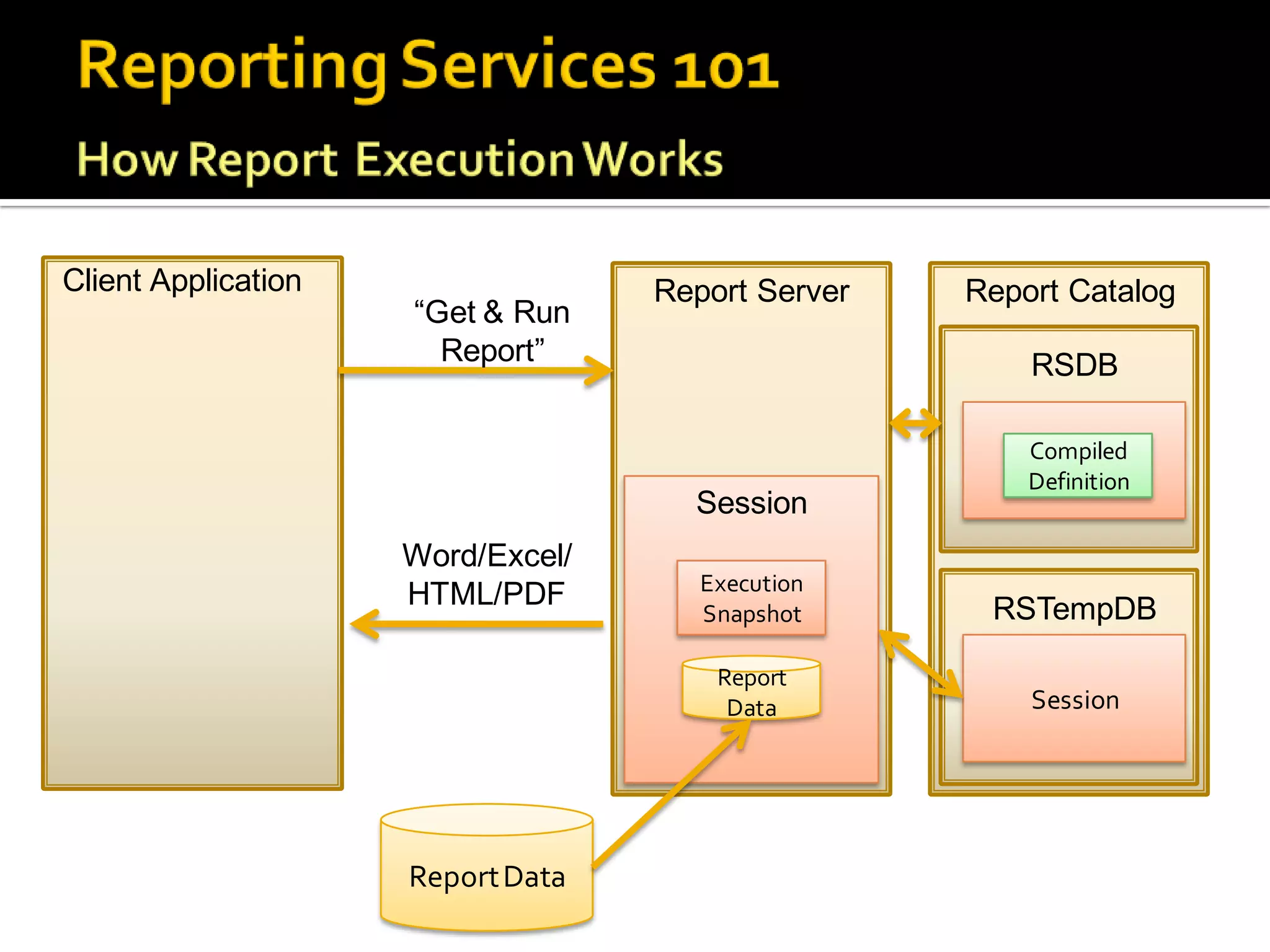
