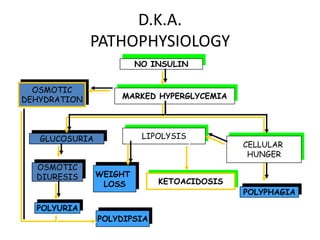
The document discusses acute and late complications of diabetes mellitus. Acute complications include diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), insulin shock, and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. Late complications involve damage to organs over time and include retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Treatment of diabetic nephropathy focuses on blood pressure control using ACE inhibitors or ARBs to slow disease progression.