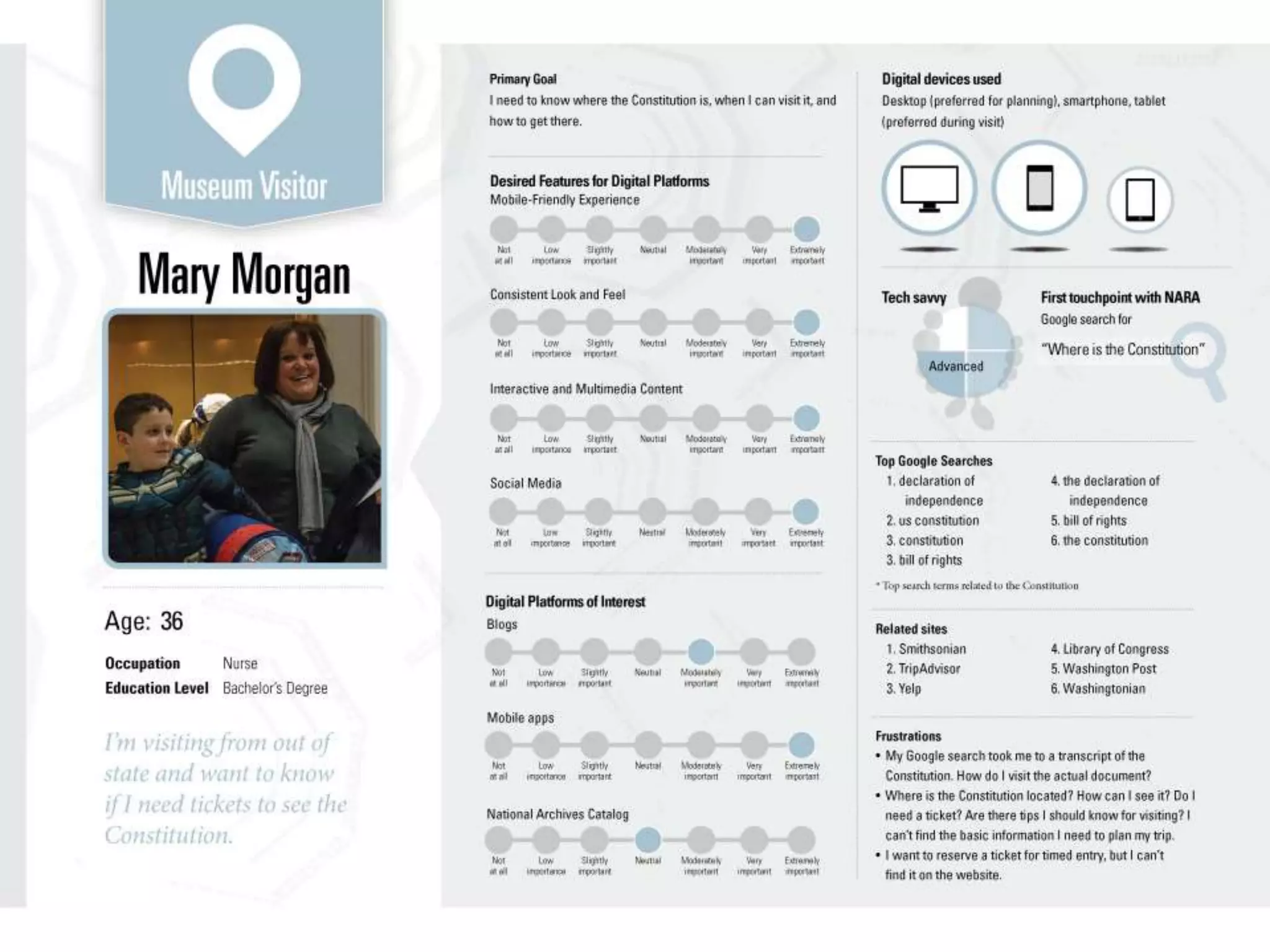
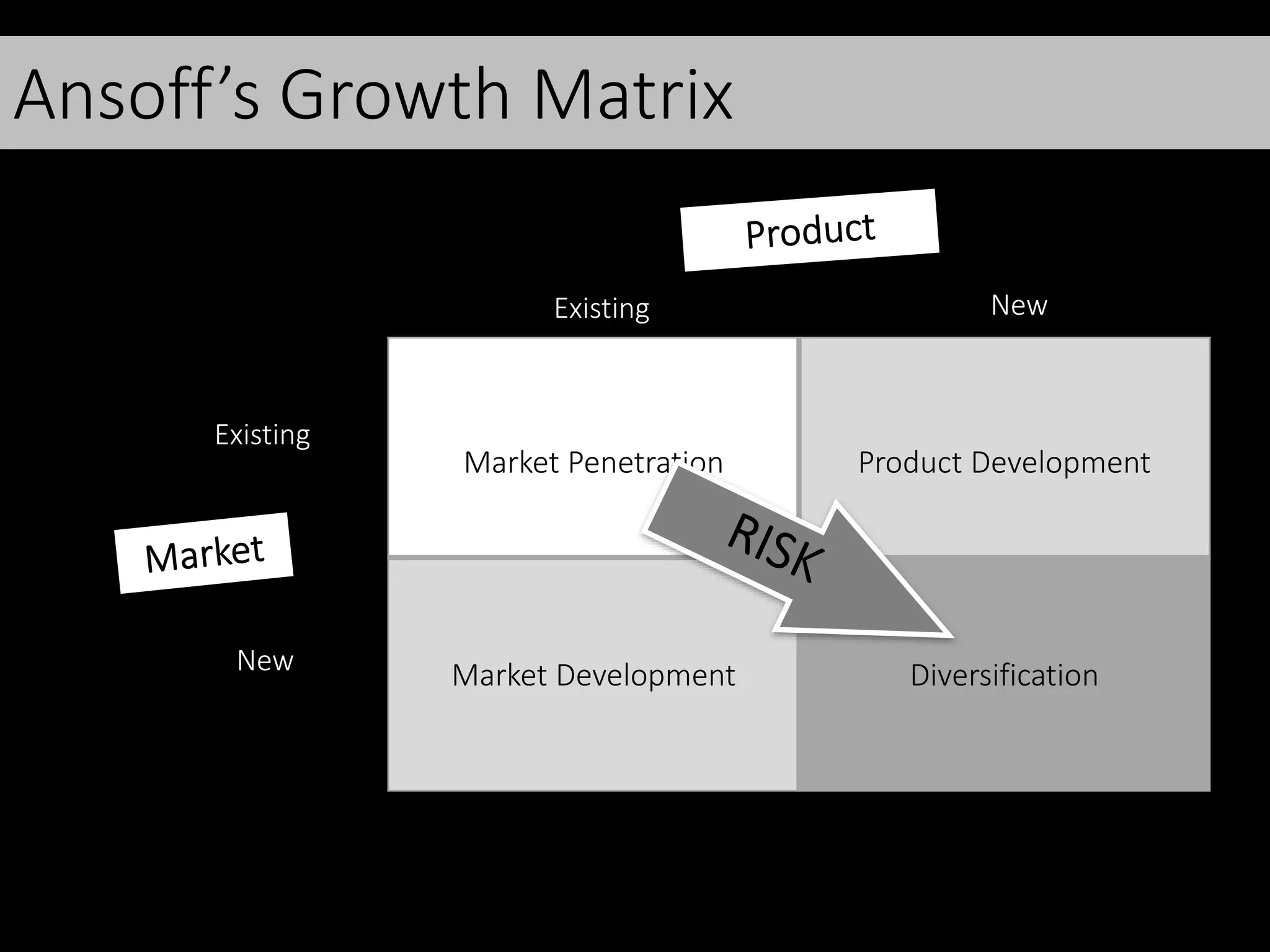
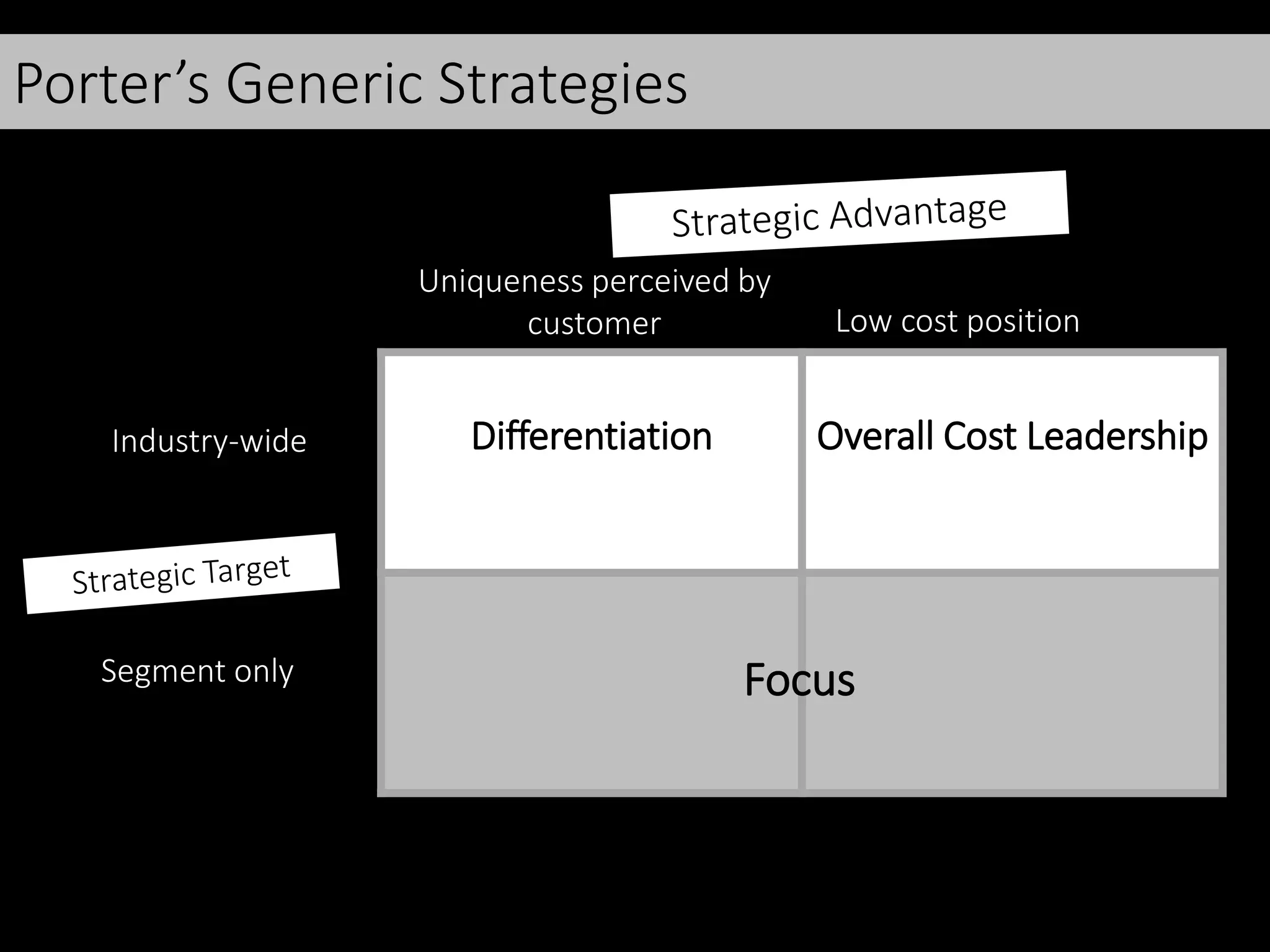
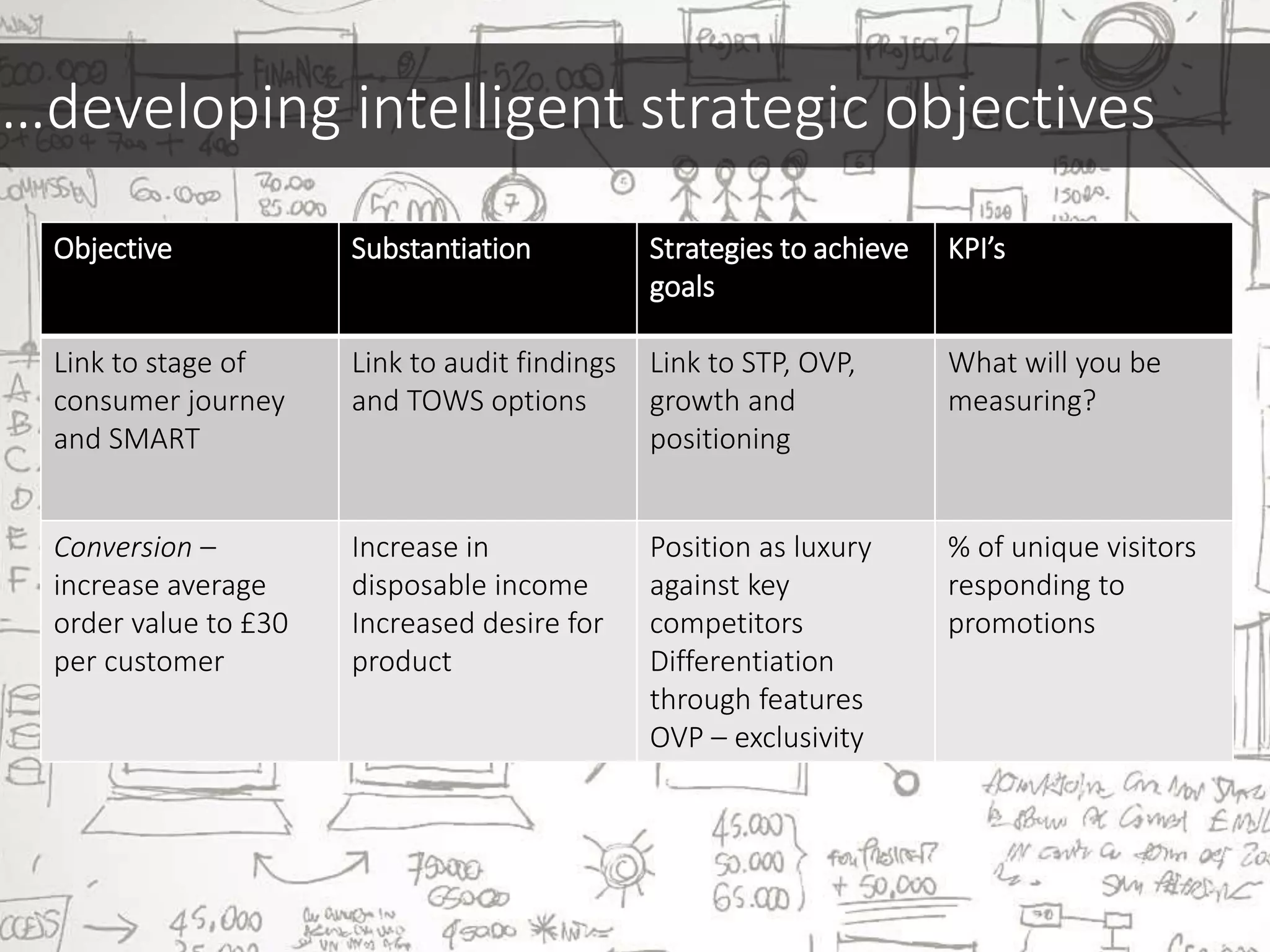
This document discusses various frameworks and models for developing a digital marketing strategy, including the SOSTAC model, TOWS analysis, persona development, and defining strategic objectives. It emphasizes that digital strategies should link to overall marketing and corporate objectives, consider the customer journey from acquisition to retention, and establish key performance indicators to evaluate success. Different strategic approaches are outlined such as segmentation, positioning, and Ansoff's and Porter's generic strategies to determine how best to achieve objectives.