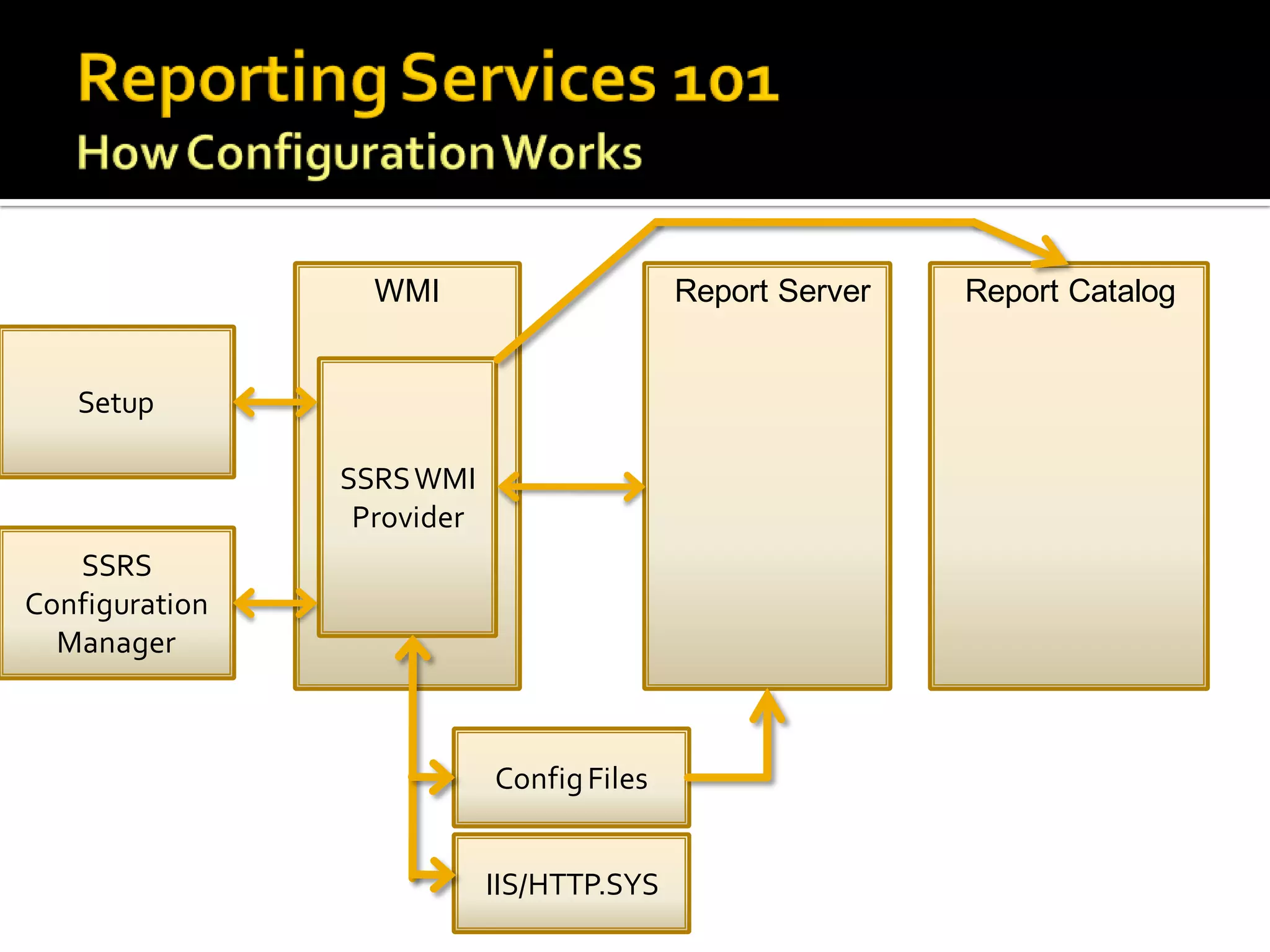
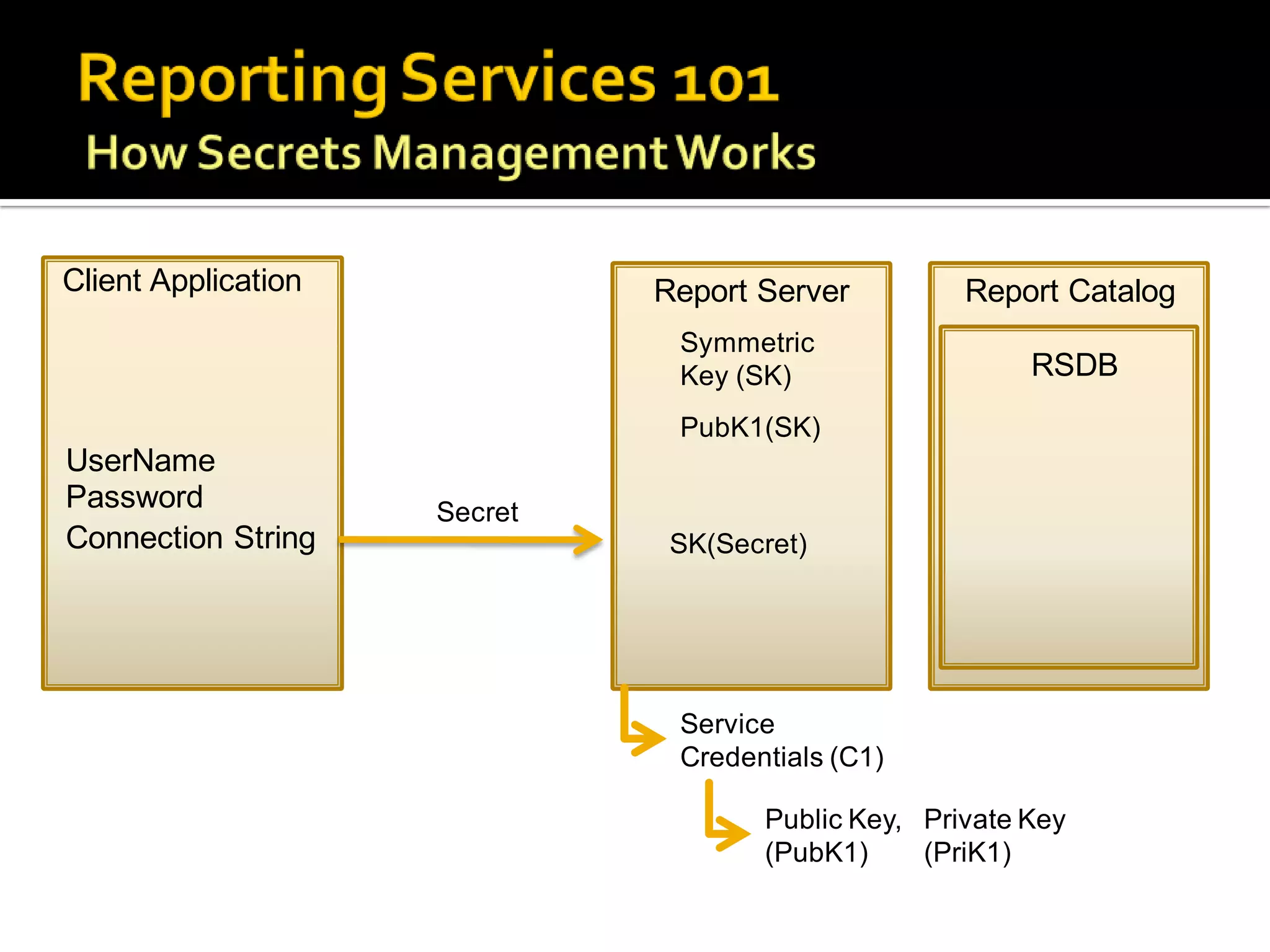
