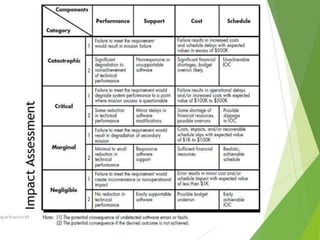
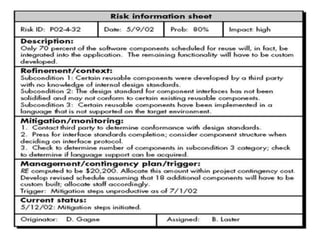
There are two main types of risk strategies: reactive and proactive. A reactive strategy monitors for risks but does not plan for them, while a proactive strategy identifies potential risks early and develops contingency plans. Some key risks include project delays or cost overruns, technical issues, and business risks. Risk identification involves checking known risk categories like project size, staff experience, and technology complexity. Risks are then estimated based on their probability and potential impact. Quality management aims to produce high quality software through techniques like quality control, assurance, and cost analysis. Six Sigma is a widely used strategy that defines requirements, measures current quality, analyzes defects, designs processes to avoid defects, and verifies the new process.