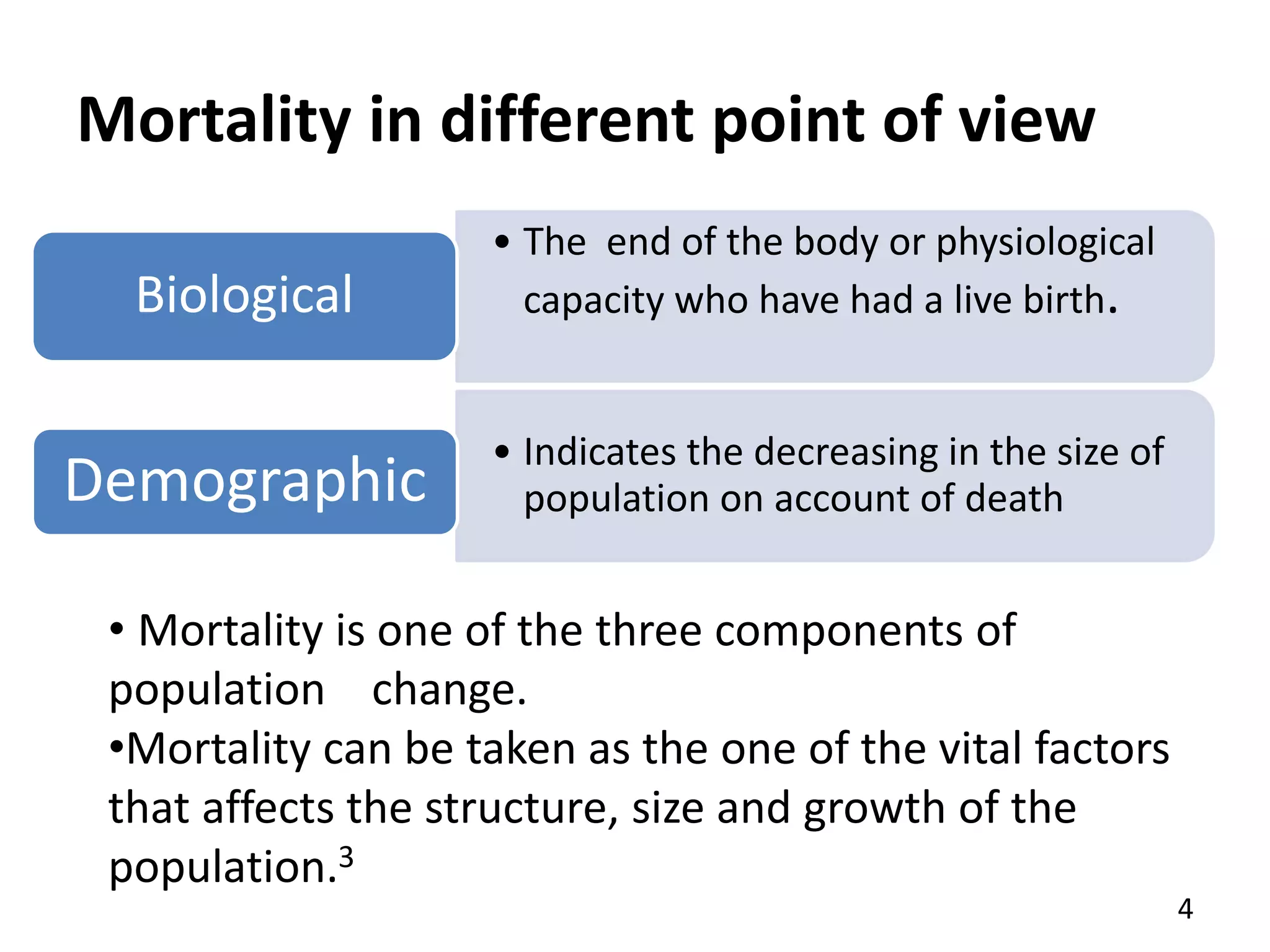
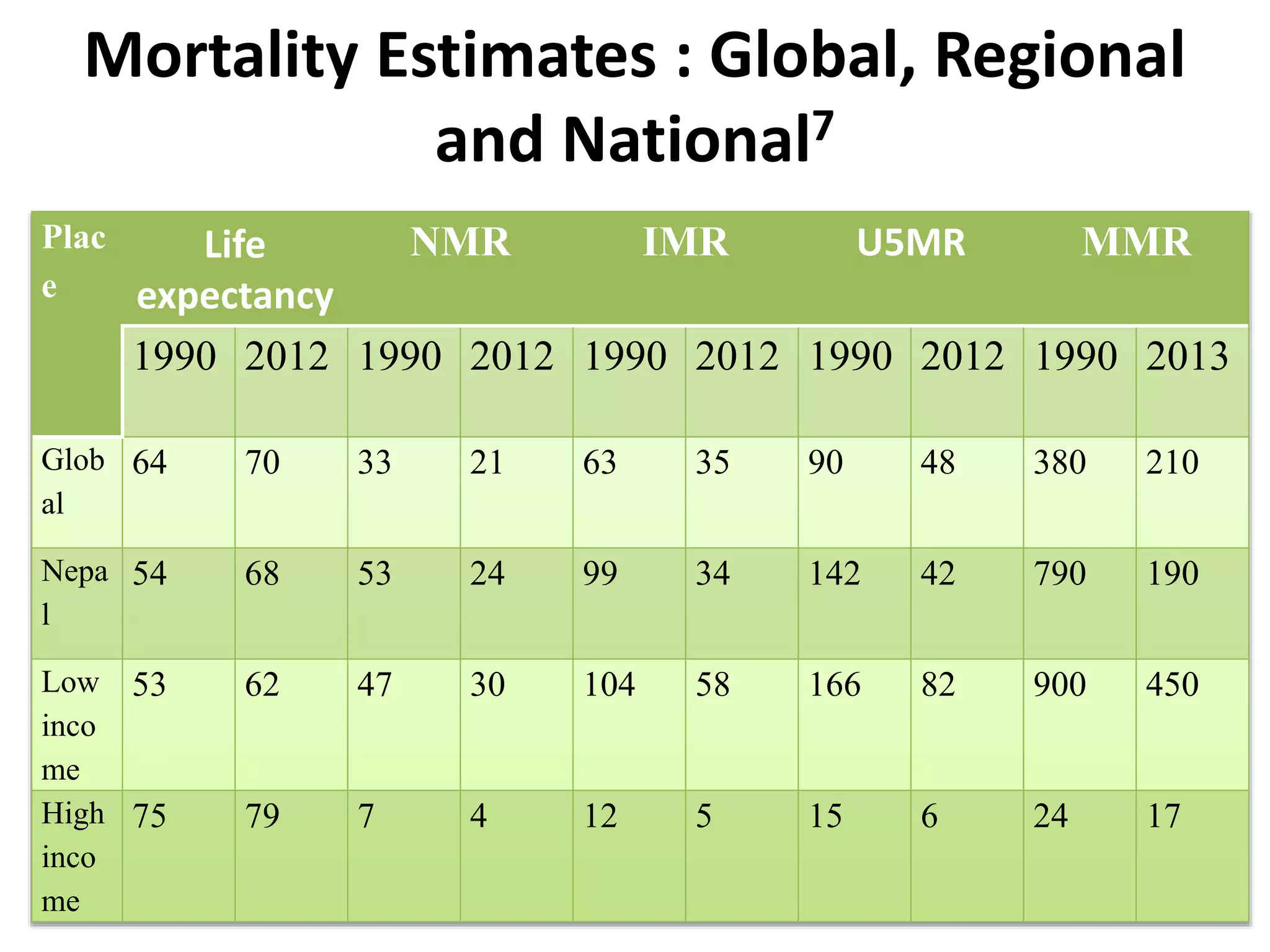