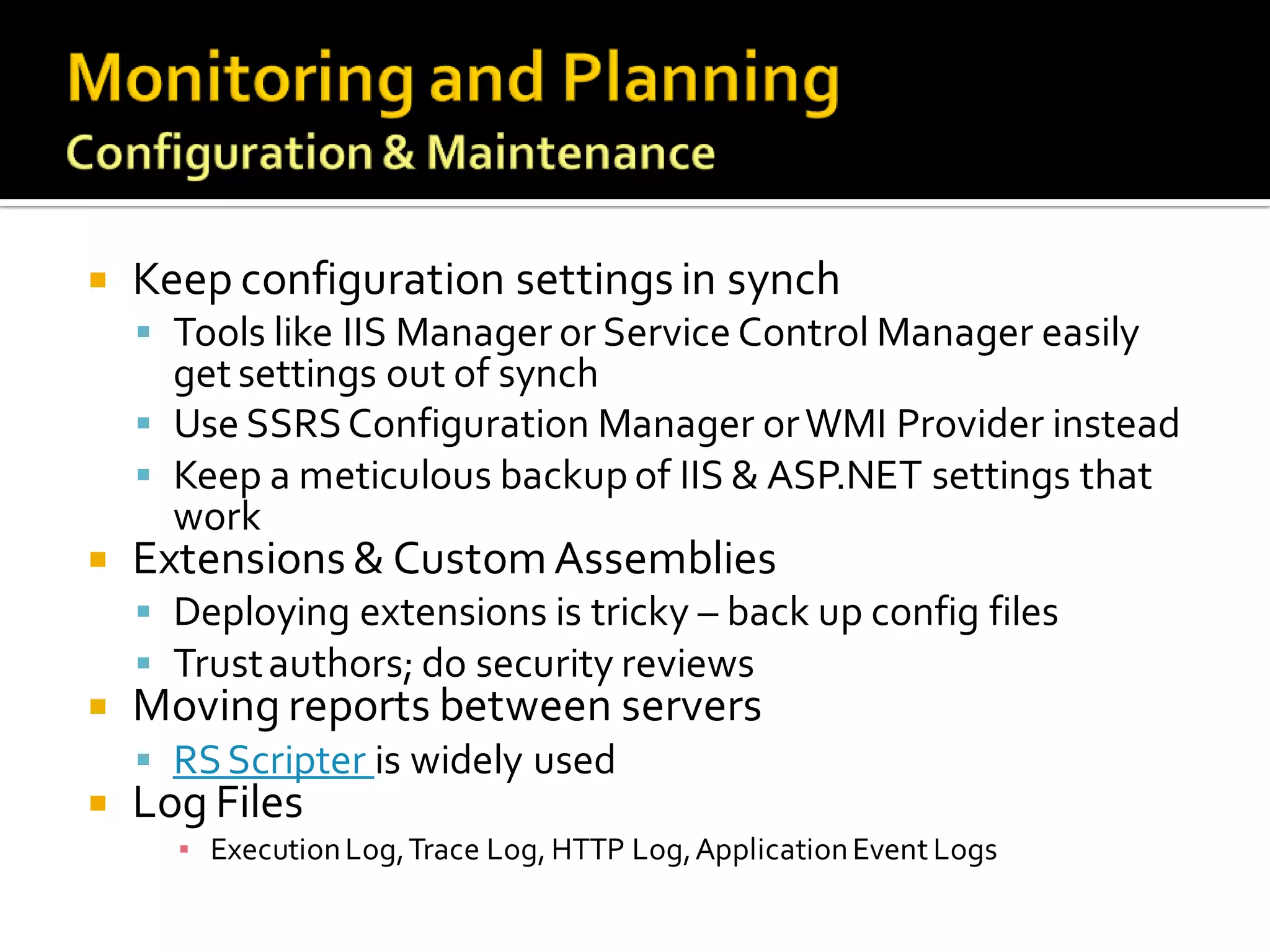
