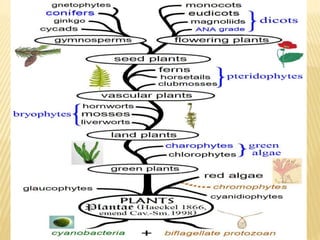
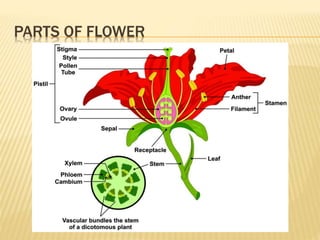
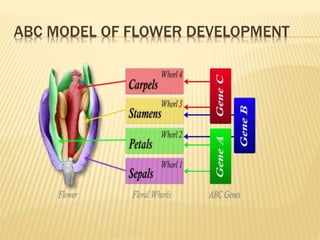
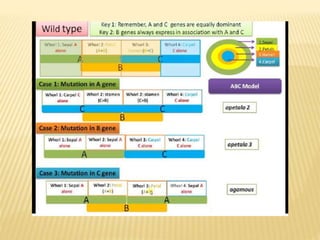
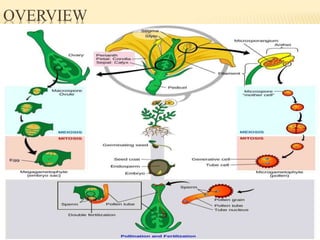
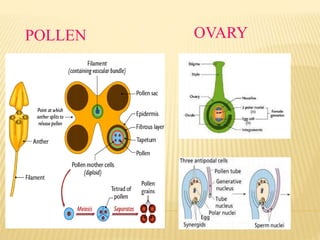
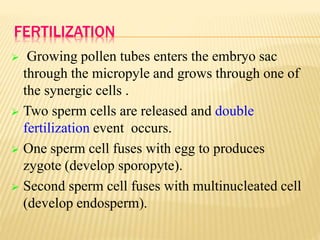
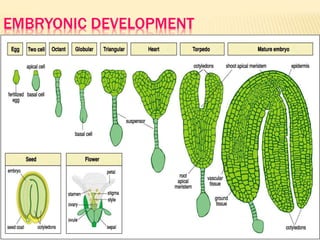
This document provides an overview of plant development patterns in flowering plants. It discusses developmental strategies of plants including that plant cells do not migrate and life cycles involve diploid and haploid multicellular stages. It also describes parts of flowers like the ABC model of flower development. Reproductive structures in flowering plants like being monoecious or dioecious are explained. The document further summarizes gamete production in angiosperms involving haploid and diploid stages. Key processes like pollination, fertilization, and embryogenesis leading to the establishment of basic body plans in plants are outlined in less than 3 sentences.