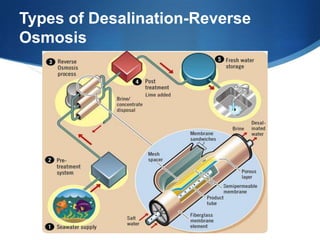
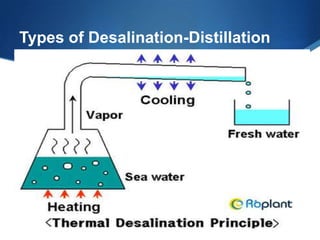
Desalination is the process of removing salts and minerals from sea water to produce fresh water for drinking and irrigation. Currently 230 million people rely on desalination from the over 14,500 plants operating worldwide. However, desalination is an important future source of fresh water as population growth and climate change are reducing conventional fresh water supplies in many regions of the world. While desalination helps meet water demand, its high energy use and briny wastewater disposal require regulations and technologies to minimize environmental impacts.