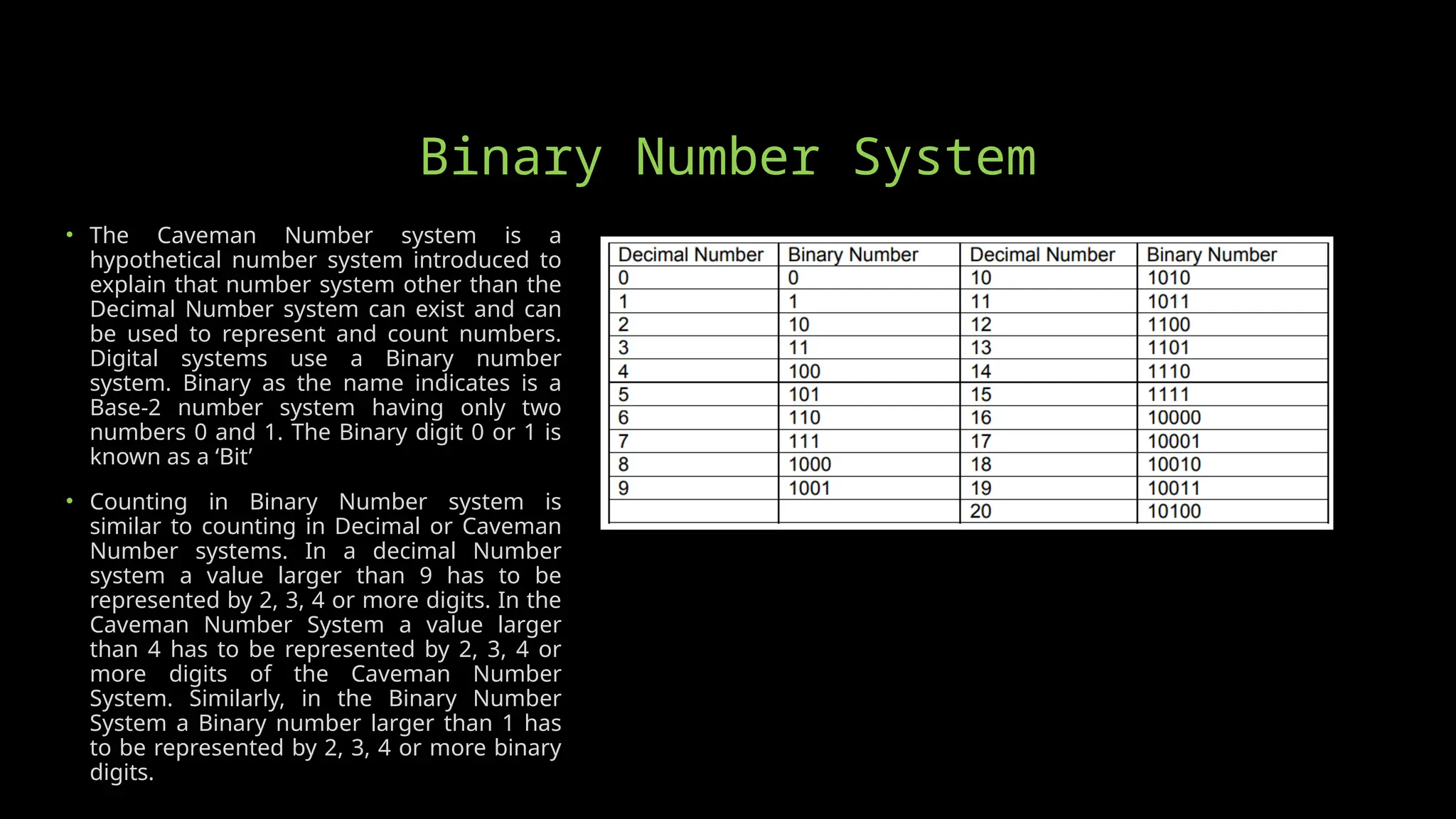
The document discusses various number systems, starting with the decimal system, which uses ten digits and is positional. It introduces the caveman number system, a base-5 system with distinct symbols for numbers, and explains the binary number system, a base-2 system that uses only 0 and 1. The document also addresses representing integers and fractions in these systems using expressions based on their respective base values and weights.