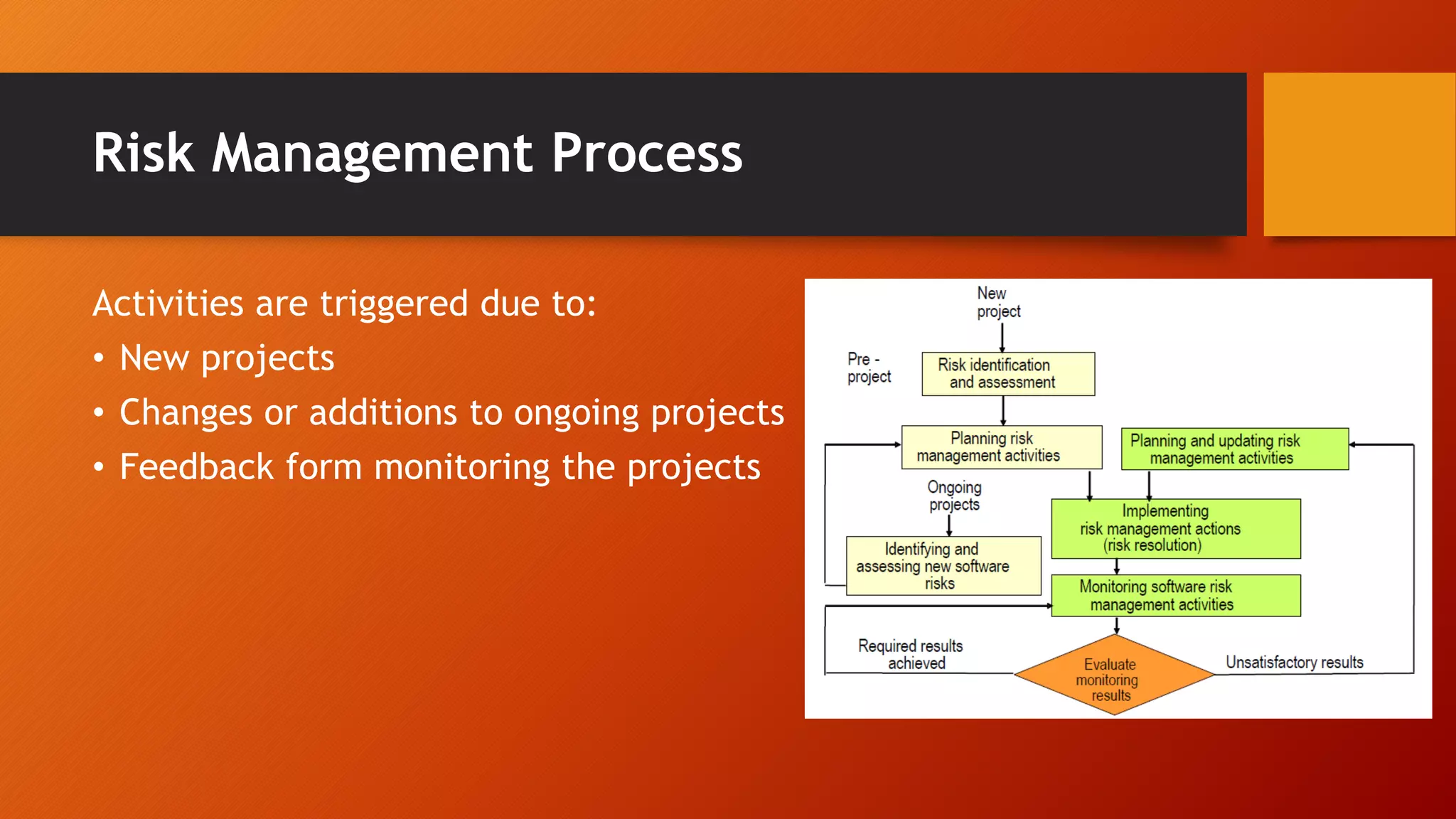
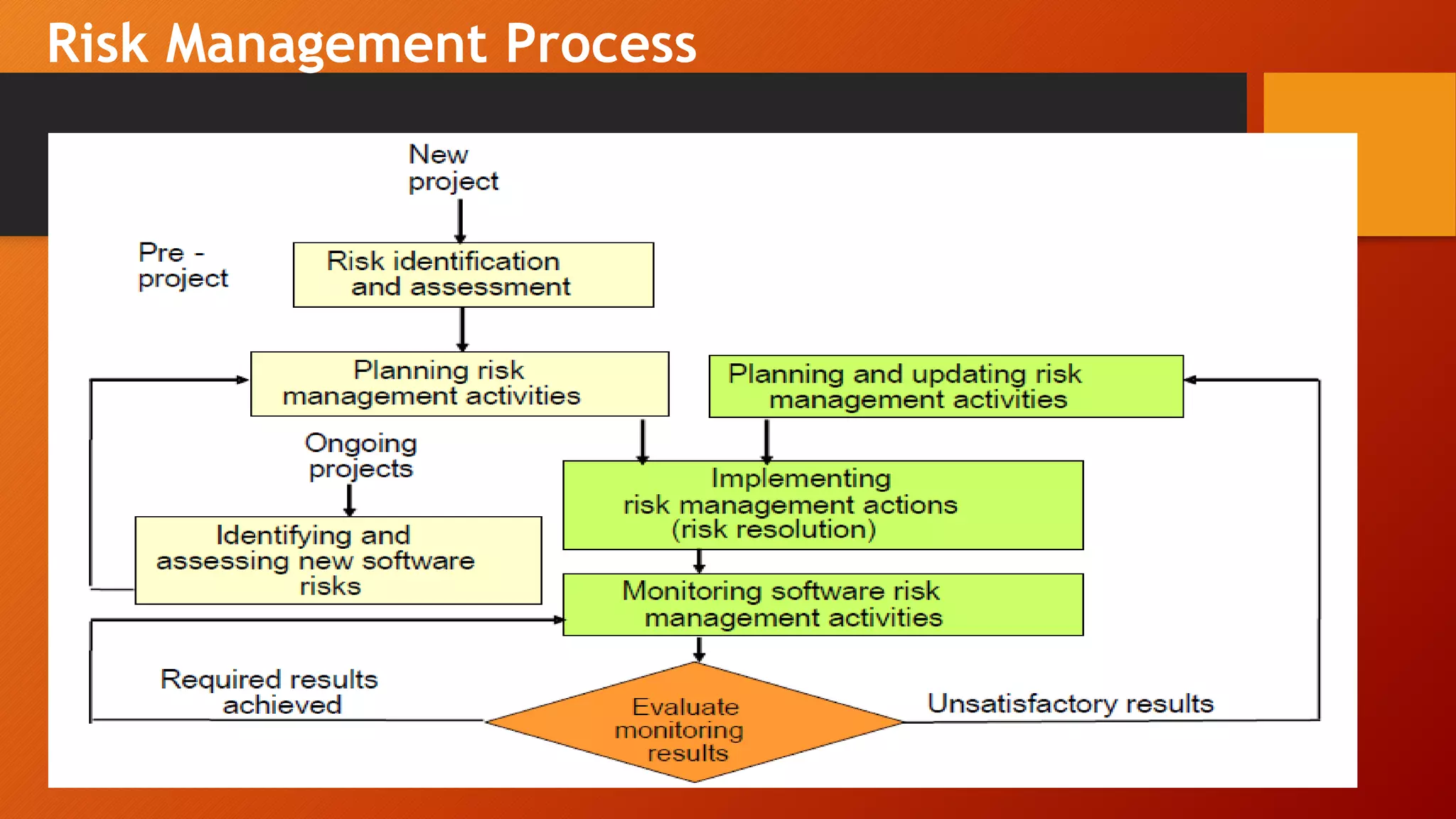
The document outlines elements of a development plan and quality assurance plan for a software project. The development plan covers deliverables, interfaces, methodology, standards, milestones, organization, facilities, risks, and costs. The quality assurance plan defines quality goals, review activities, tests, and configuration management. It also discusses classes of development risks like scheduling and requirements, and provides examples of top risks. Finally, it describes a risk management process and potential actions to prevent and resolve risks through prevention, identification, and resolution. The overall objectives are to plan adequately for successful and timely project completion through scheduling, resource allocation, risk resolution, quality activities, and management control.








