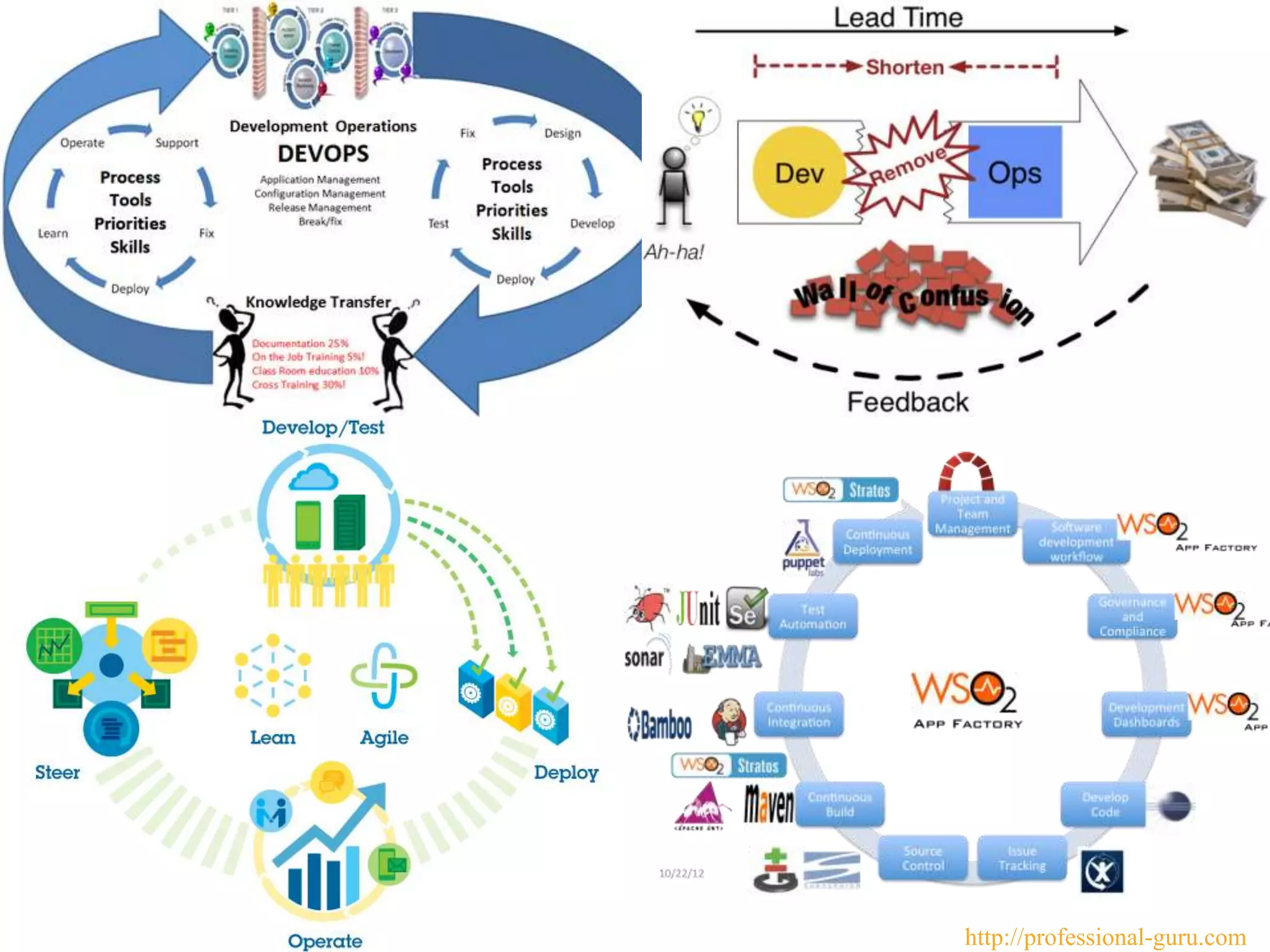
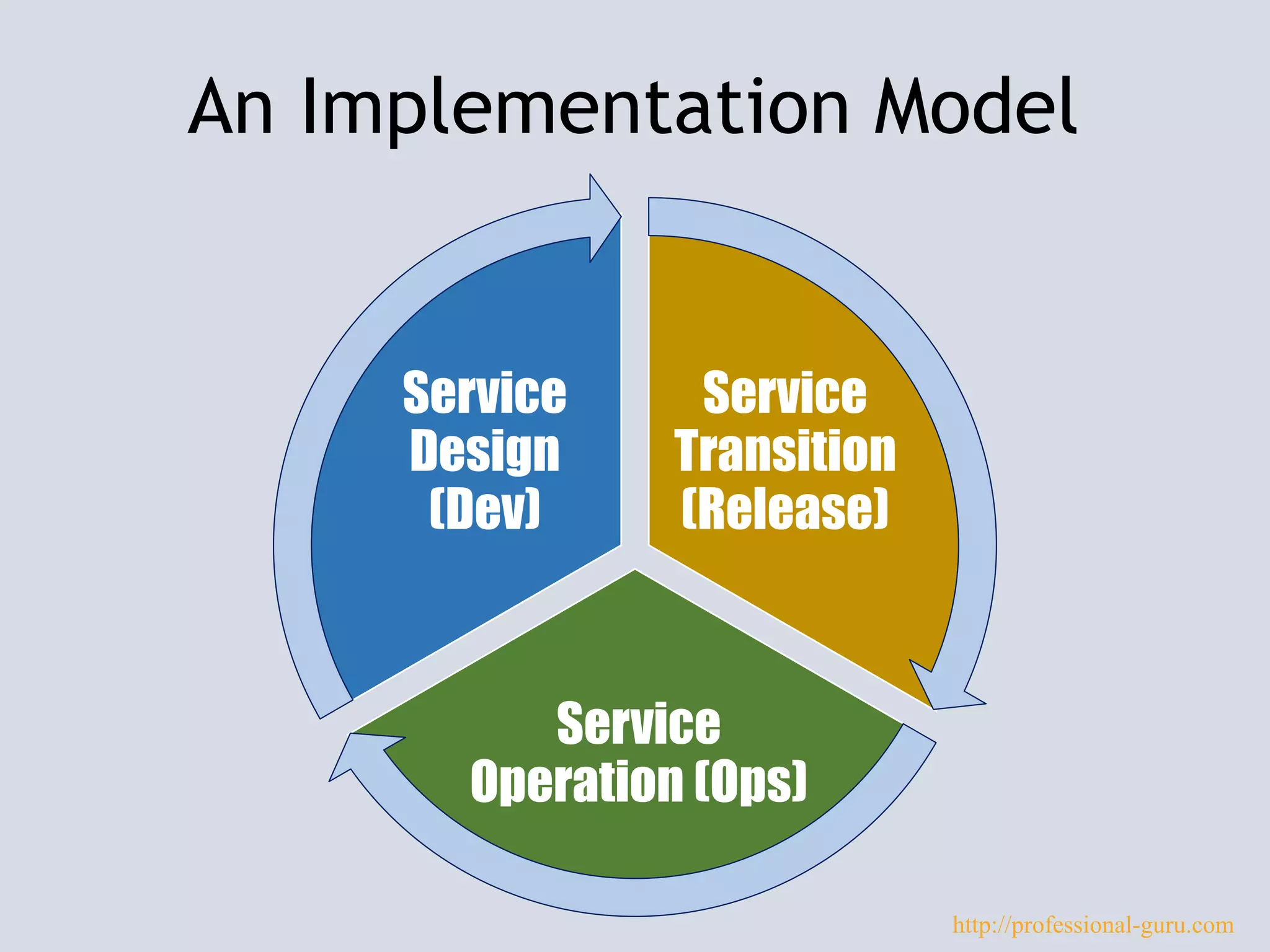
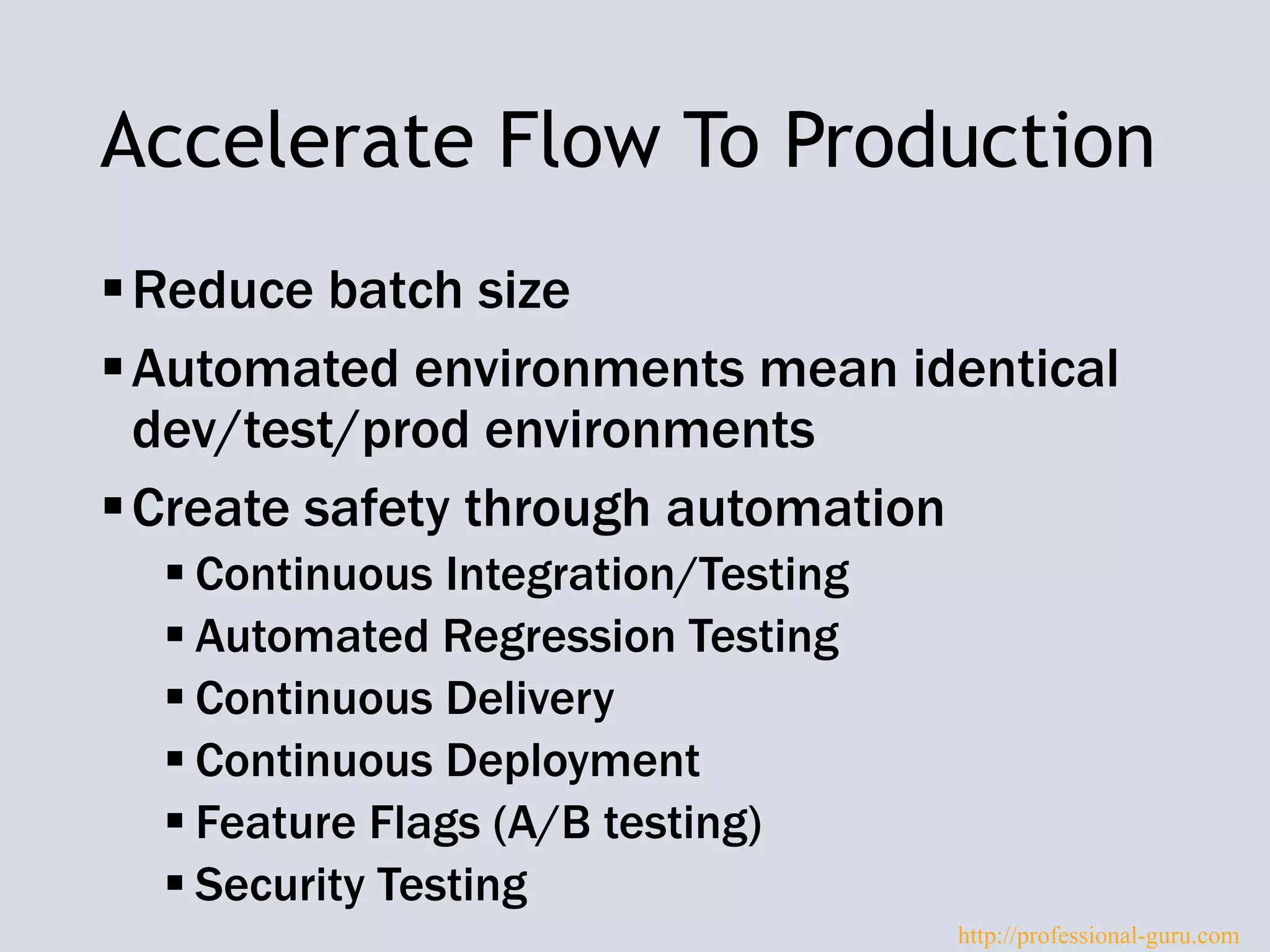
The document discusses DevOps, emphasizing its role in improving collaboration between development and operations teams throughout the service lifecycle to address issues such as slow delivery and high error rates. It outlines key principles, practices, and an implementation model for integrating DevOps, along with common pitfalls to avoid and evidence of its benefits in high-performing organizations. Resources for further learning about DevOps are also provided.