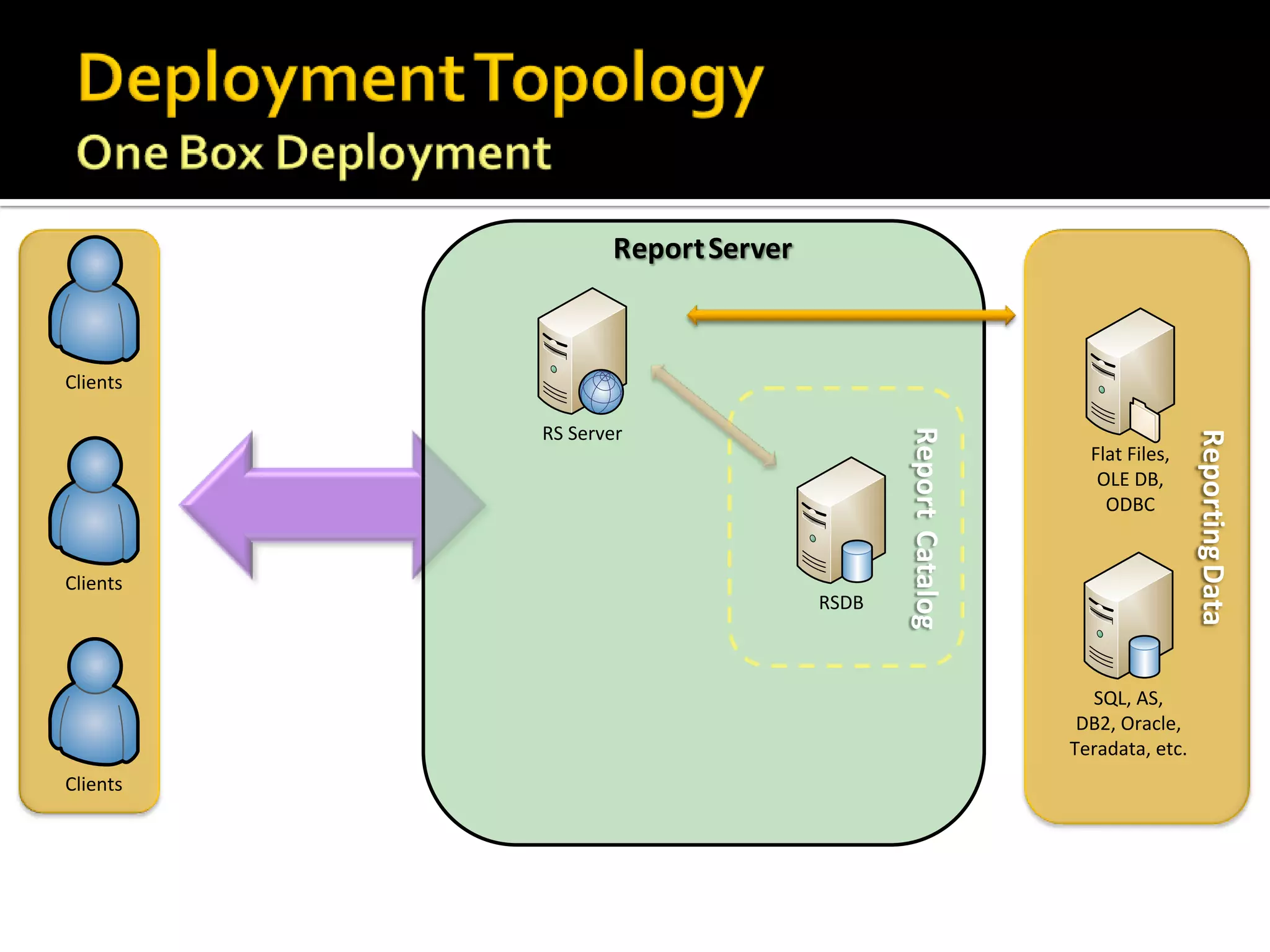
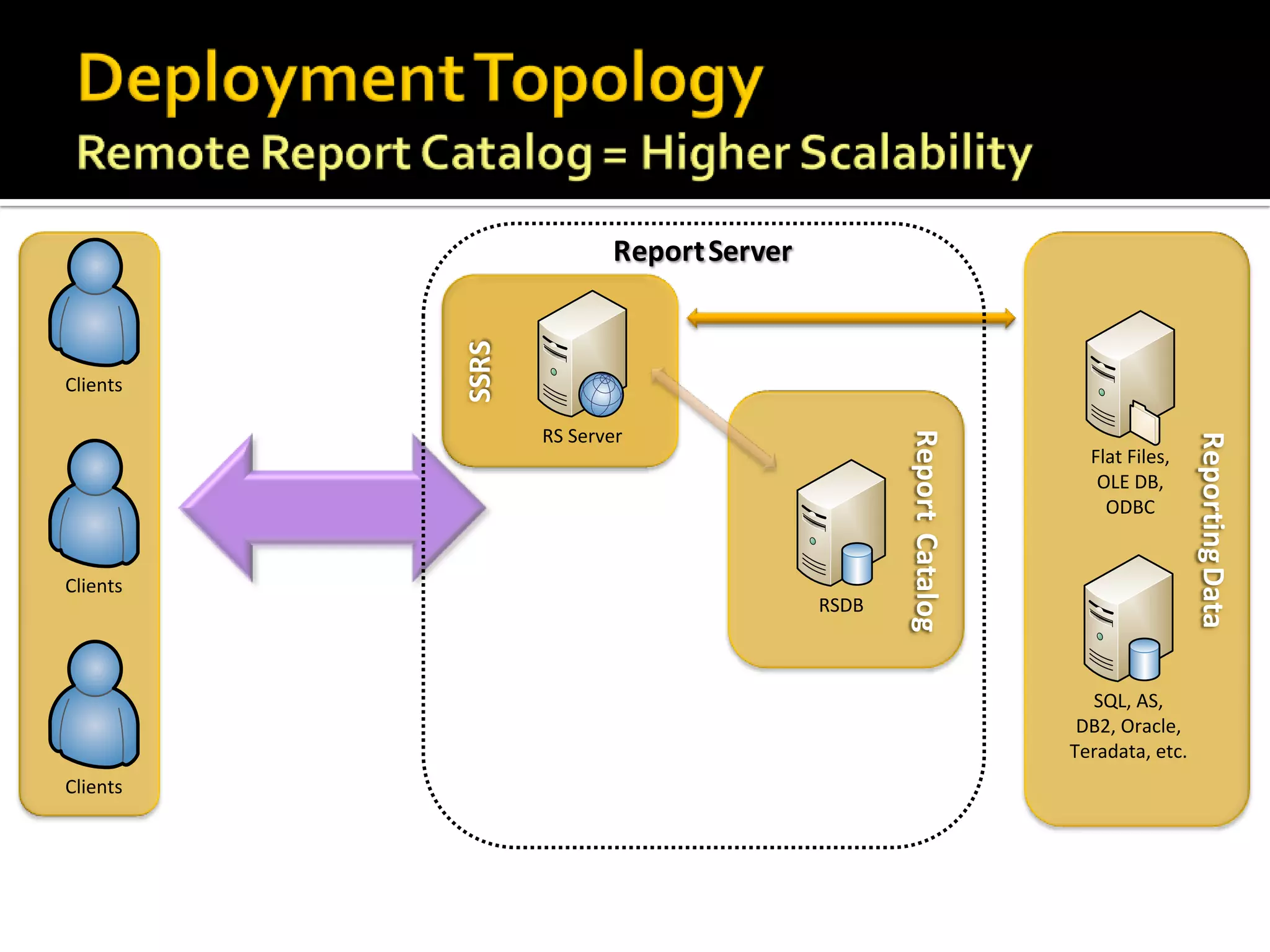
