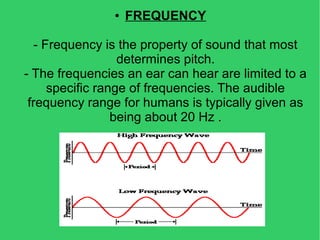
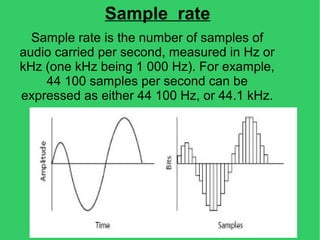
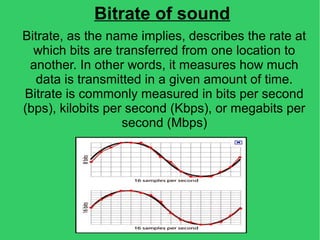
This document discusses various concepts related to digital data including multimedia, file formats, digital and analog information. It then provides details on digital text formats like DOC, DOCX, HTML, PDF; digital image formats like JPG, BMP, RAW; digital audio formats like WAV, MP3, WMA; and digital video formats like AVI, DivX, MPG, MOV, WMV. Finally, it mentions some web programs that can be used for converting between different digital data formats.











![HTML
HyperText Markup Language, commonly referred
to as HTML, is the standard markup language
used to create web pages.[1] It is written in the
form of HTML elements consisting of tags
enclosed in angle brackets (like <html>)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitaldata-150429013409-conversion-gate02/85/DIGITAL-DATA-Lucia-Luis-13-320.jpg)