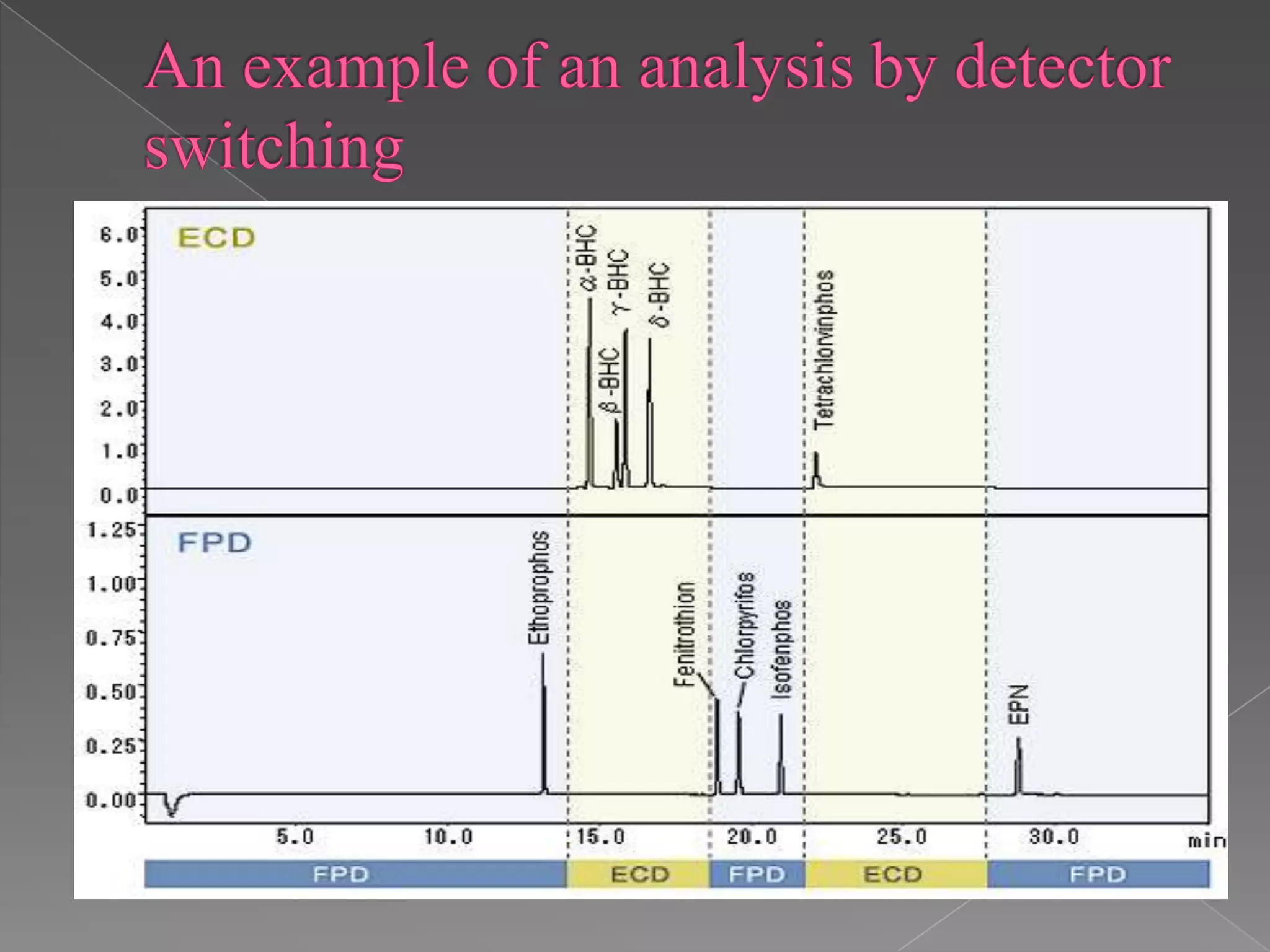
This presentation discusses pesticide pollution detection and analysis. It defines pesticides as agrochemicals used to control pests that compete with humans for food and spread disease. Pesticide pollution occurs when chemicals from pesticides contaminate soil, water, and air, bringing mostly negative environmental impacts. Detection can be done through gas chromatography with atomic emission detectors or biosensors. Accurate detection is important to prevent issues from overuse of pesticides like resistant pests, decreased biodiversity, water pollution, and air pollution.