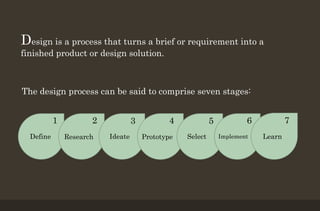
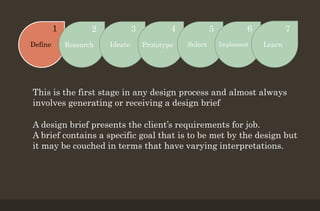
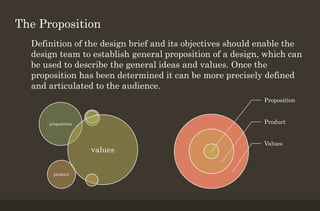
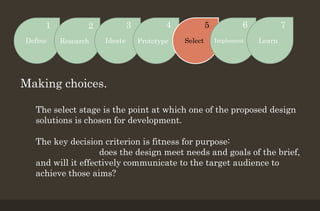
The 7-stage design thinking process begins with defining the problem and requirements through a design brief. Researchers then gather information to identify drivers and barriers to help ideate potential solutions. Designers create prototypes to visualize and test ideas before selecting the optimal solution. The final solution is implemented, and feedback is obtained to improve future projects. The process enables transforming needs into finished designs through research, creativity, and iterative improvement.