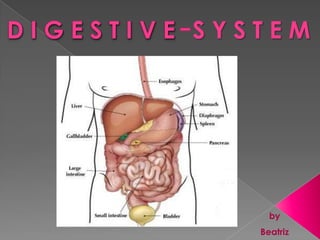
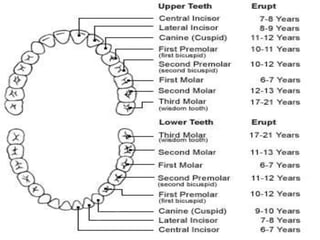
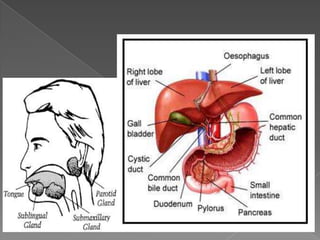
The digestive system begins breaking down food through mechanical and chemical digestion in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream in the small intestine, while waste is eliminated. The digestive system includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and small and large intestines. It begins digestion in the mouth through chewing and saliva before food moves to the stomach and small intestine where most absorption occurs.