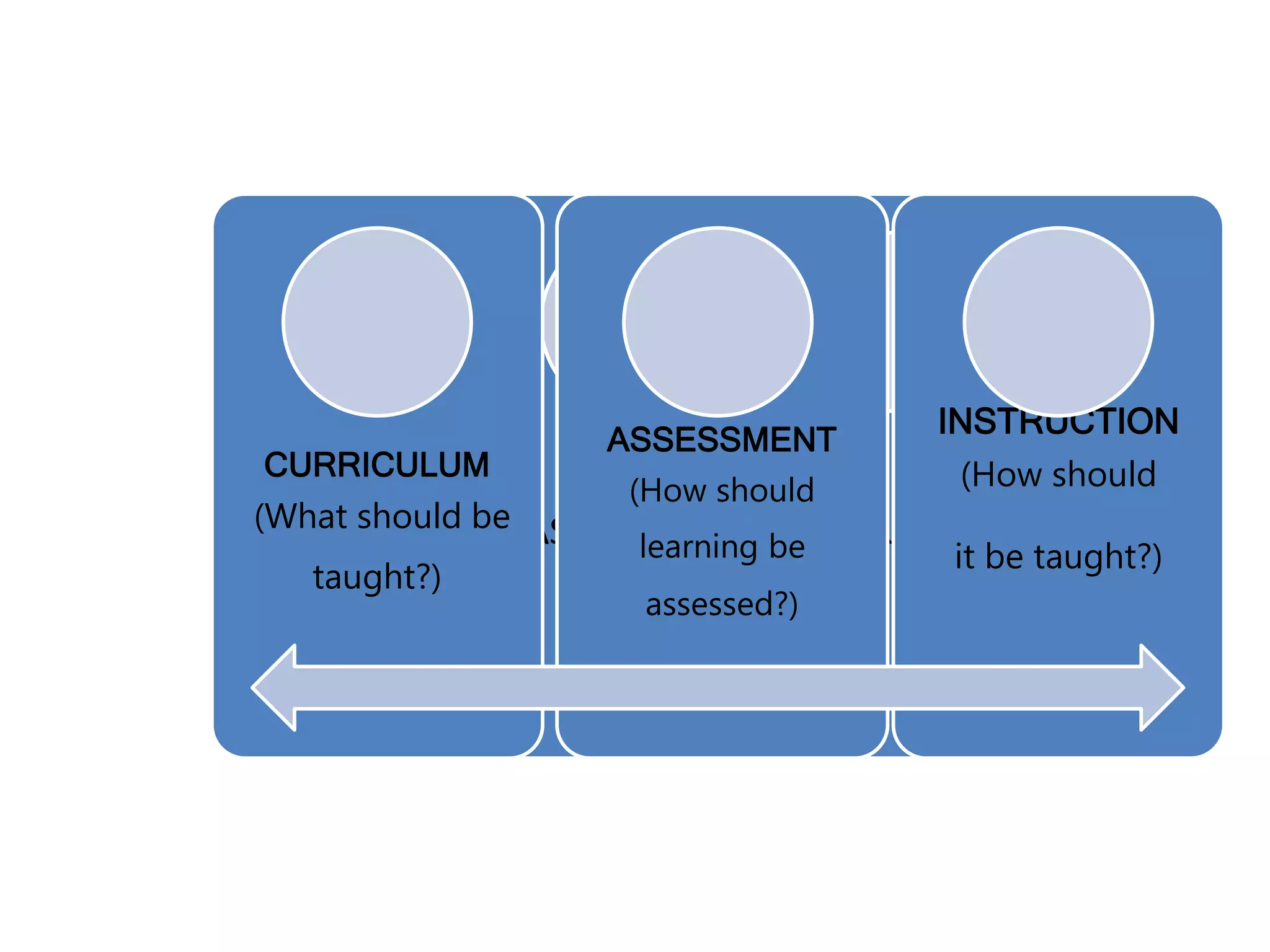
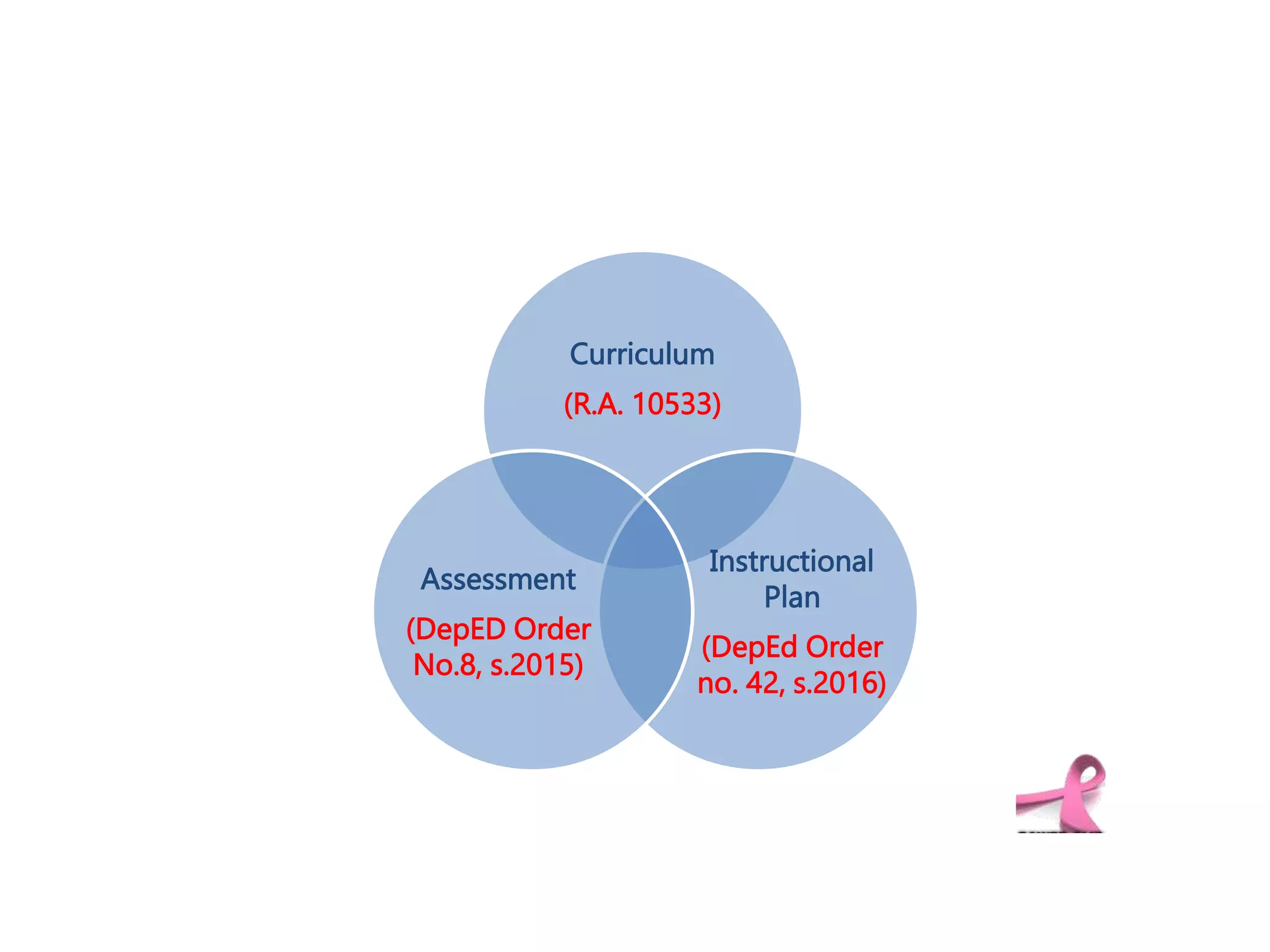
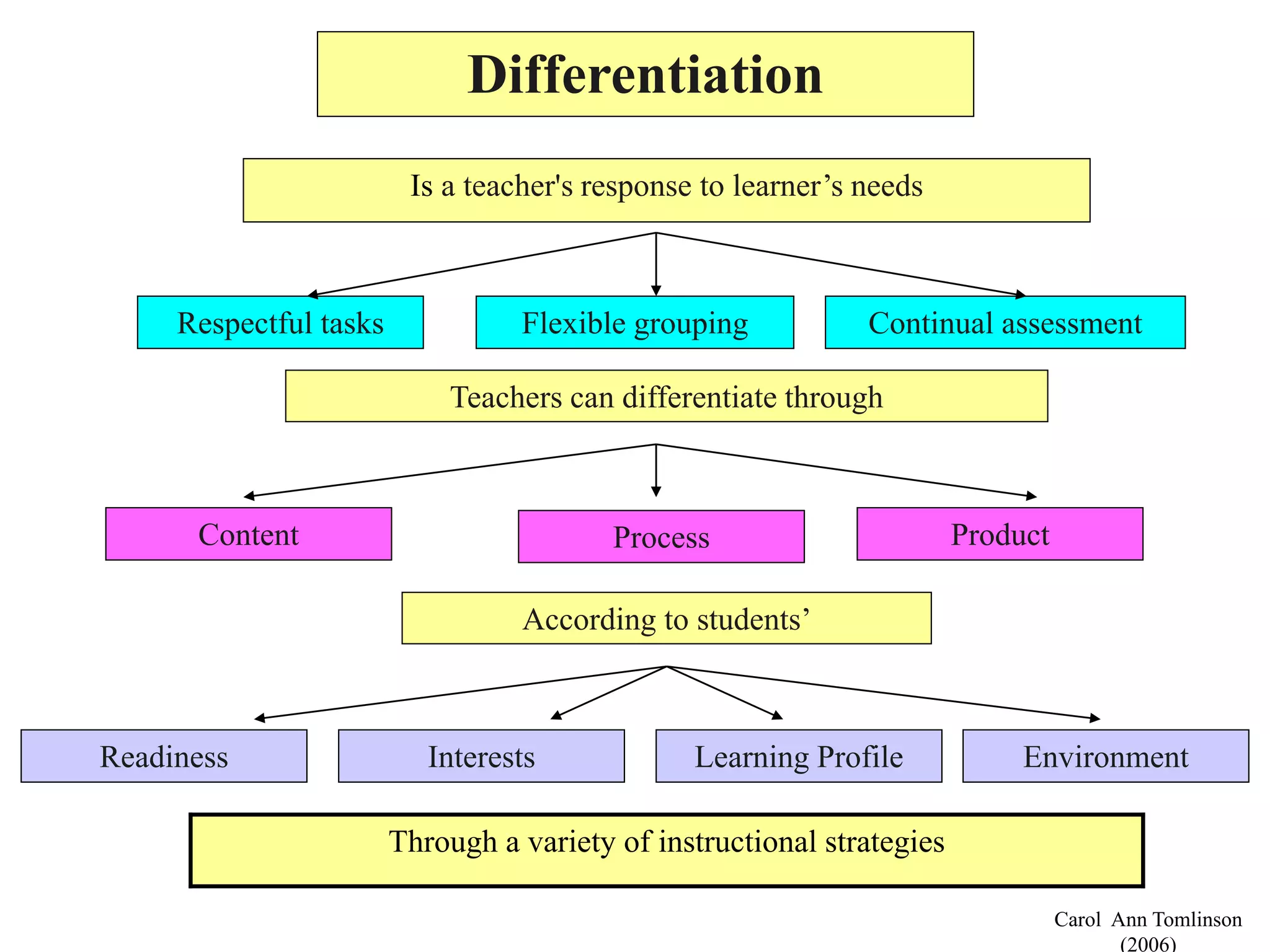
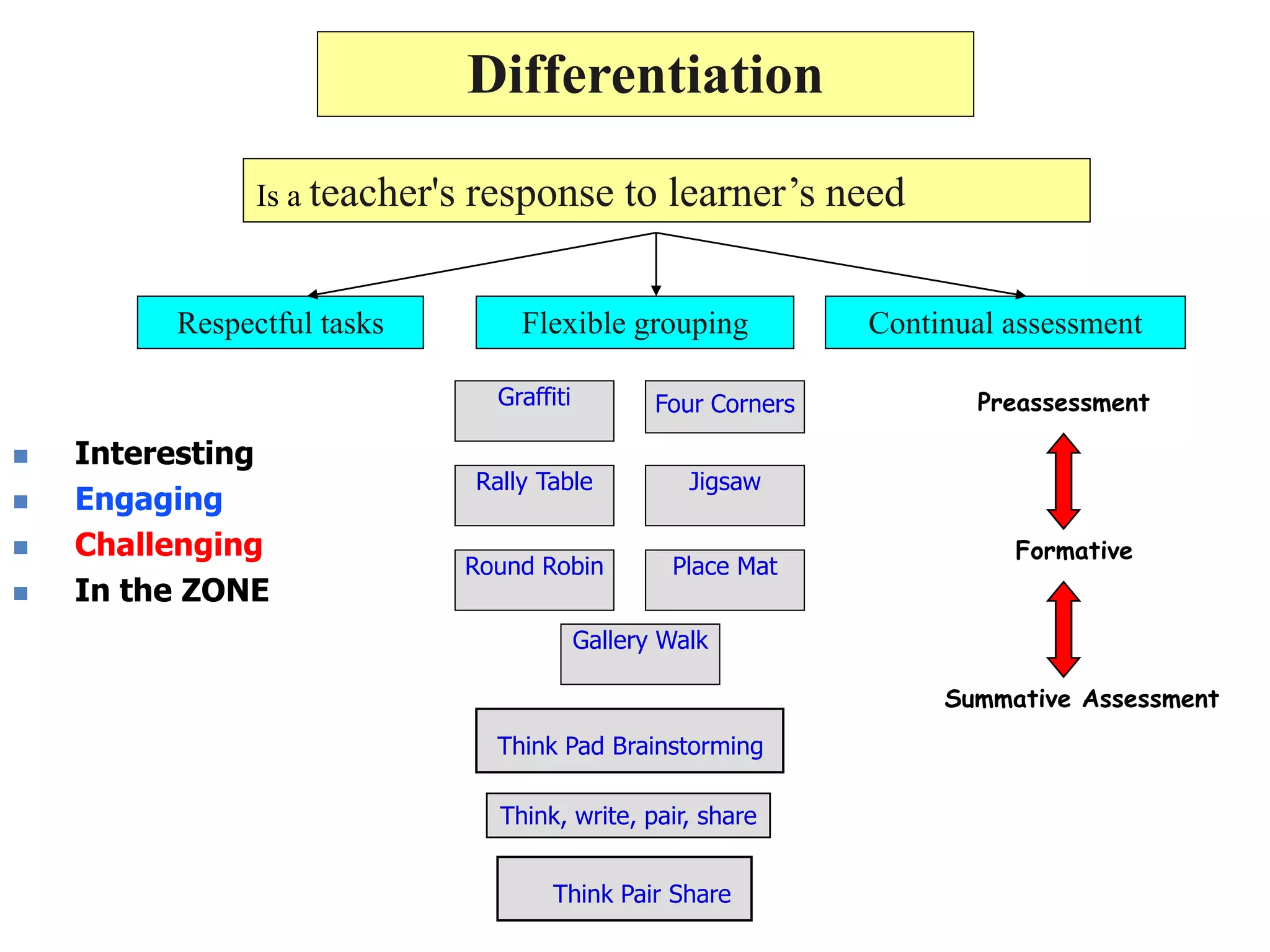
