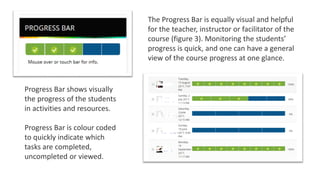
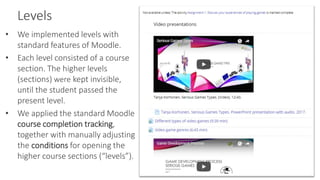
This document discusses the development of a gamified online course on serious games in collaboration between Tampere and Kajaani universities, funded by a national project. Gamification was implemented across five courses using various Moodle plugins, enhancing student engagement and motivation, though technical issues were encountered. Overall, the use of gamification in the courses proved beneficial, but careful selection of tools and features is essential for effective application.