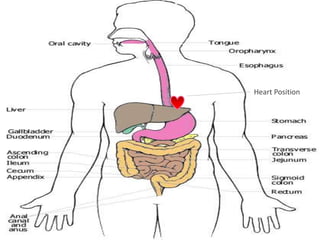
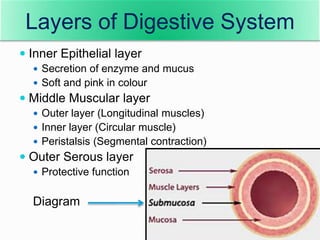
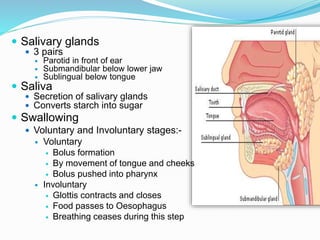
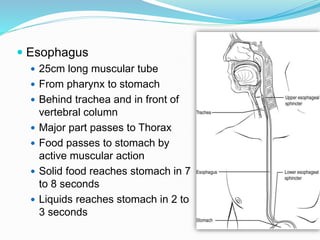
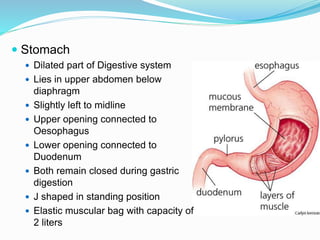
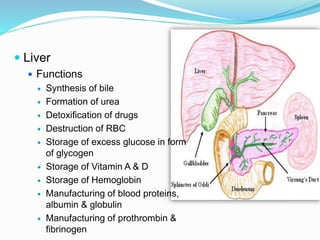
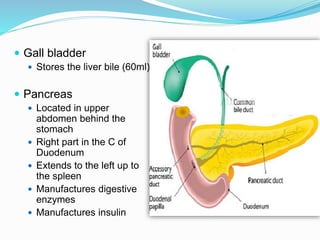
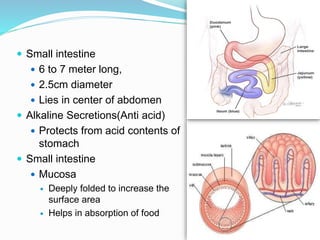
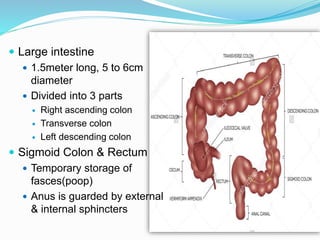
The document describes the organization and function of the human digestive system. It begins by explaining the levels of organization in the body from cells to tissues to organs to organ systems. It then details each organ in the digestive system from the mouth to the stomach to the small and large intestines. Key functions of digestion like ingestion, digestion, absorption and excretion are also outlined. The digestive system breaks down ingested food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body.