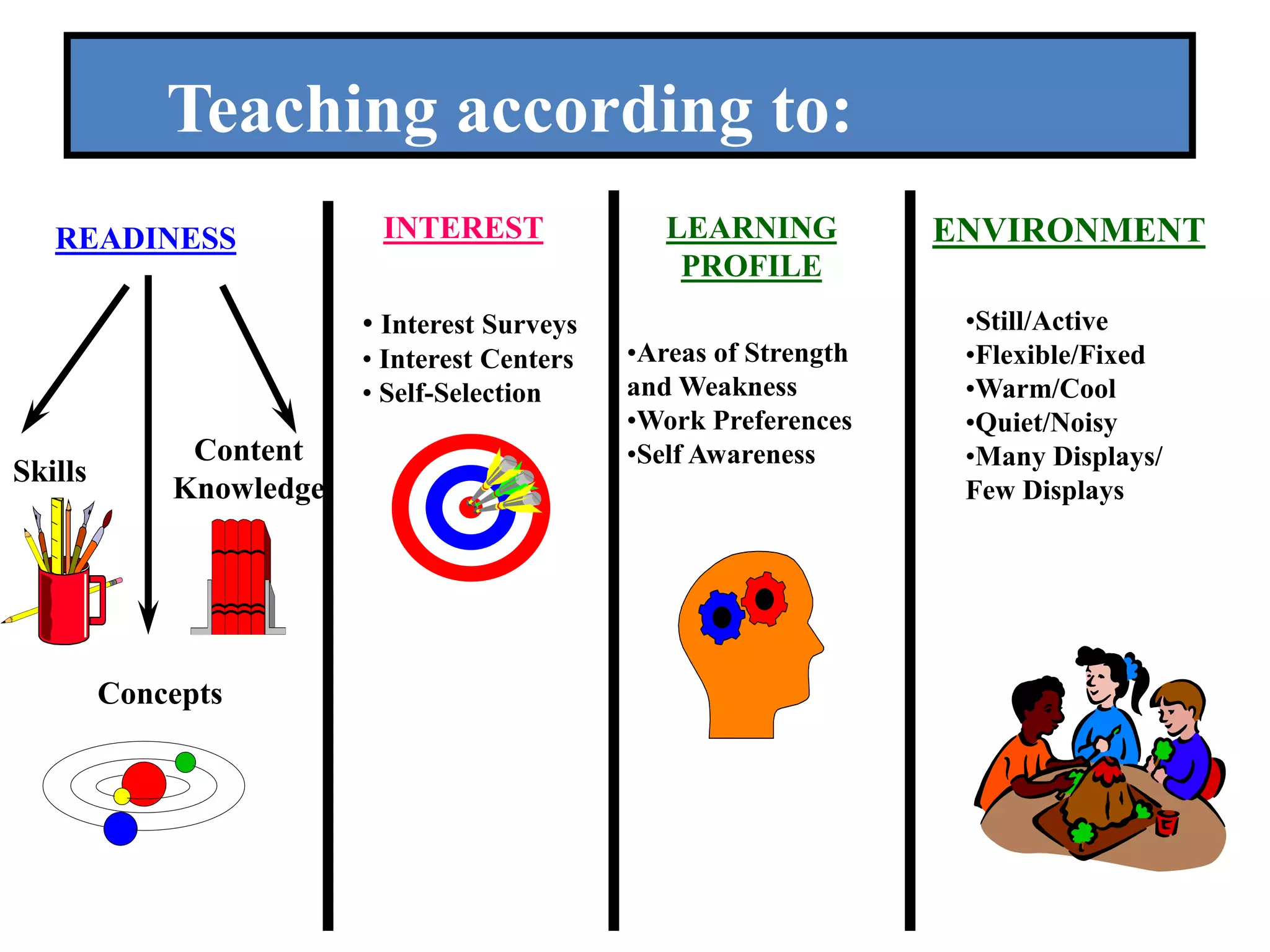
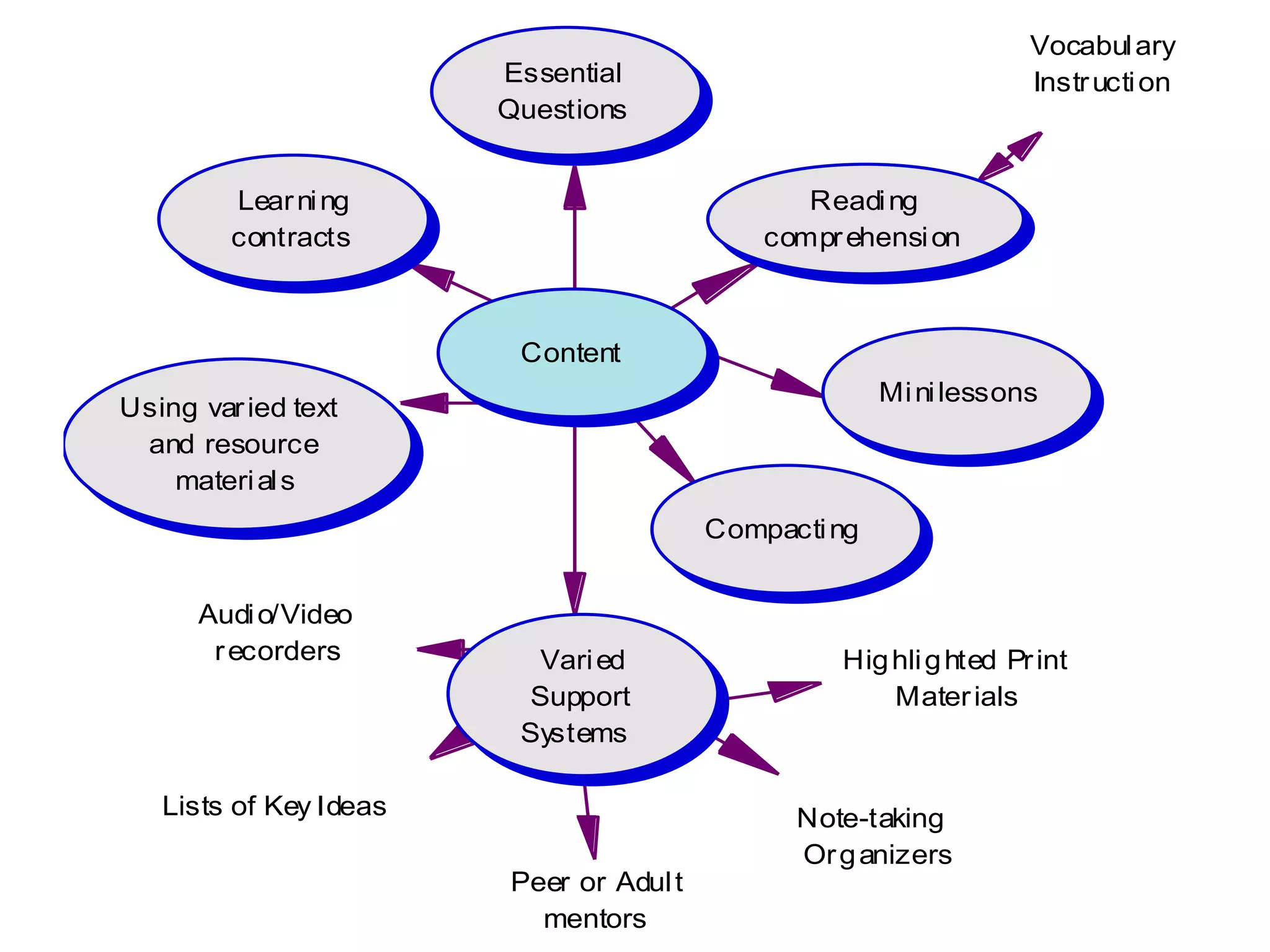
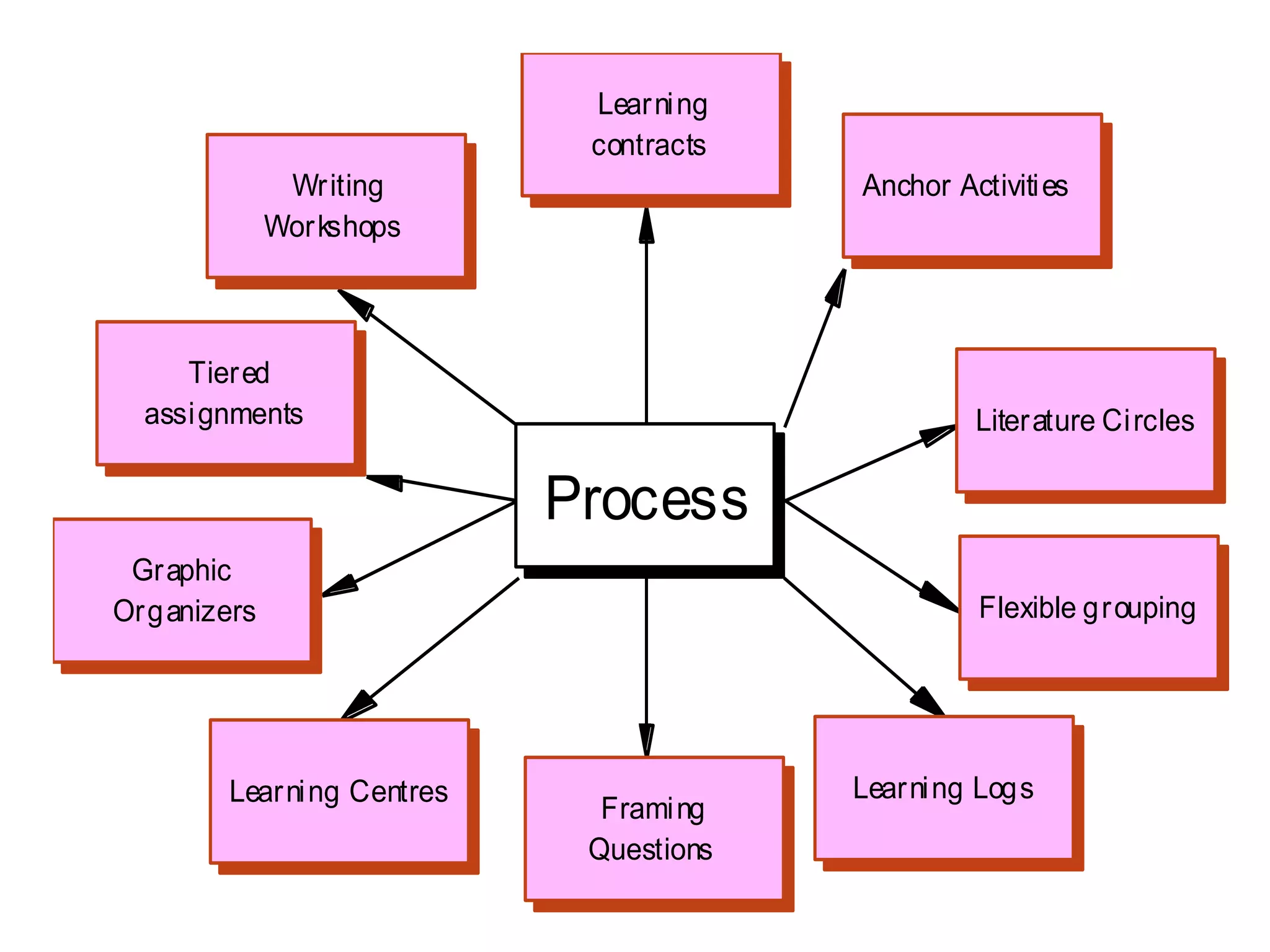
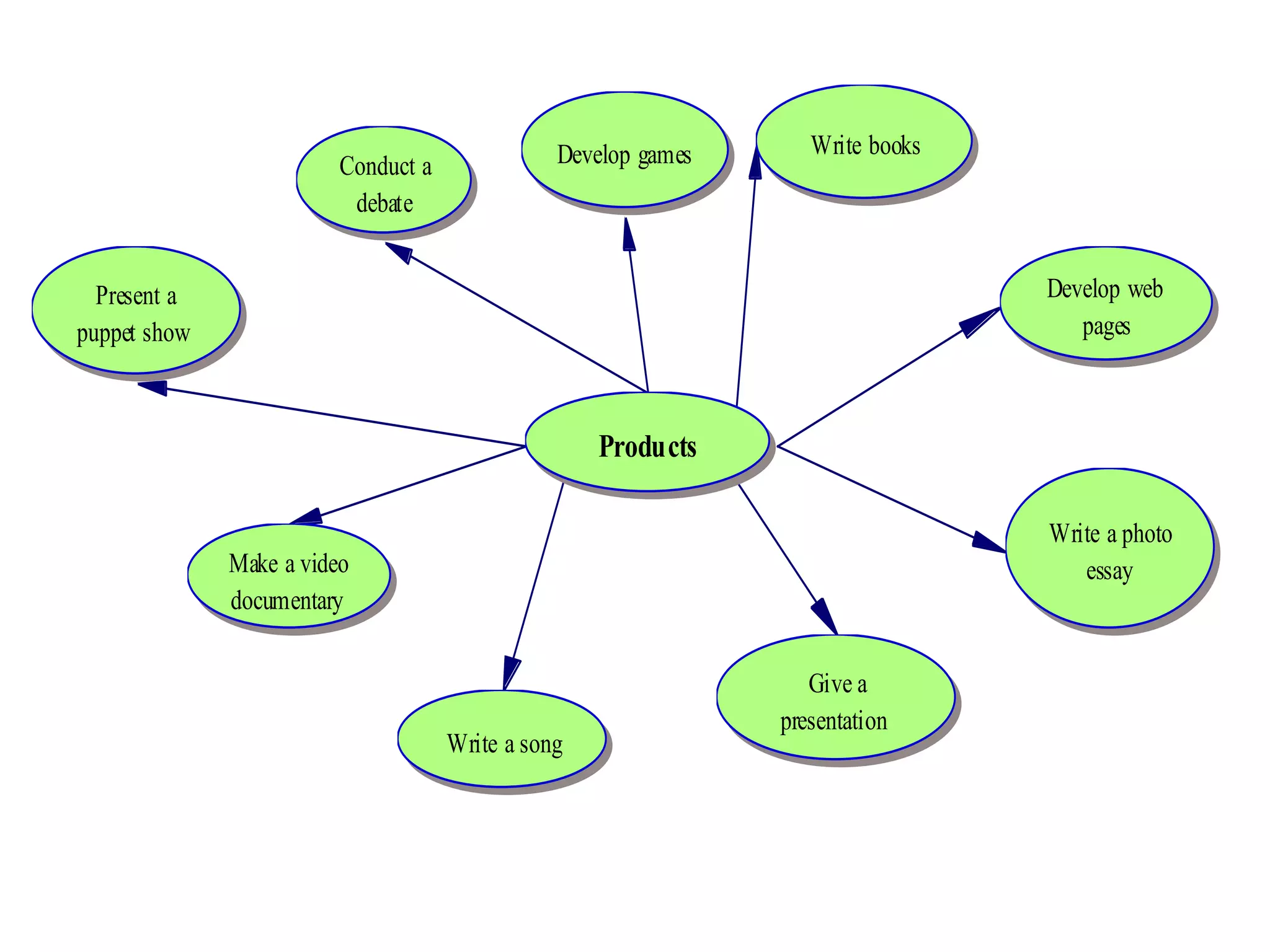
