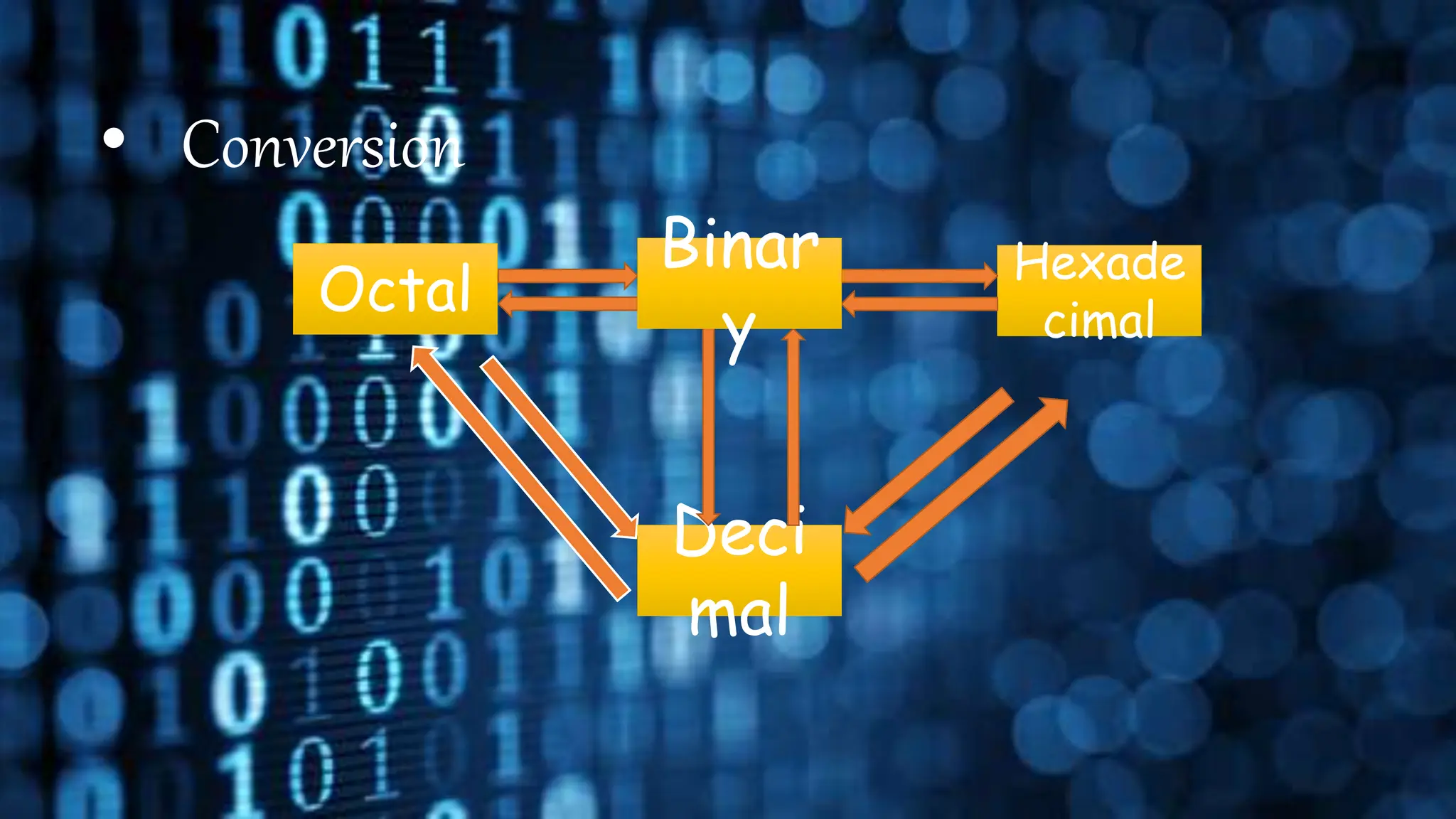
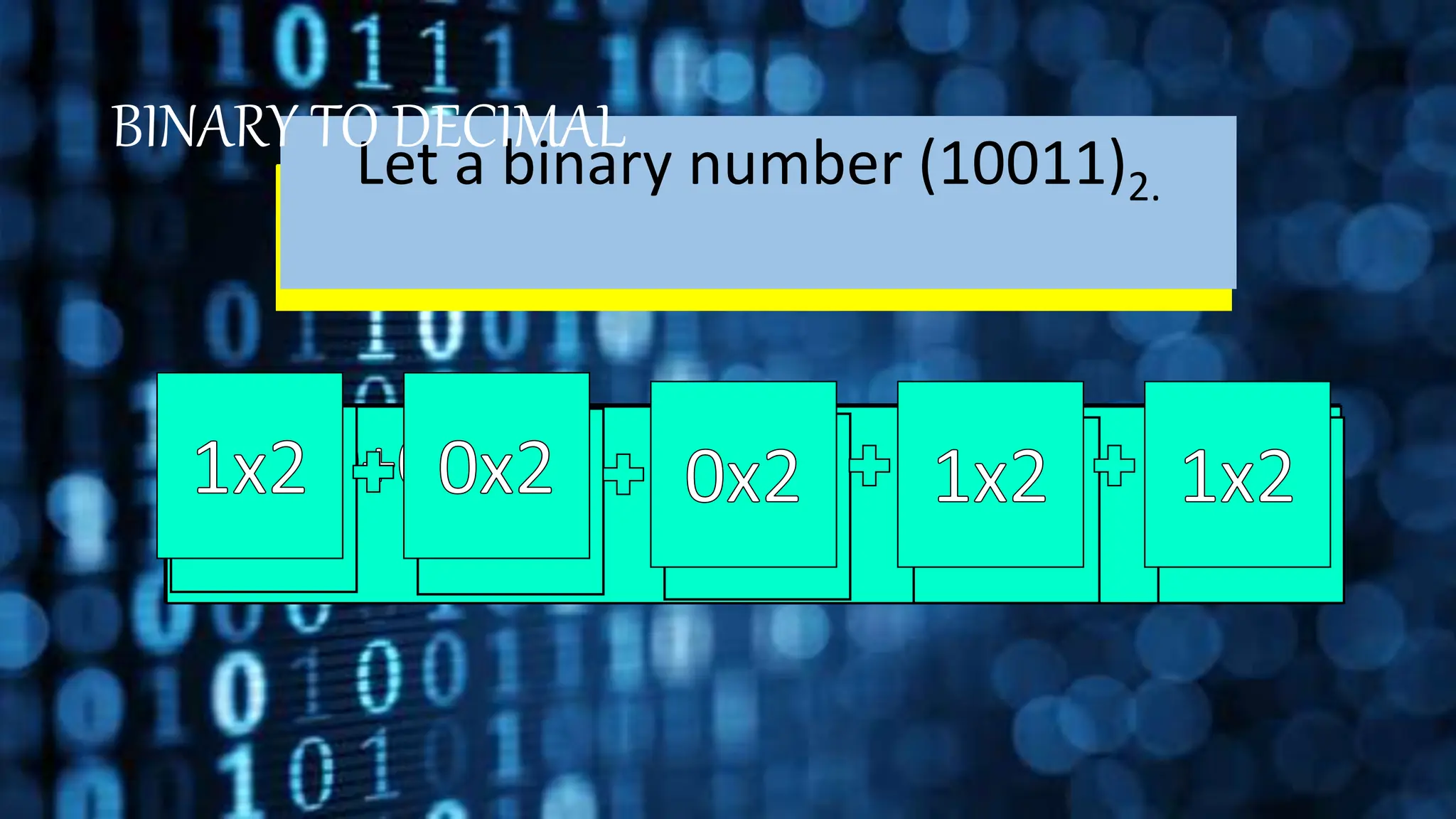
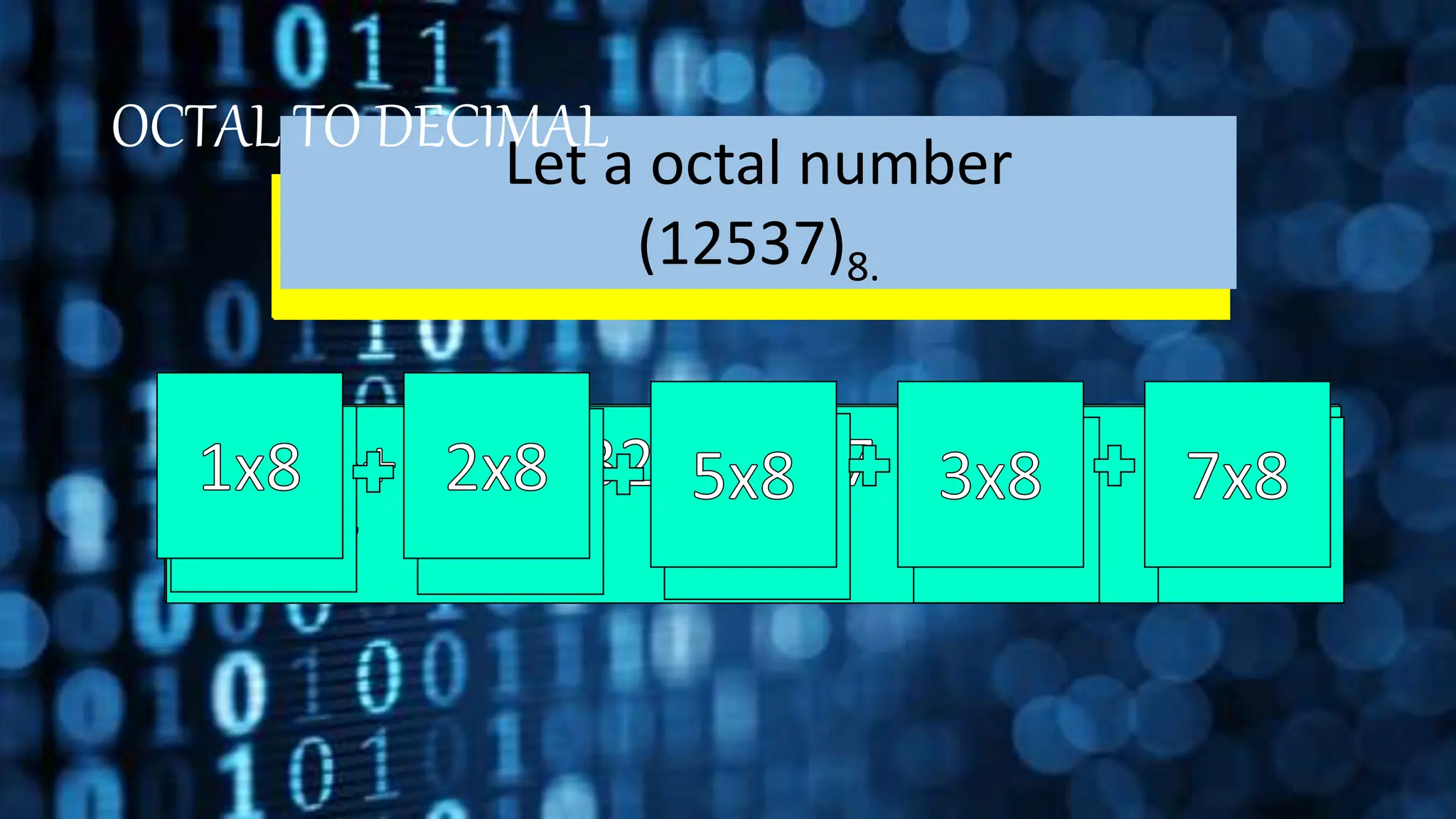
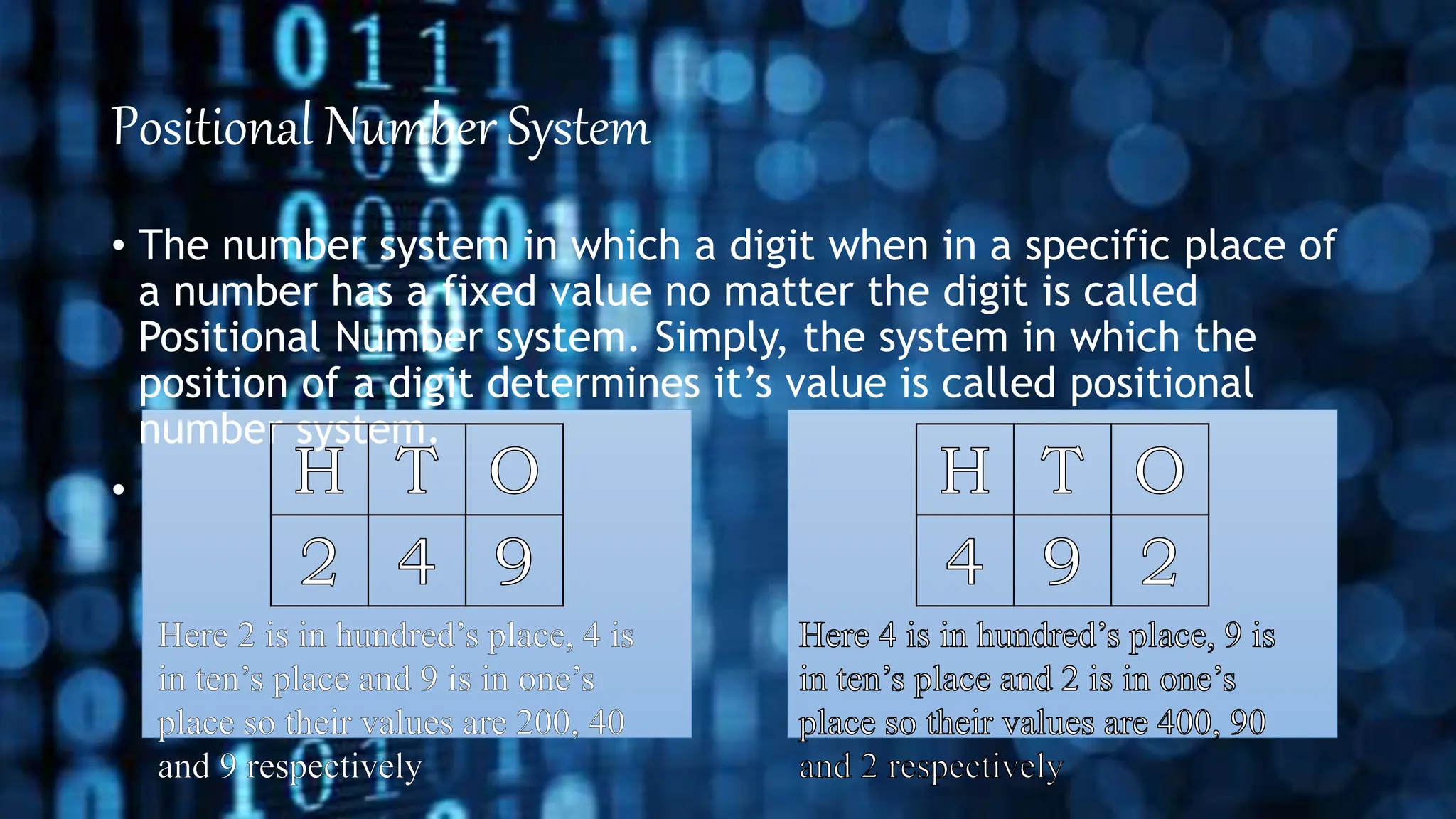
