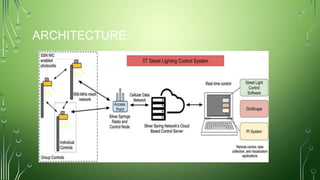
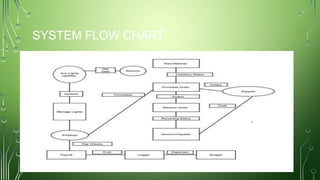
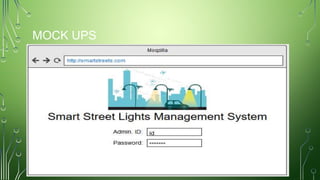
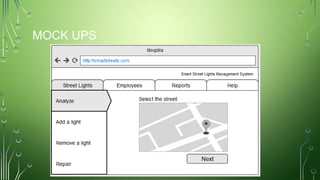
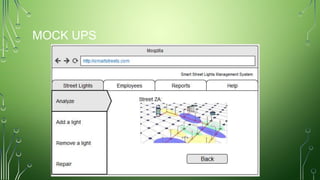
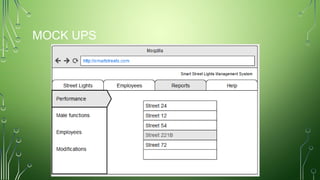
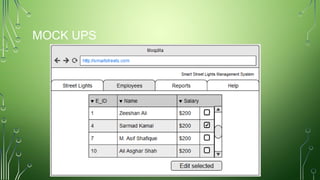
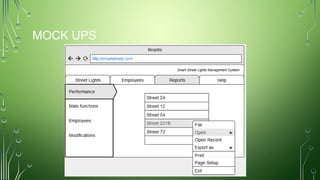
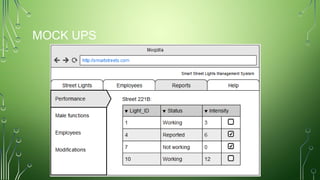
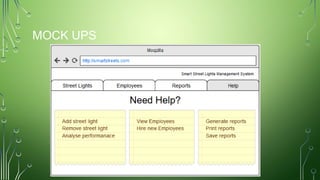
The document outlines a smart street lights management system that uses adaptive lighting controlled by sensors to enhance energy efficiency and public safety. It discusses automation processes for monitoring street light status, energy consumption analysis, and fault detection, highlighting the use of LoRa technology. Additionally, it addresses security features, potential risks associated with IoT vulnerabilities, and ethical issues related to data protection.