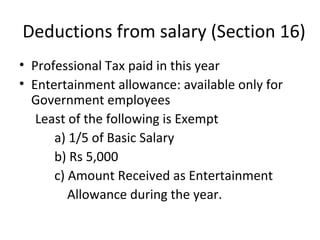
Salary includes remuneration received for personal services under a contract of employment. For income to be categorized as salary, there must be an employer-employee relationship. Salary is taxable on a due or receipt basis, whichever is earlier. Components of taxable salary include basic salary, bonuses, commissions, allowances, perquisites, and profits in lieu of salary. Certain allowances such as transport, house rent, and leave travel are partially or fully tax exempt. Perquisites include benefits provided by employers and are taxed as salary. Specified employees who are directors, substantial interest holders, or high salary earners face additional taxes on perquisites.















![PROFIT IN LIEU OF SALARY
[ U/S 17(3) ] includes
• Any compensation due or received in connection with the termination
of the employment of due to modification of the terms and conditions
of his employment.
• Payments from an employer or former employer from provident fund or
such other funds, excluding the amounts exempt from tax under Section
10 and excluding the amounts of contribution made by the assessee and
the interest thereon
• Any sum received under a Keyman Insurance Policy including the sum
allocated by way of Bonus on such policy.
• Amounts due to or received, whether in Lumpsum or otherwise by any
assessee from any person.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-salary-141209104554-conversion-gate02/85/Lecture-7-salary-16-320.jpg)