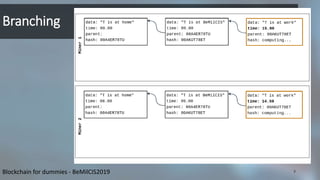
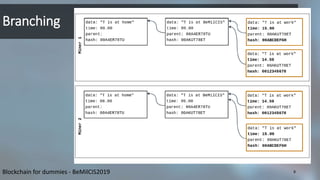
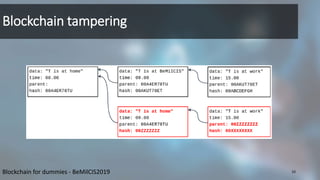
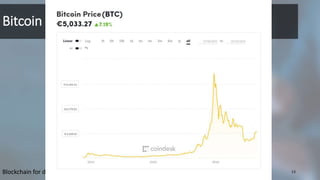
Blockchain is a distributed database that records transactions in chronological order in digitally signed blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block, forming a chain. Miners on the network verify and record new transactions in blocks, which are then broadcast to the network. While branching can occur, the blockchain resolves it automatically by continuing on the longest branch. Tampering with past transactions requires overcoming the main branch through computational power. The first blockchain application was Bitcoin, which uses this structure to record ownership of digital currency through public/private key cryptography.