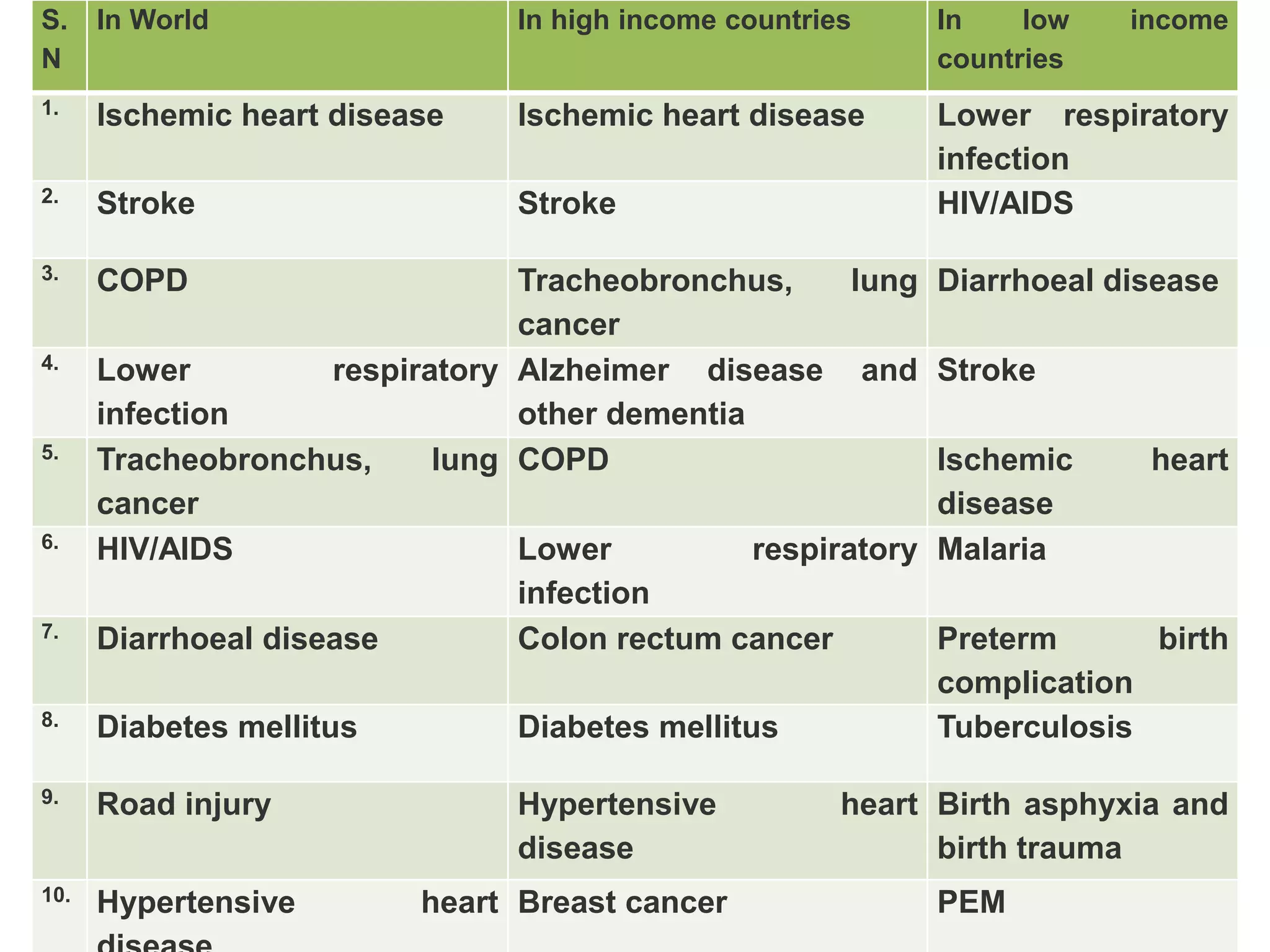
