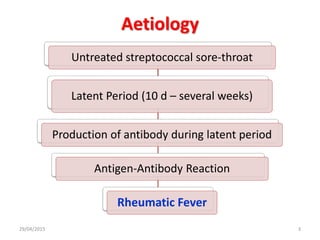
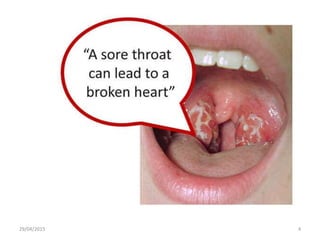
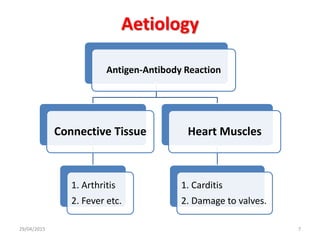
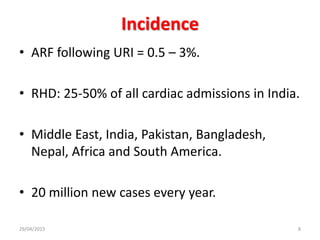
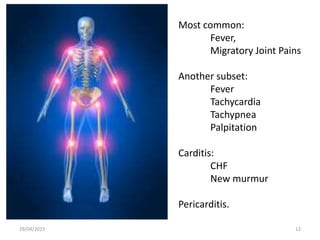
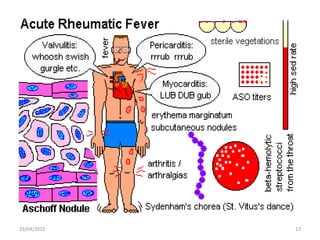
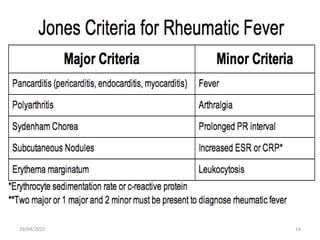
Acute rheumatic fever is an immunological response that most commonly affects children between 5-15 years of age from poorer socioeconomic backgrounds. It occurs as a result of an untreated streptococcal throat infection, where antibodies formed against the bacteria can mistakenly attack heart muscles and valves. Common symptoms include fever, migratory joint pains, and potential heart complications such as congestive heart failure or new heart murmurs. Treatment focuses on activity limitations, a heart-healthy diet, antibiotics to prevent future throat infections, and potentially long-term preventative antibiotics or corticosteroids to manage symptoms like chorea.