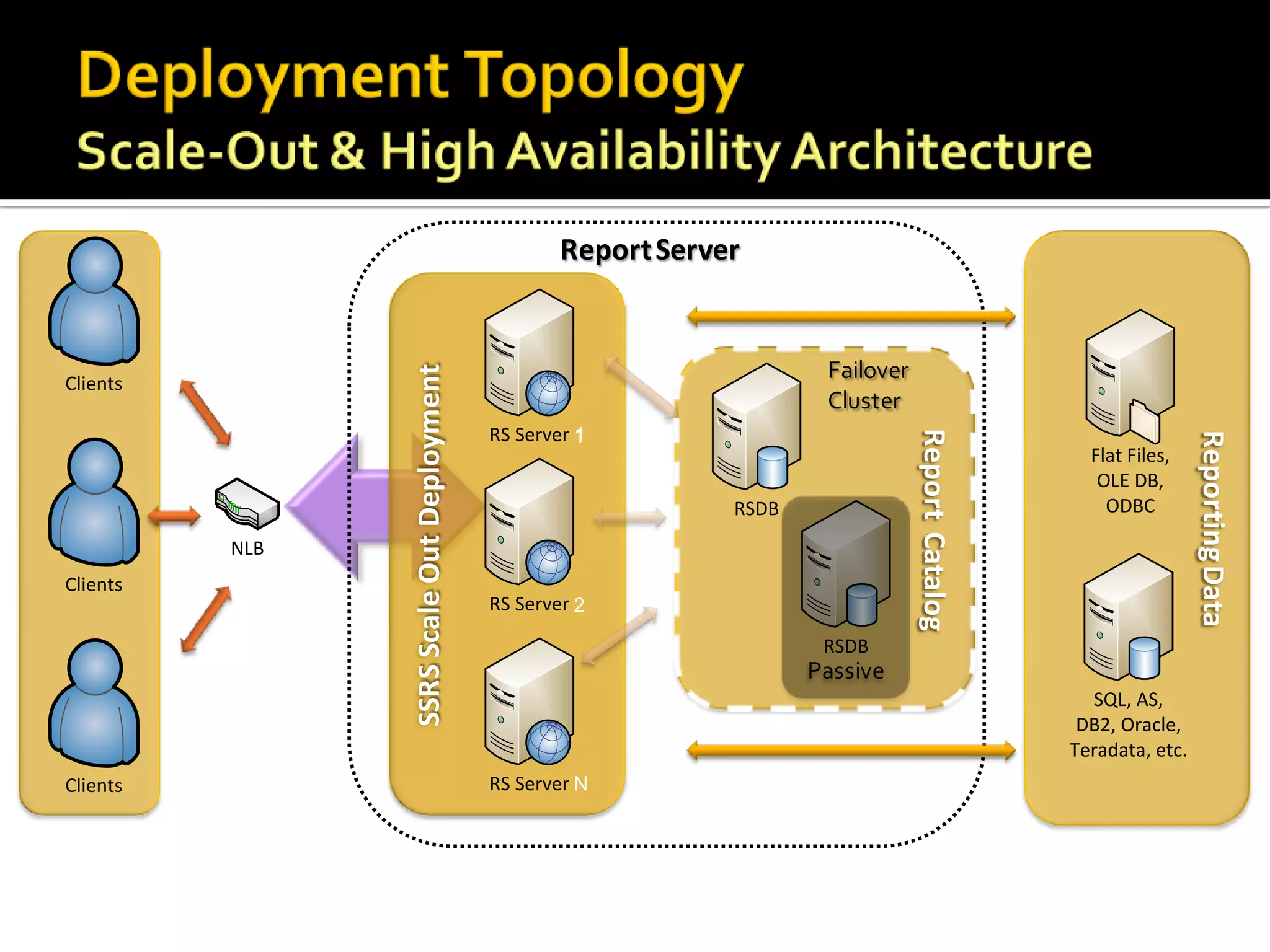
