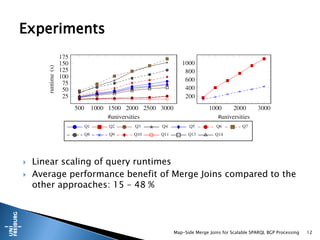
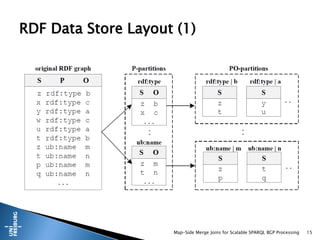
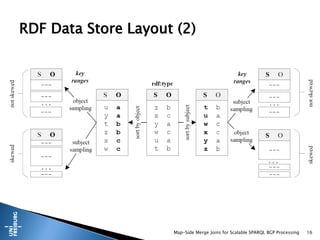
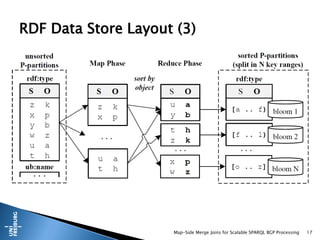
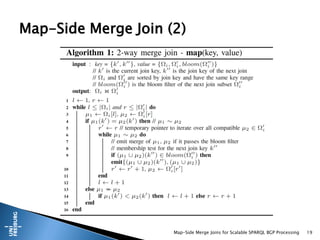
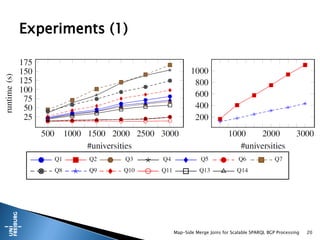
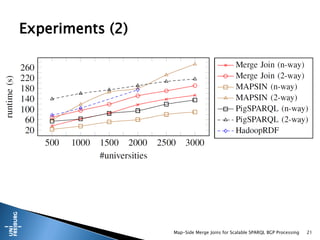
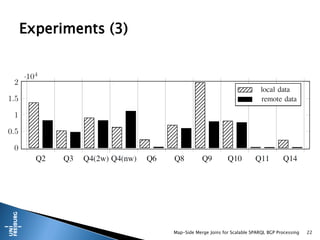
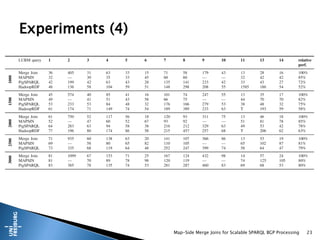
This document presents a method for scalable SPARQL BGP processing using map-side merge joins, focusing on fast, low-latency query execution while avoiding costly joins. It details the implementation of sort-merge joins within a MapReduce framework, highlighting the necessary challenges and contributions such as dynamic bloom filters and guaranteed pre-sorted data. Experimental results indicate improved performance of 15-48% in query runtimes compared to traditional methods.
![ Approach:
◦ Divide Join task into N independent subtasks
◦ Each subtask is processed by exactly one machine
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 6
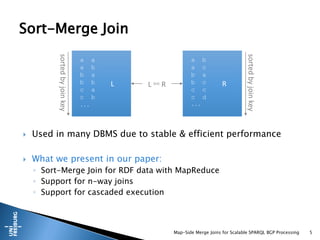
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
[a … c)
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
[a … c)
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-6-320.jpg)
![ Challenges:
◦ Datasets must be sorted according to the join key
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 7
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
[a … c)
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
[a … c)
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-7-320.jpg)
![ Challenges:
◦ Datasets must be sorted according to the join key
◦ Datasets must be split into N partitions
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 8
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
[a … c)
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
[a … c)
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-8-320.jpg)
![ Challenges:
◦ Datasets must be sorted according to the join key
◦ Datasets must be split into N partitions
◦ Same join key values must be processed on the same machine
i.e. they must be in the same partition
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 9
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN
[a … c) [a … c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-9-320.jpg)
![ Challenges:
◦ Datasets must be sorted according to the join key
◦ Datasets must be split into N partitions
◦ Same join key values must be processed on the same machine
i.e. they must be in the same partition
◦ Cascaded joins: Output must be sorted & partitioned according to
the requirements of the following join
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 10
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
[a … c)
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
[a … c)
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-10-320.jpg)
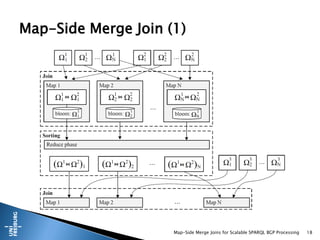
![ Main Contributions:
(1) RDF data store that guarantees that one side is already presorted
and partitioned we only have to sort & split the output
(2) Merge Join is processed in the Map phase
Reduce phase used to postprocess the output for the next join
(3) Dynamic Bloom Filter to remove dangling intermediate results
Map-Side Merge Joins for Scalable SPARQL BGP Processing 11
Sort-Merge Joins with MapReduce
L1
[a … c)
L2
[c … e)
…
LN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
R1
[a … c)
R2
[c … e)
…
RN
[x … z]
sortedbyjoinkey
L1 R1
L2 R2
LN RN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mergejoins-presentation-150407034706-conversion-gate01/85/Map-Side-Merge-Joins-for-Scalable-SPARQL-BGP-Processing-11-320.jpg)