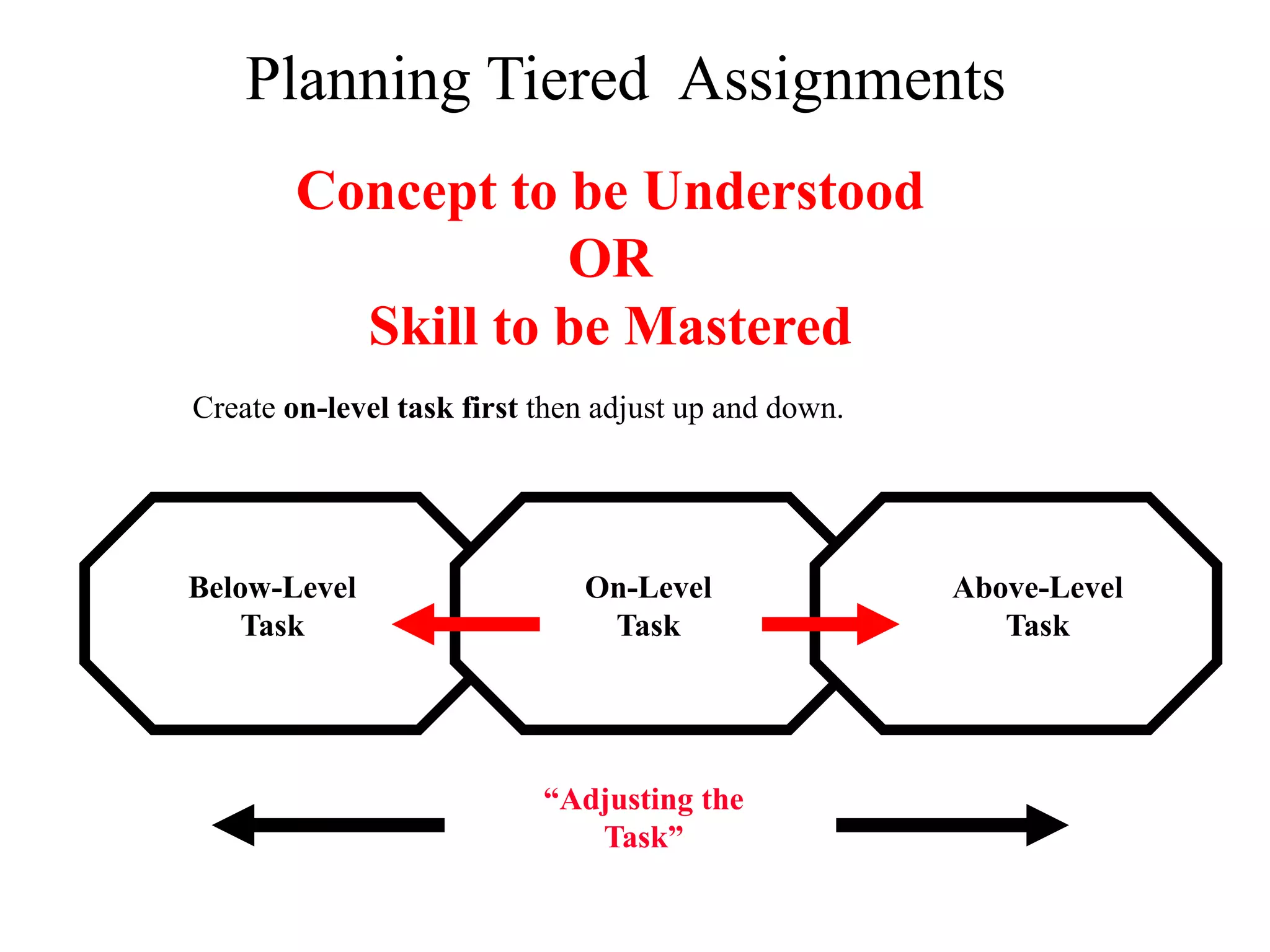
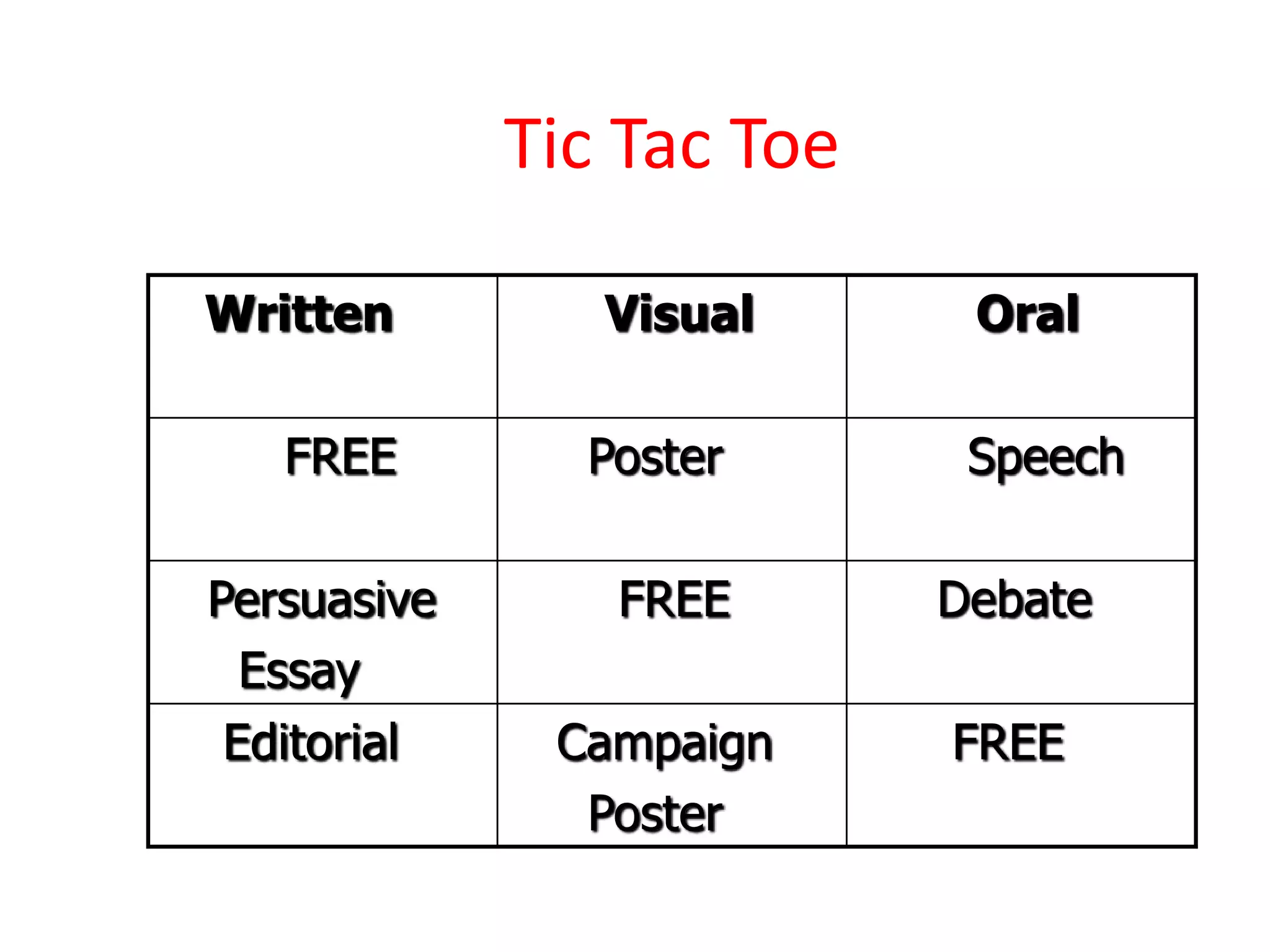
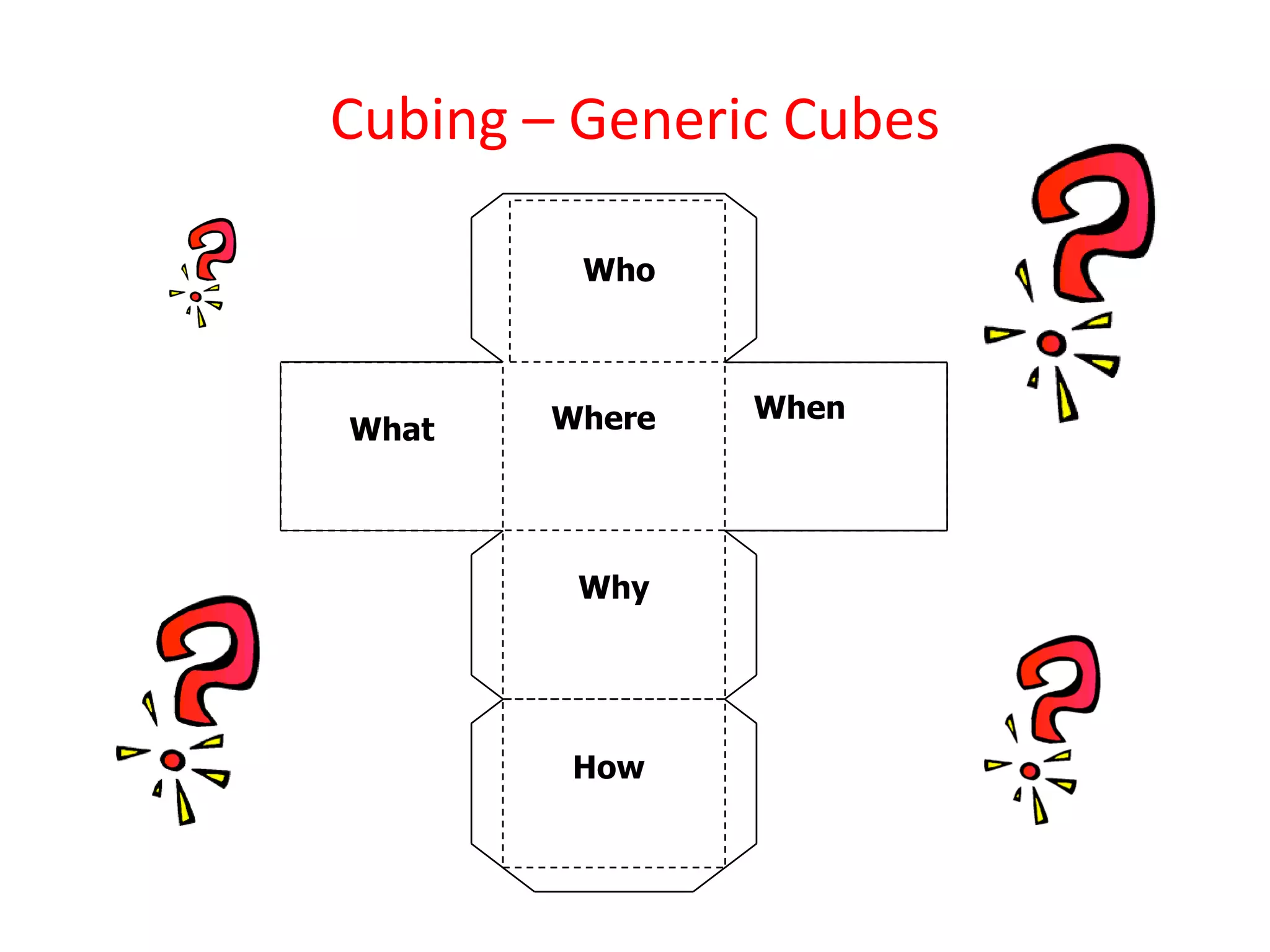
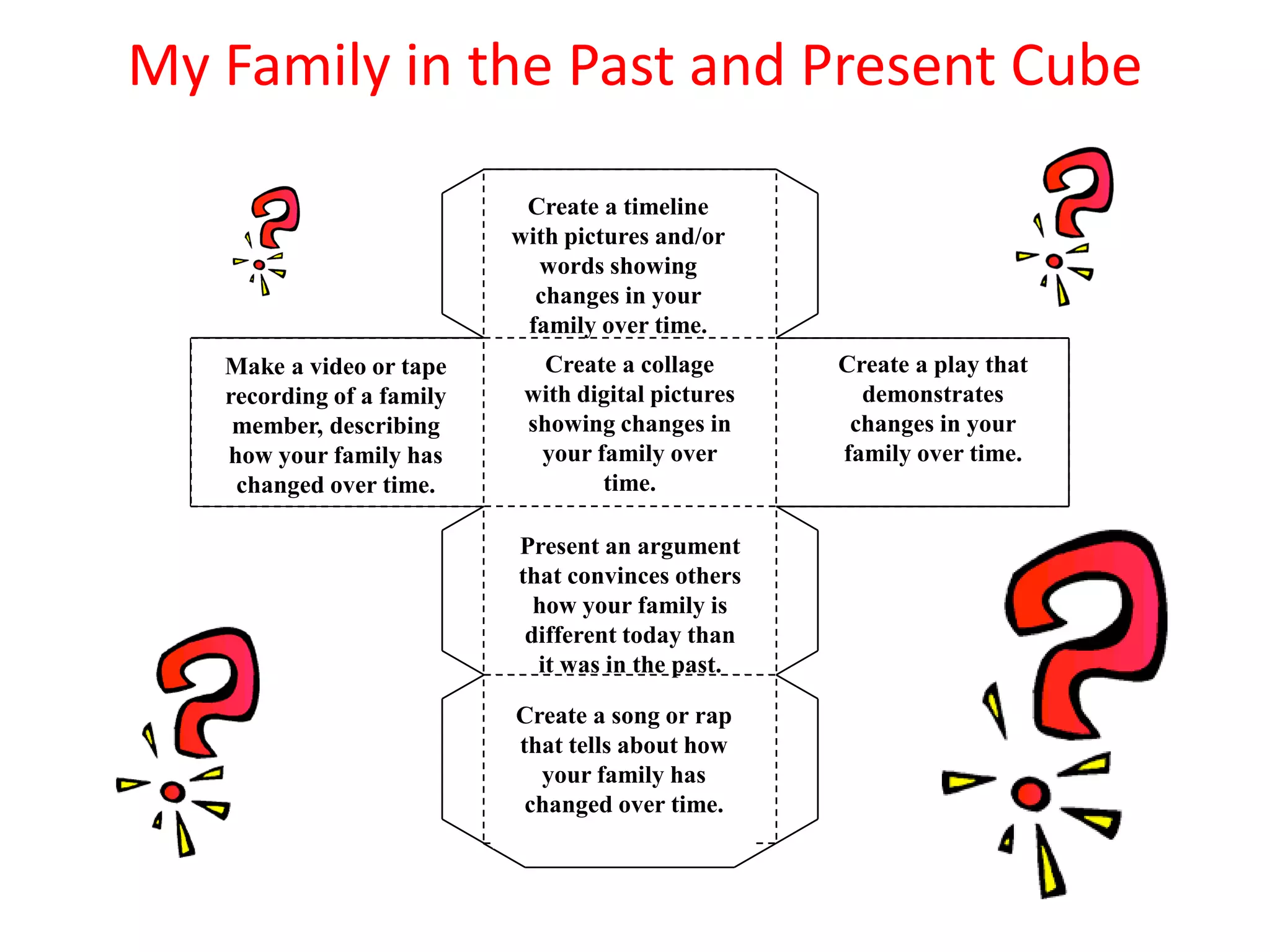
