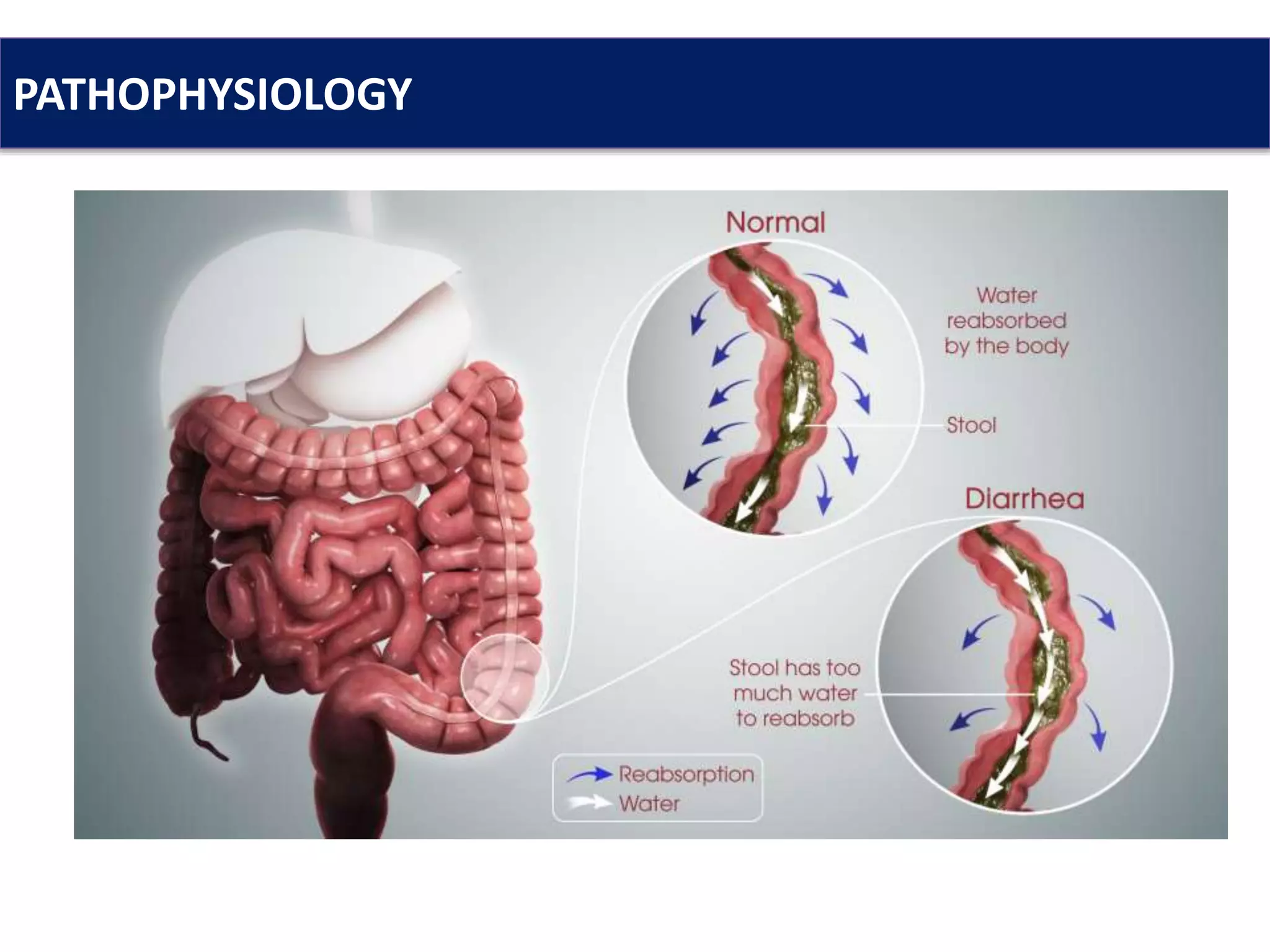
Diarrhea is characterized by an increase in bowel movement frequency and a decrease in stool consistency, often caused by infections or systemic diseases. Treatment focuses on dietary management, rehydration, and addressing underlying causes, with chronic diarrhea requiring a thorough evaluation of potential disorders. Common therapeutic approaches include the use of antimotility agents, antisecretory compounds, and antibiotics, though many treatments are primarily symptomatic.





![1.Secretory diarrhea
Occurs when a stimulating substance
(eg, vasoactive intestinal peptide [VIP], laxatives, or bacterial
toxin) increases secretion or decreases absorption of large
amounts of water and electrolytes.
Cholera infection stimulates the secretion of negatively
charged chloride ions.
Sodium and water present in the secretion, help maintain the
charge balance in the gastrointestinal tract.
In this type of diarrhea, intestinal fluid secretion is isotonic
with plasma.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diarrhoea-200220093659/75/Diarrhoea-7-2048.jpg)



















![Recommendations for treating chronic
diarrhea. Follow these steps:
(1) Perform a careful history and physical examination.
(2) The possible causes of chronic diarrhea are many. These can
be classified into intestinal infections (bacterial or protozoal),
inflammatory disease (Crohn diseas or ulcerative colitis),
malabsorption (lactose intolerance), secretory hormonal
tumor (intestinal carcinoid tumor or vasoactive intestinal
peptide [VIP]–secreting tumors), drug (antacid), factitious
(laxative abuse), or motility disturbance (diabetes mellitus,
irritable bowel syndrome, or hyperthyroidism).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diarrhoea-200220093659/75/Diarrhoea-27-2048.jpg)










