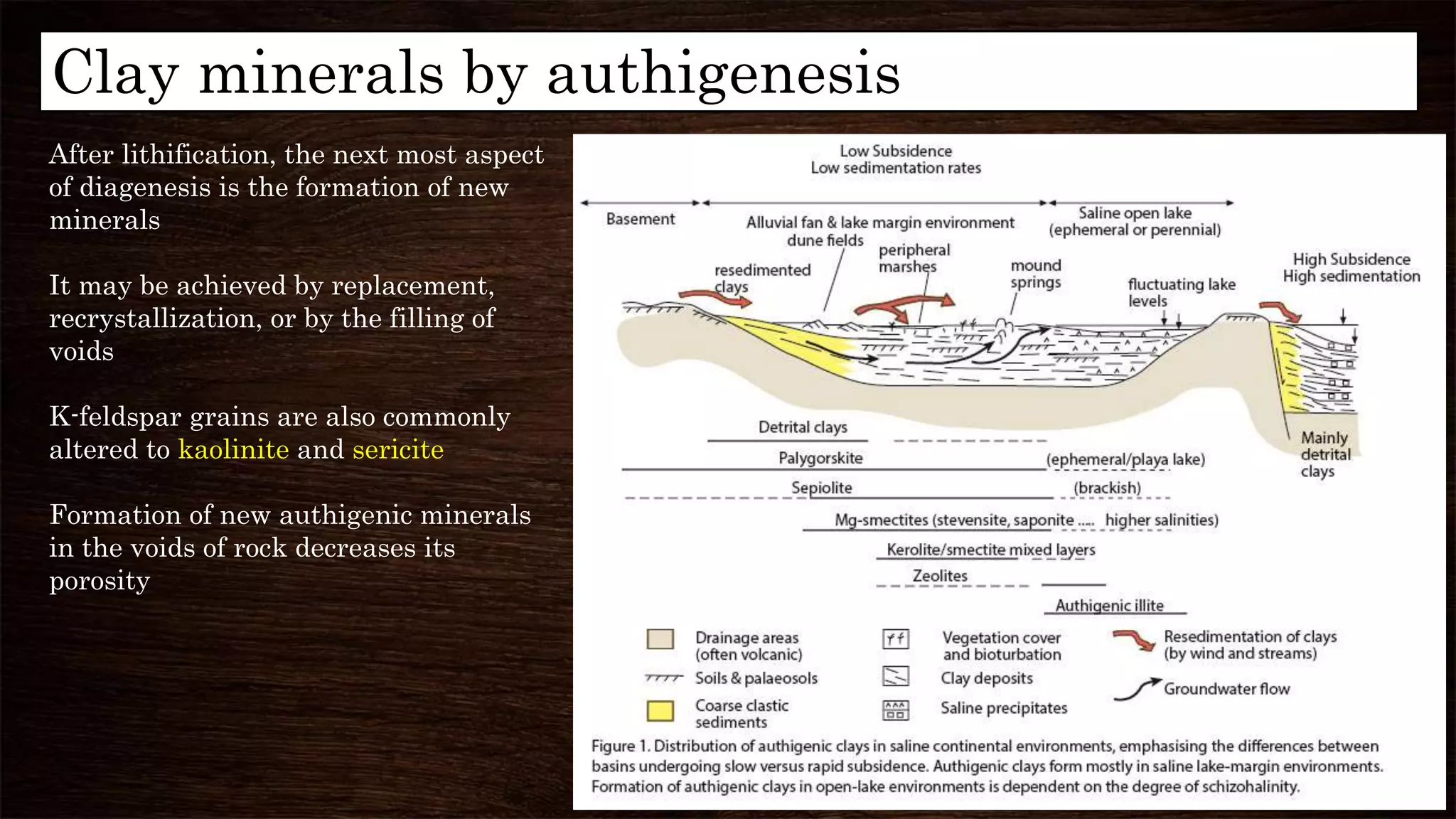
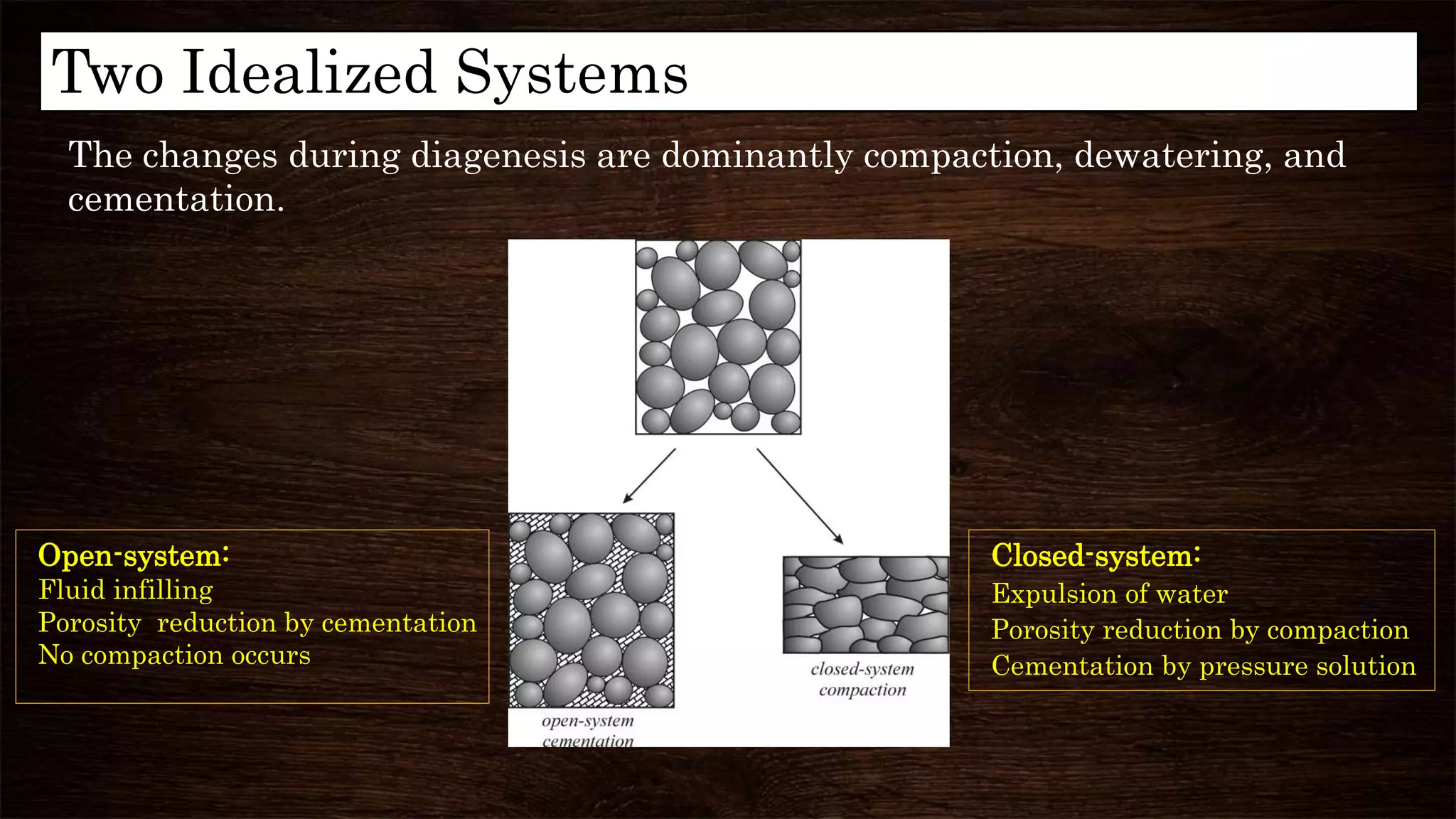
Diagenesis refers to the physical, chemical, and biological changes that sediments undergo after deposition to form sedimentary rock. It can include compaction, cementation, replacement of minerals, and formation of new minerals. There are three main stages of diagenesis: syndiagenesis during sedimentation, anadiagenesis involving compaction and maturation, and epidigenesis during emergence before erosion. Common diagenetic processes in mudrocks include mechanical and chemical compaction, which reduce porosity, and the formation of authigenic minerals like calcite, illite, and kaolinite via replacement or precipitation. Clay minerals are important indicators in hydrocarbon exploration as they can provide information about tectonics, hydrocarbon generation





![• Illite (low alumina clays, 10-20%)
• Kaolinite (high alumina clays, 20-40%)
• Smectite (Montmorillonite [Al], Saponite [Mg], Nontronite [Fe])
• Chlorite
Common clay minerals
Hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates
kaolinite
illite smectite chlorite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/claydiagenesis-181009190241/75/Diagenesis-of-clay-minerals-7-2048.jpg)