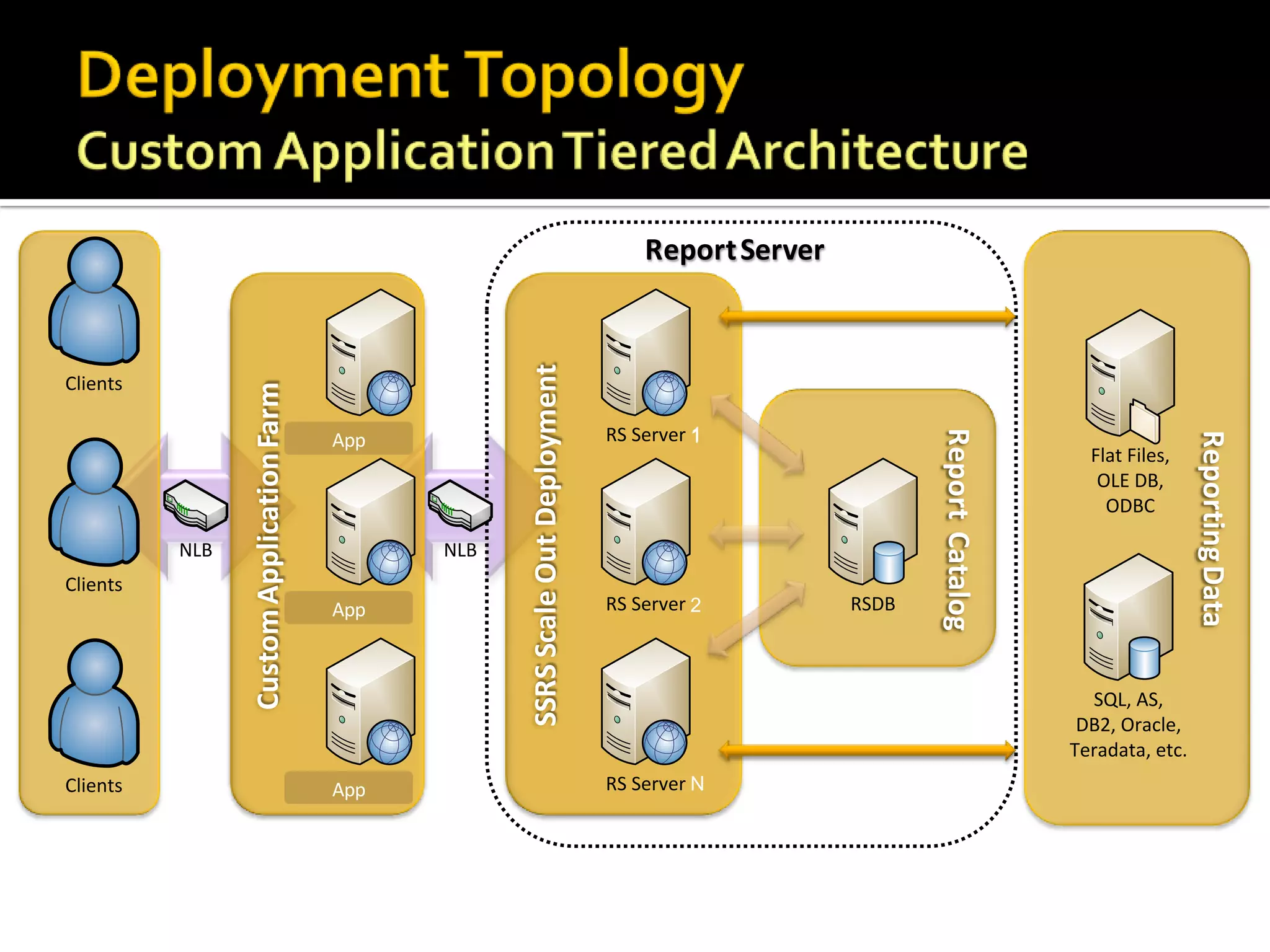
