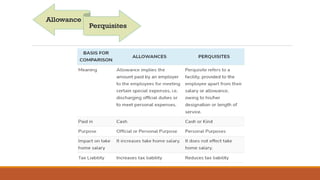
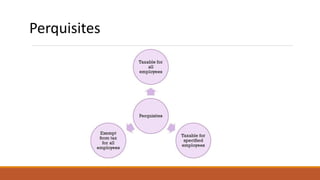
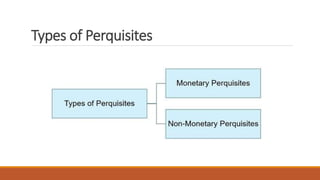
This document discusses the key differences between allowances and perquisites provided by employers to employees. Allowances are a fixed amount given to employees periodically to cover job-related expenses. They are considered part of salary and fully taxable. Perquisites are non-monetary benefits like company cars or housing provided for free or at reduced costs. Only specified employees like directors pay tax on certain perquisites. The document provides examples of allowances like Dearness Allowance and examples of taxable and non-taxable perquisites.