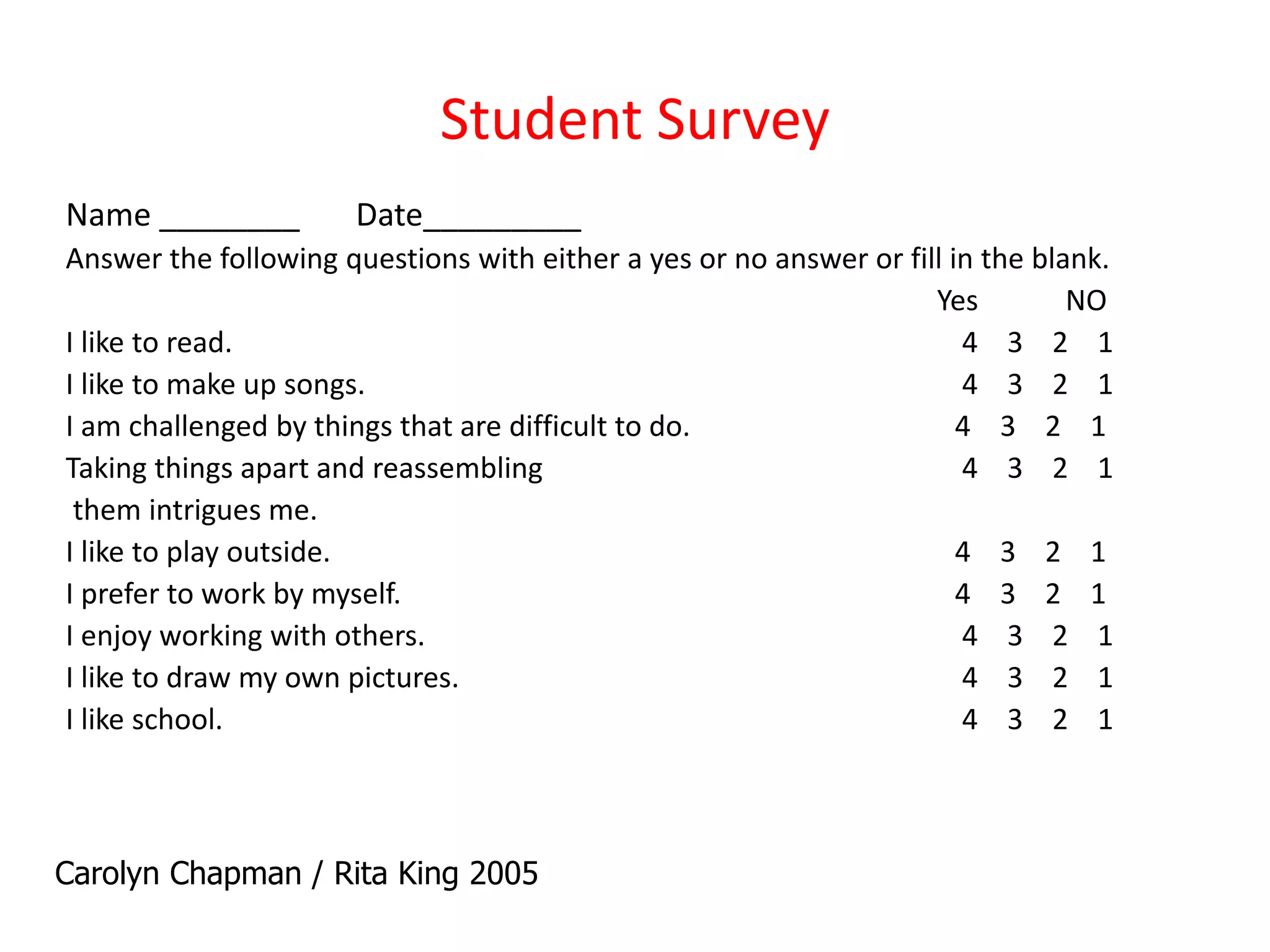
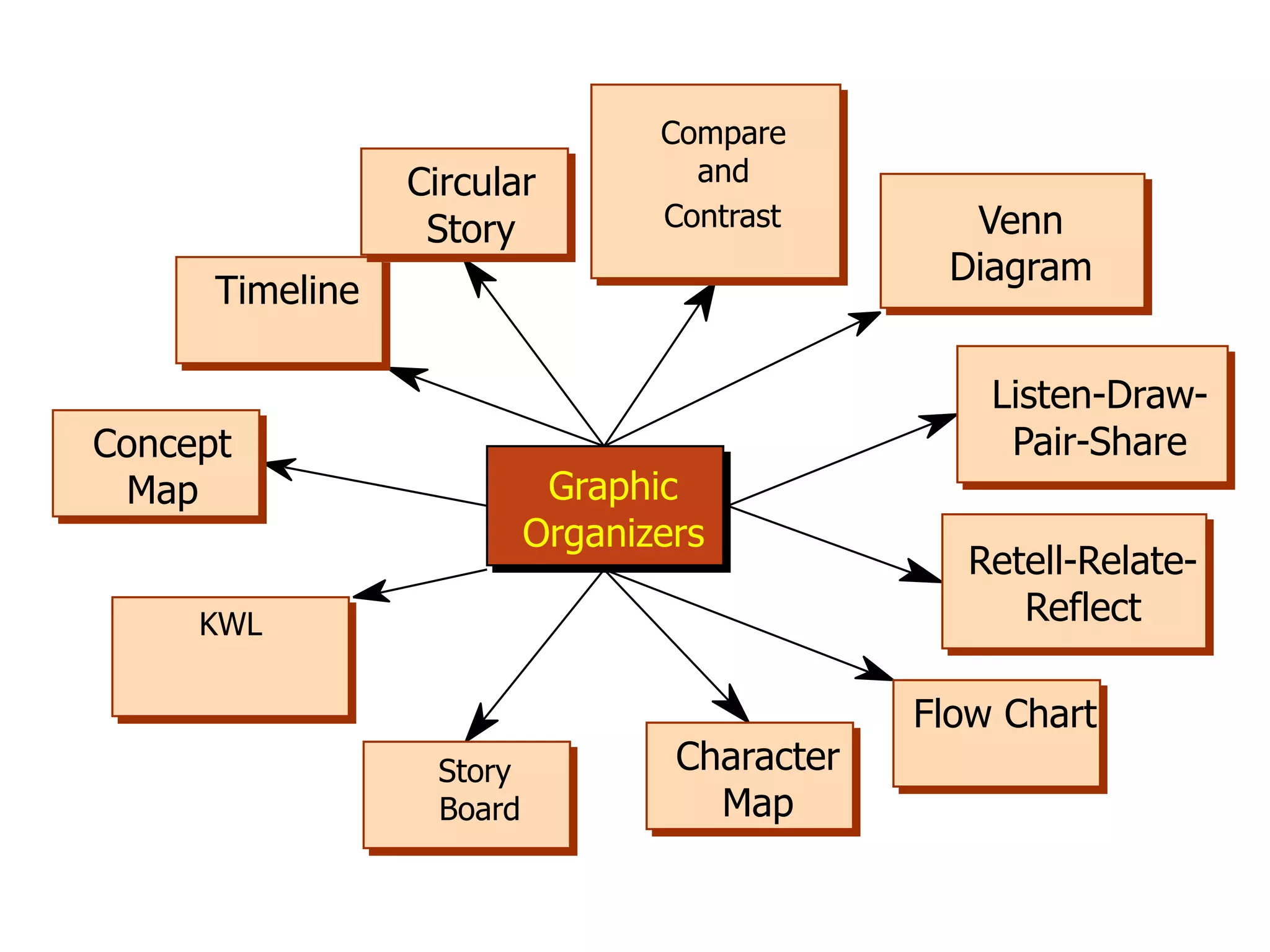
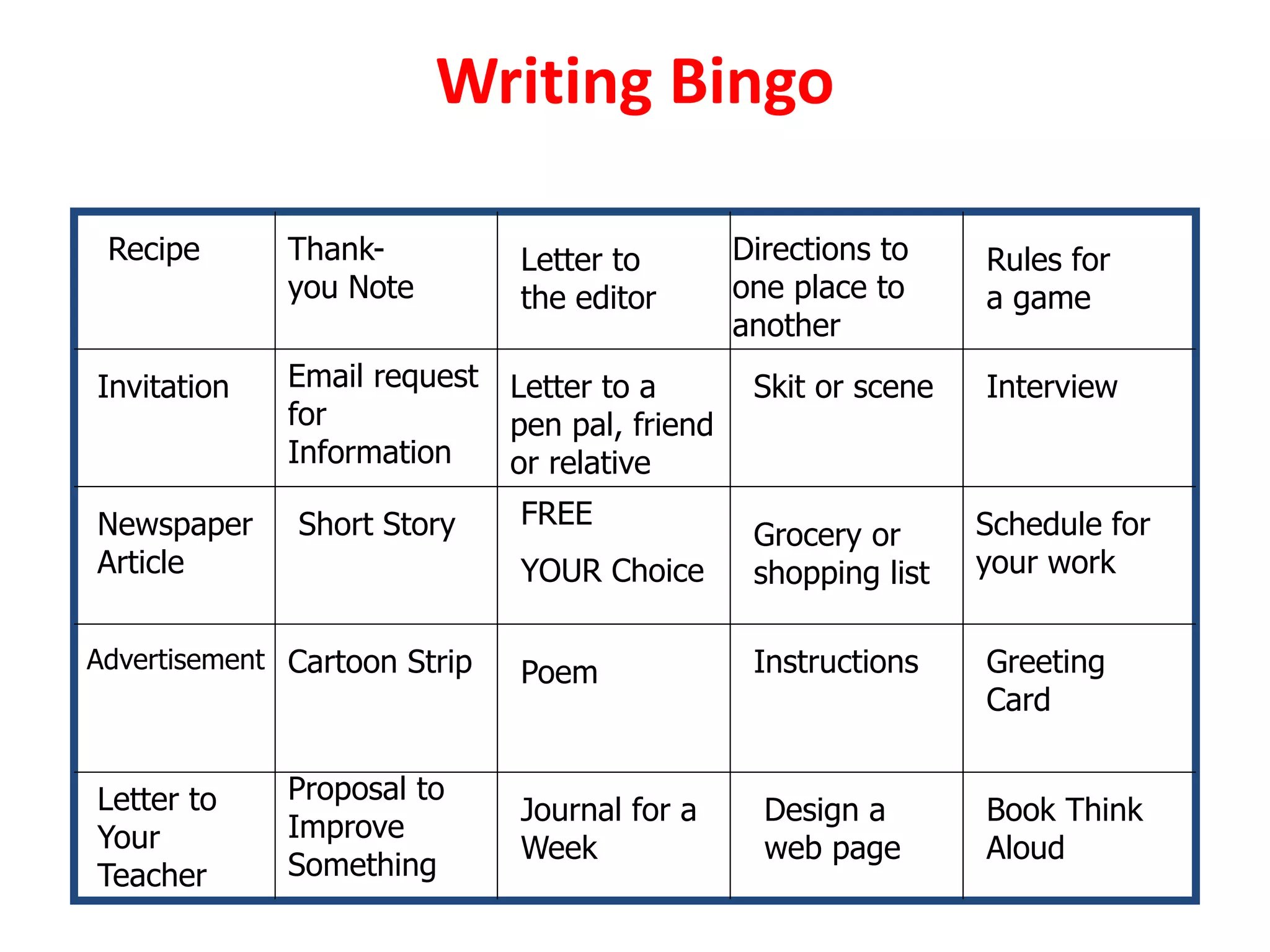
This document discusses differentiating instruction to meet the needs of diverse learners. It defines differentiation as a teacher's response to learner needs through respectful tasks and continual assessment with flexible grouping according to students' readiness, interests, and learning profiles. The document provides examples of differentiating content, process, product, and environment. Activities include tiered assignments, learning contracts, graphic organizers, and interest surveys to engage students at their levels. The goal is to create an inclusive, learner-centered environment where all students are challenged and successful.