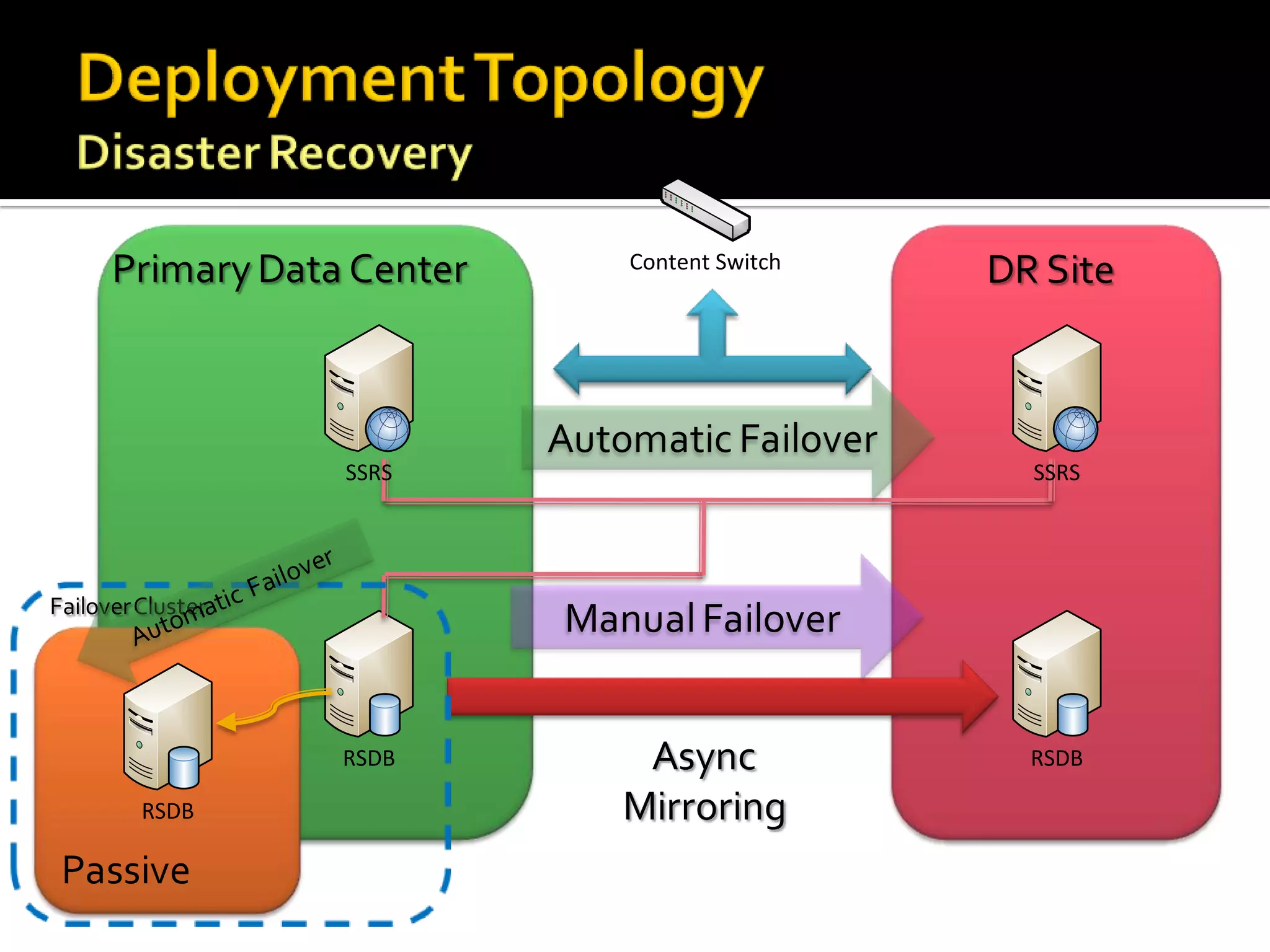
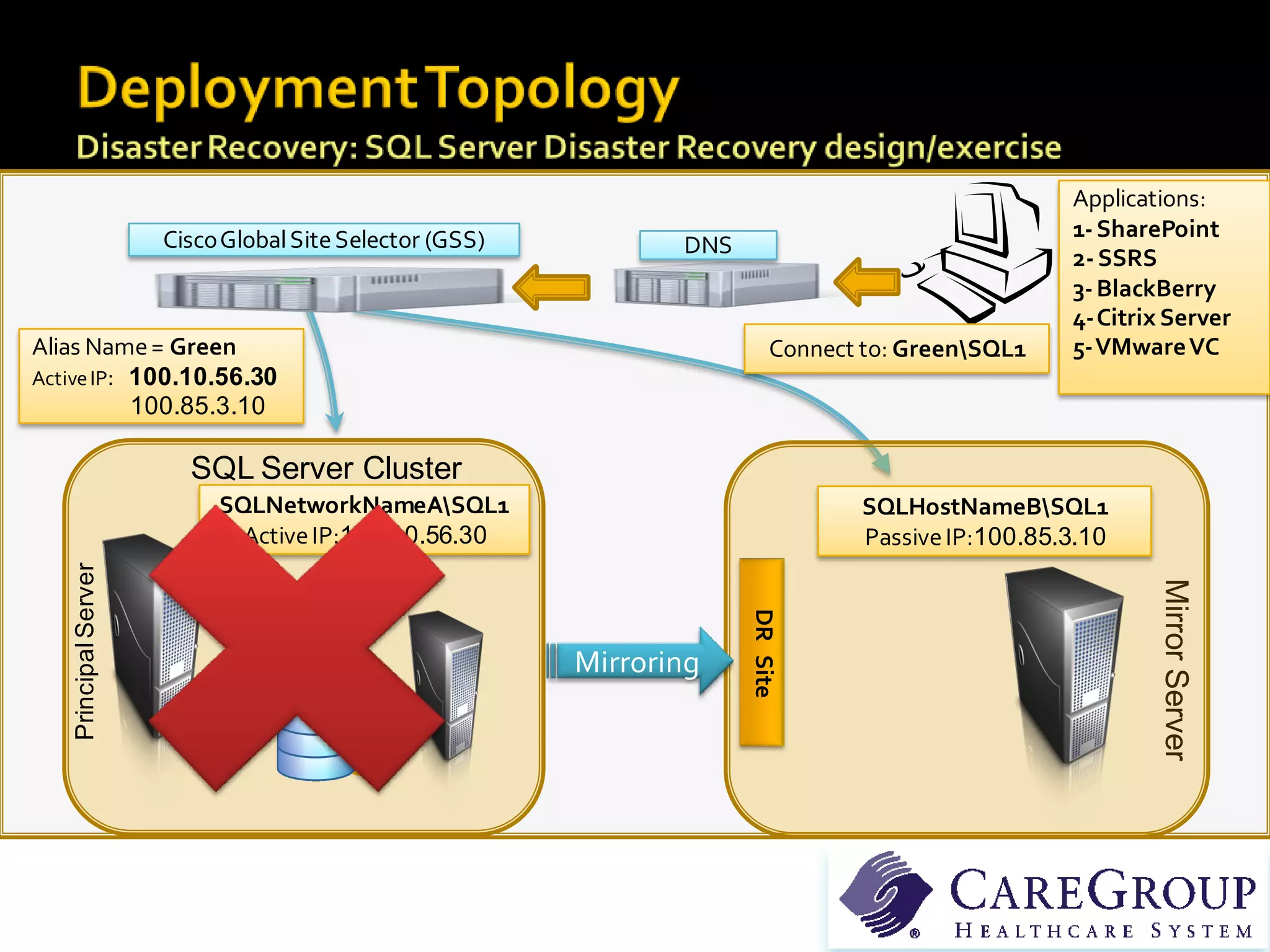
