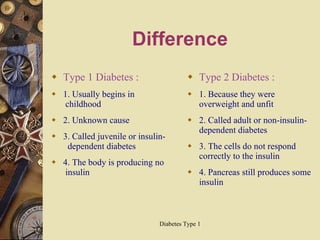
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin and is an autoimmune disease where immune cells attack pancreatic beta cells responsible for insulin production. Symptoms include increased thirst, urination, weight loss, and fatigue. It is diagnosed through blood tests showing low or undetectable insulin and C-peptide levels. While there is no cure, it can be controlled through insulin administration, blood glucose monitoring, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in childhood and the body produces no insulin, whereas type 2 diabetes is associated with overweight/unfitness and the cells do not correctly respond to insulin.