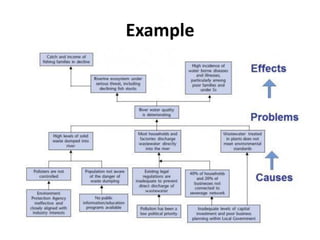
Dokumen ini membahas analisis masalah, pengujian situasional, dan diskusi kelompok dalam konteks asesmen untuk mengevaluasi kompetensi kandidat dalam suatu pekerjaan. Metode yang dibahas meliputi studi kasus, diskusi kelompok tanpa pemimpin, serta berbagai alat untuk pengembangan analisis masalah guna membantu kandidat dalam perencanaan dan pengambilan keputusan. Penekanan juga diberikan pada pentingnya validitas, praktik, serta pengukuran kompetensi seperti pemecahan masalah, kemampuan analitis, dan komunikasi.