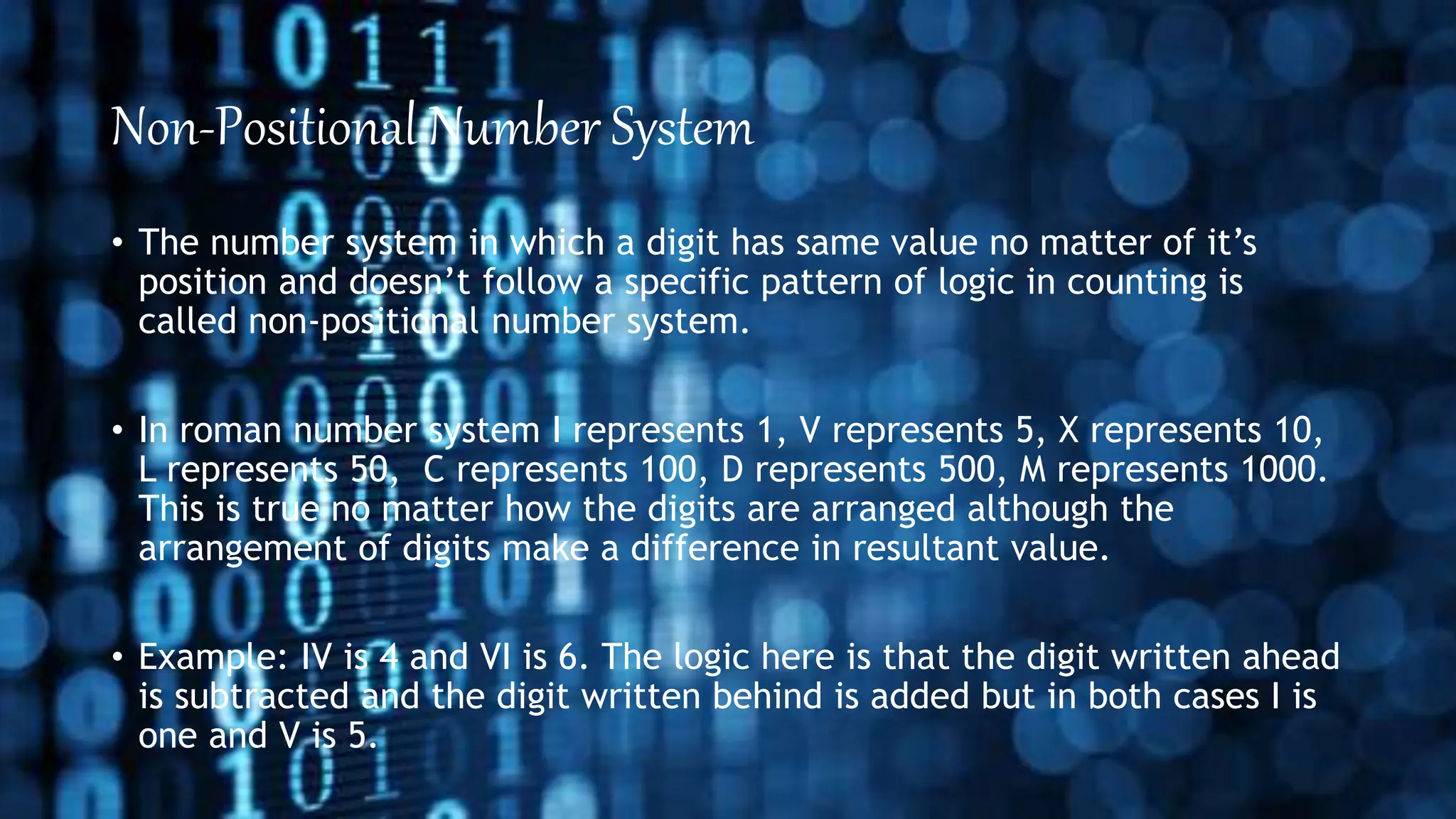
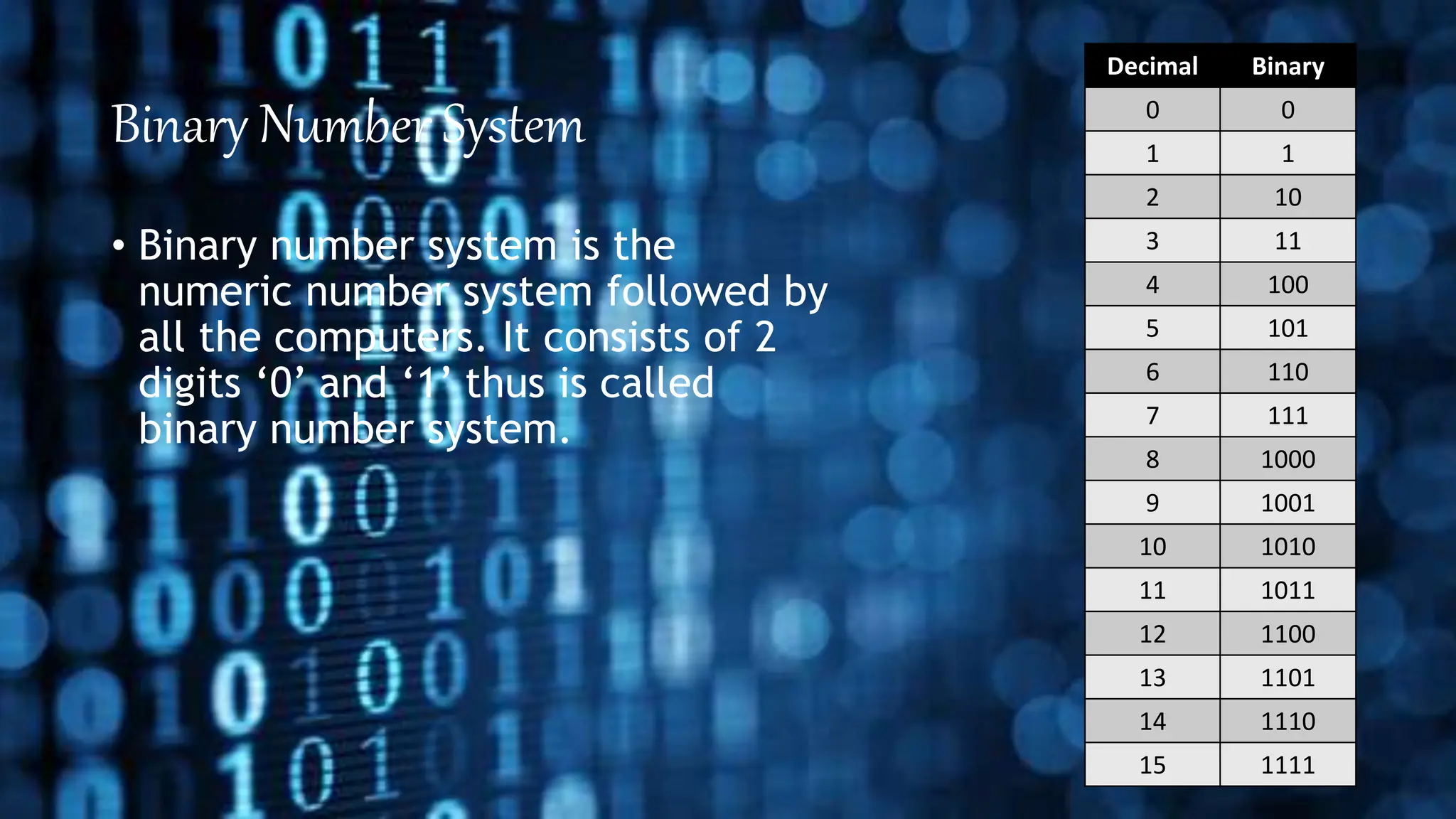
This document discusses different number systems including positional and non-positional systems. It provides examples of the binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal number systems. It also describes how to convert between these different number systems by first converting to decimal as an intermediate step if needed.





![• Things to remember
A number is always written within
brackets and it’s radix must be
written. Radix is the number of
digits in the system.
Binary: (101101)2 -2 is the radix
Octal: (654)8 -8 is the radix
Decimal: (198)10 -10 is the radix
Hexadecimal: (6A5)16 -16 is the radix
Binary Subtraction:
0-0=0
1-0=1
0-1 [Not Possible]
1-1=0
10-1=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numbersystem-240123154040-b918e3e9/75/A-presentation-on-number-system-and-conversion-10-2048.jpg)