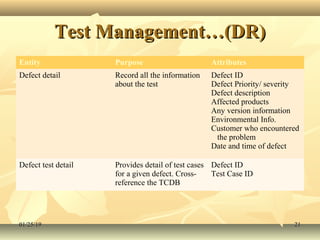
This document discusses test planning and management. It covers preparing a test plan by determining what to test, how to test, resources needed, and timelines. It also discusses scope management, prioritizing features for testing, deciding the test approach/strategy, and identifying test deliverables, risks, and responsibilities. The document provides details on test infrastructure management, configuration management, and people management for testing.