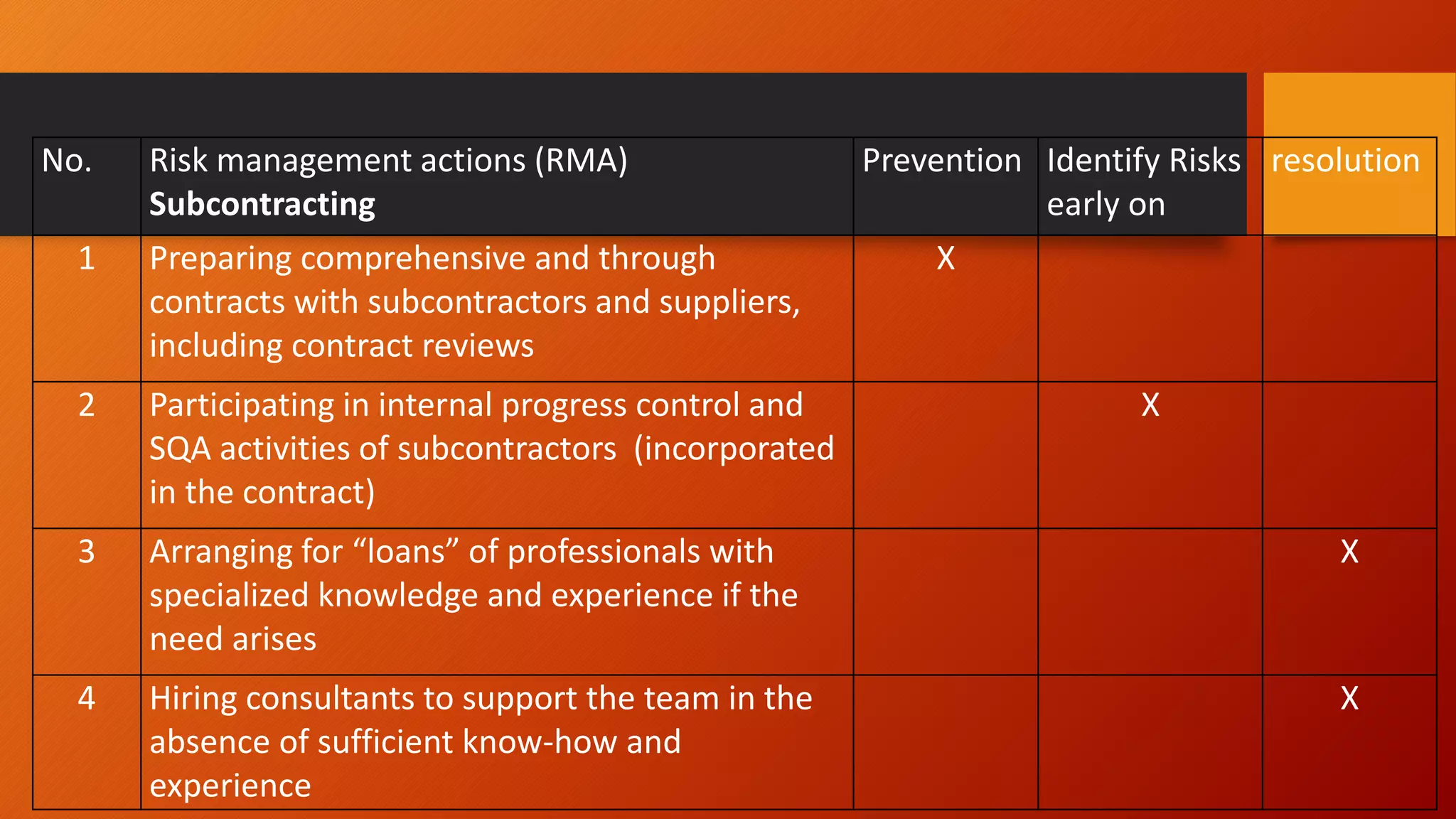
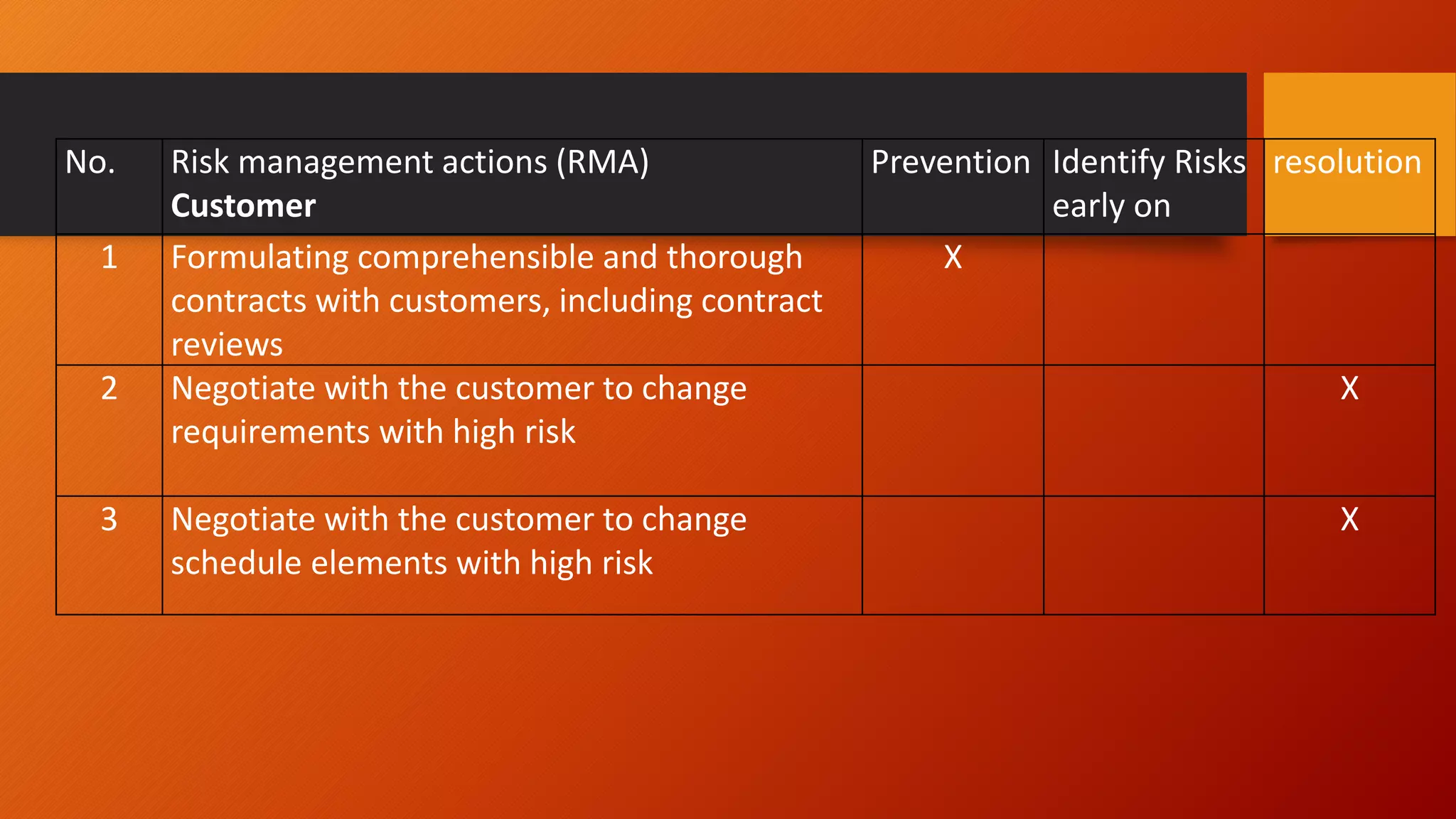
![Risk Management Actions [Galin2004]
No. Risk management actions (RMA)
Internal risk management
Prevention Identify Risks
early on
resolution
1 Detailed analysis of the requirements and
estimated schedules and costs
X
2 Efficient project organization, adequate staff
and team size
X
3 Personal Training X
4 Arranging for take over in case of turnover
and unanticipated workloads
X
5 User participation in the development
process
X
6 User participation in the development
process
X
7 Intensive SQA measures such as inspections,
X design reviews, and benchmarking
X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developmentandqualityplanedited-150310231514-conversion-gate01/75/Development-and-quality-plan-11-2048.jpg)
![Risk Management Actions [Galin2004]
No. Risk management actions (RMA)
Internal risk management
Prevention Identify Risks
early on
resolution
8 Periodic checking for timely availability of firm
professionals currently occupied with other
projects
X
9 Arranging for participation of professional staff
members with experience with SRIs
X
10 Scheduling SRI-related activities as early as
possible
X
11 Prototyping SRI related modules or
applications
X
12 Preparing scenarios for complicated SRI-
related modules or applications
X
13 Simulating related modules or applications X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developmentandqualityplanedited-150310231514-conversion-gate01/75/Development-and-quality-plan-12-2048.jpg)