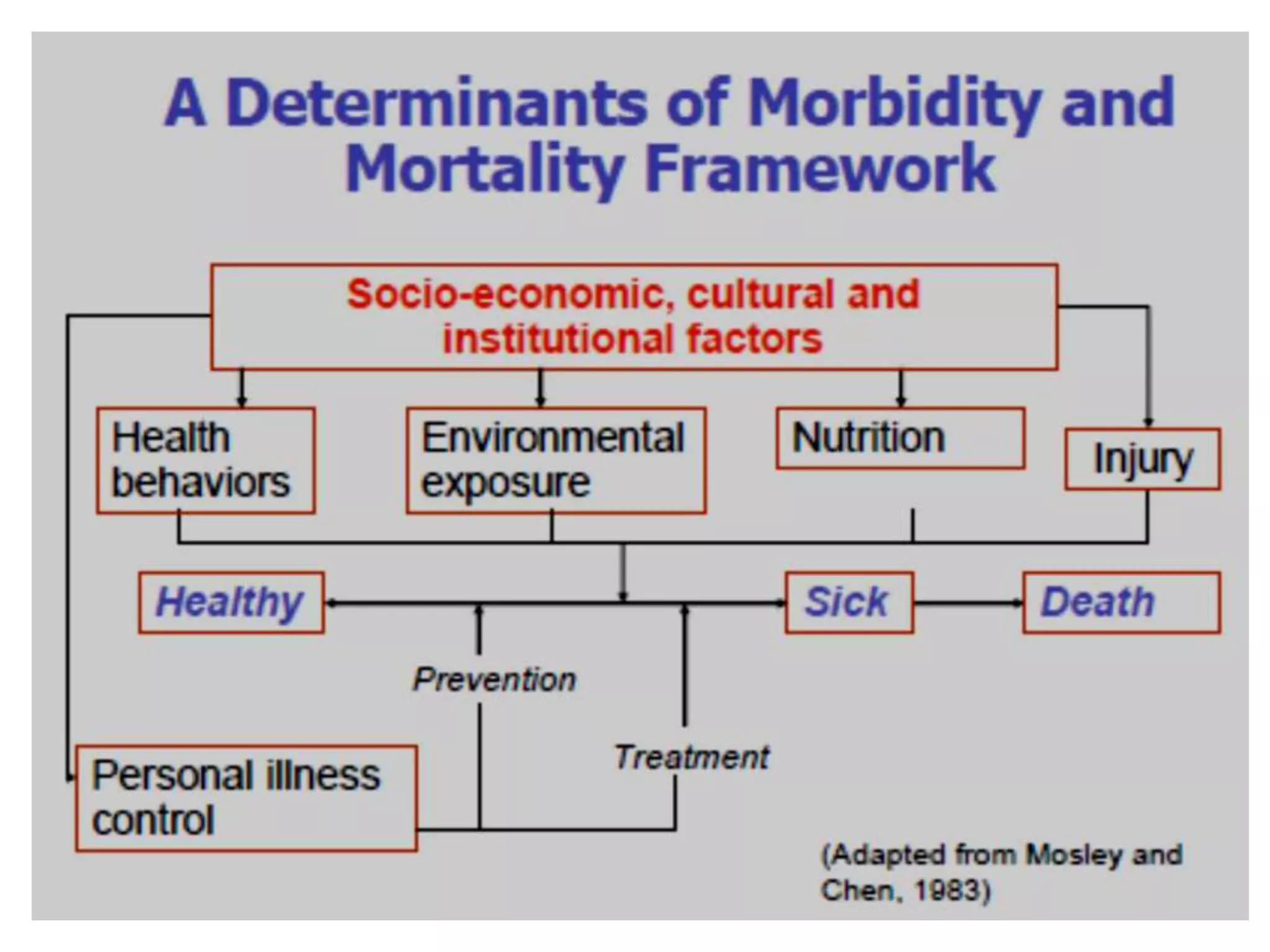
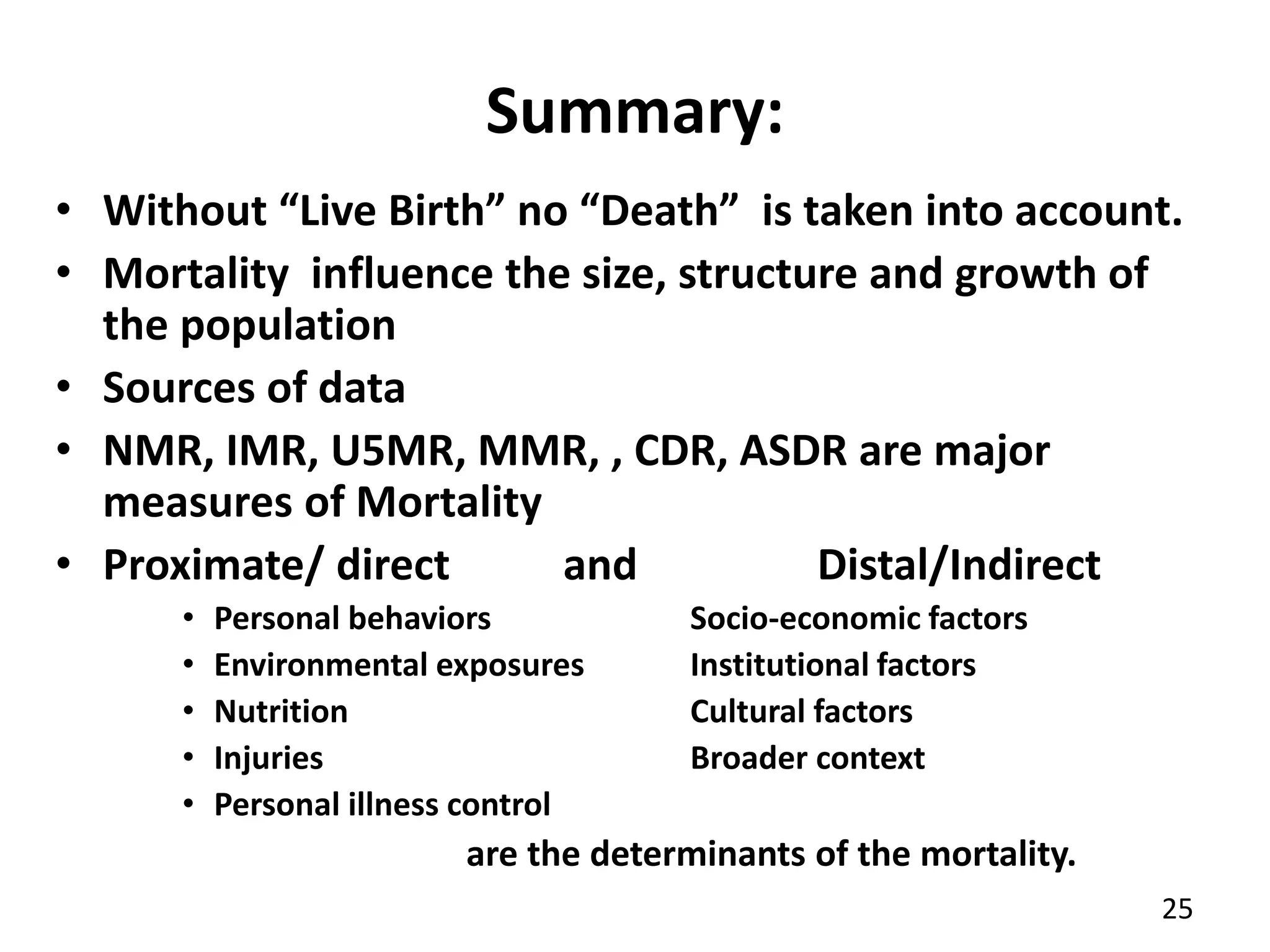
The document identifies ten important determinants of mortality based on a review of sources. The top ten determinants are:
