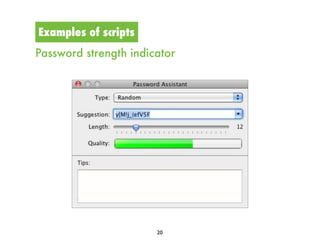
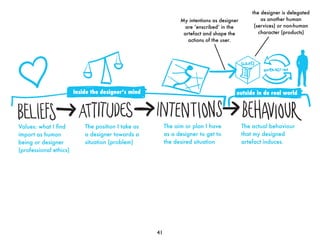
This document discusses design scripts and how designers plan actions to achieve desired future states. It provides examples of how artifacts can "prescribe" or delegate actions through scripts. Design scripts shape human behavior by encouraging or discouraging certain actions. Examples include speed bumps that say "slow down", paper coffee cups that say "dispose of me", and password indicators that challenge users to create strong passwords. The document explores how scripts are present throughout a product's lifecycle from conception to disposal. It argues that scripts reflect a designer's intentions for how an artifact will interact with users and contexts.