1. Income level and employment status, as wealthier nations have lower mortality rates.
2. Nutritional status, as malnutrition increases risk of death from infection.
3. Epidemics, as disease outbreaks can cause many deaths, like the 1918 influenza pandemic.
4. Injuries, both intentional and unintentional, account for around 9% of deaths globally.
5. Personal behaviors like diet, alcohol and tobacco use, and hygiene practices impact mortality.
6. Education levels, especially of women, influence health behaviors and outcomes.




















![References:
1. Arthur Haupt , Thomas T.kane and Carl Haub, PRB's Population Hand Book, 6th Edition, PRB Washington , 2011.
2. Bhende A A, Kanitkar T. Mortality. In: Principles of population studies, 21st Ed. Mumbai: Himalayan Publishing House, 2011.
3. MOHP, Nepal Population Report, Ministry of Health and Population, Population Division Ramshah path , Kathmandu, 2011.
4. Government of Nepal, Nepal Law commission , Local Self Government Act, 1999
5. Mishra B D: An Introduction to the study of population. 3rd edition New Delhi: South Asian Publisher Pvt. Ltd; 2004
6. K Park. Park’s text book of preventive and social medicine, 19th Ed. Jabalpur: Banarsidas Bhanot, 2007
7. WHO, World Health Statistics, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2014/world-health-statistics-2014/en/ ,
assessed 2th September 2014
8. John Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Henry Mosley, Mortality and Morbidity Trends and Differentials,
Determinants and Implications for the FutureJHU, 2006.
9. Cutler, David, Angus Deaton and Adriana Lleras-Muney.. The determinants of mortality. Journal of Economic Perspectives .
bridge University Press, reprint , 20(3): 97-120, 2006
10. Pritchett L and Lawrence H. S, “Wealthier is Healthier,” Journal of Human Resources. 1996; 31(4): 841-868.
11. DOHS, Annual Health Report 2068/69(2011/12), DOHS, MOHP, 2013.
12. Scrimshaw, Neville S., Taylor C. E., and Gordon J. E., Interactions of nutrition and infection, Geneva. World Health Organization,
1968.
13. The Influenza Pandemic of 1918, http://virus.stanford.edu/uda/, assessed 2th September 2014
14. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/en/ June 2013, assessed 2nd sep. 2014.
15. Meara, Ellen, "Why is Health Related to Socioeconomic Status? The Case of Pregnancy and Low Birth Rate" (April 2001). NBER
Working Paper No. W8231.
16. UNICEF, Breaking the silence on Violence against Indigenous Girls, Adolescents and Young Women;A call to action based on an
overview of existing evidence from Africa, Asia Pacific and Latin America;Human Rights Unit Programme Division, UNICEF, New
York, 2013
17. UNFPA, Maternal Health Thematic Fund, Annual Report 2011, UNFPA, New York , June 2012.
18. Ministry of Health and Population (MOHP) [Nepal], New ERA, and ICF International Inc. 2012. Nepal Demographic and Health
Survey 2011. Kathmandu, Nepal: Ministry of Health and Population, New ERA, and ICF International, Calverton, Maryland
19. Chaudhury, Nazmul, Hammer. J, Kremer. M, Muralidharan K and Halsey. F. R, “Missing in action: teacher and health worker
absence in developing countries,” Journal of Economic Perspective, 2005. 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/determinantsofmortality-150415102020-conversion-gate02/75/Determinants-of-mortality-26-2048.jpg)