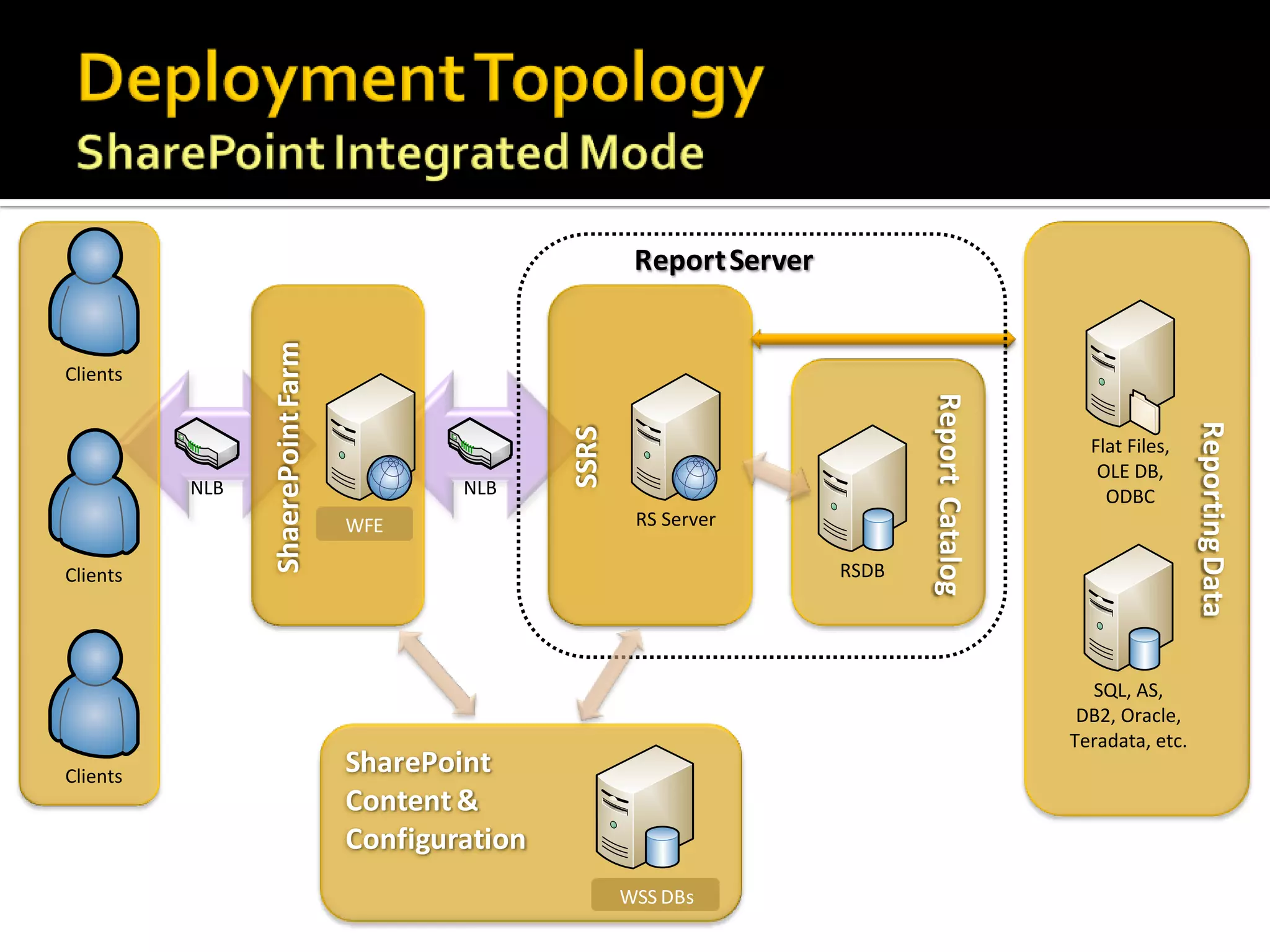
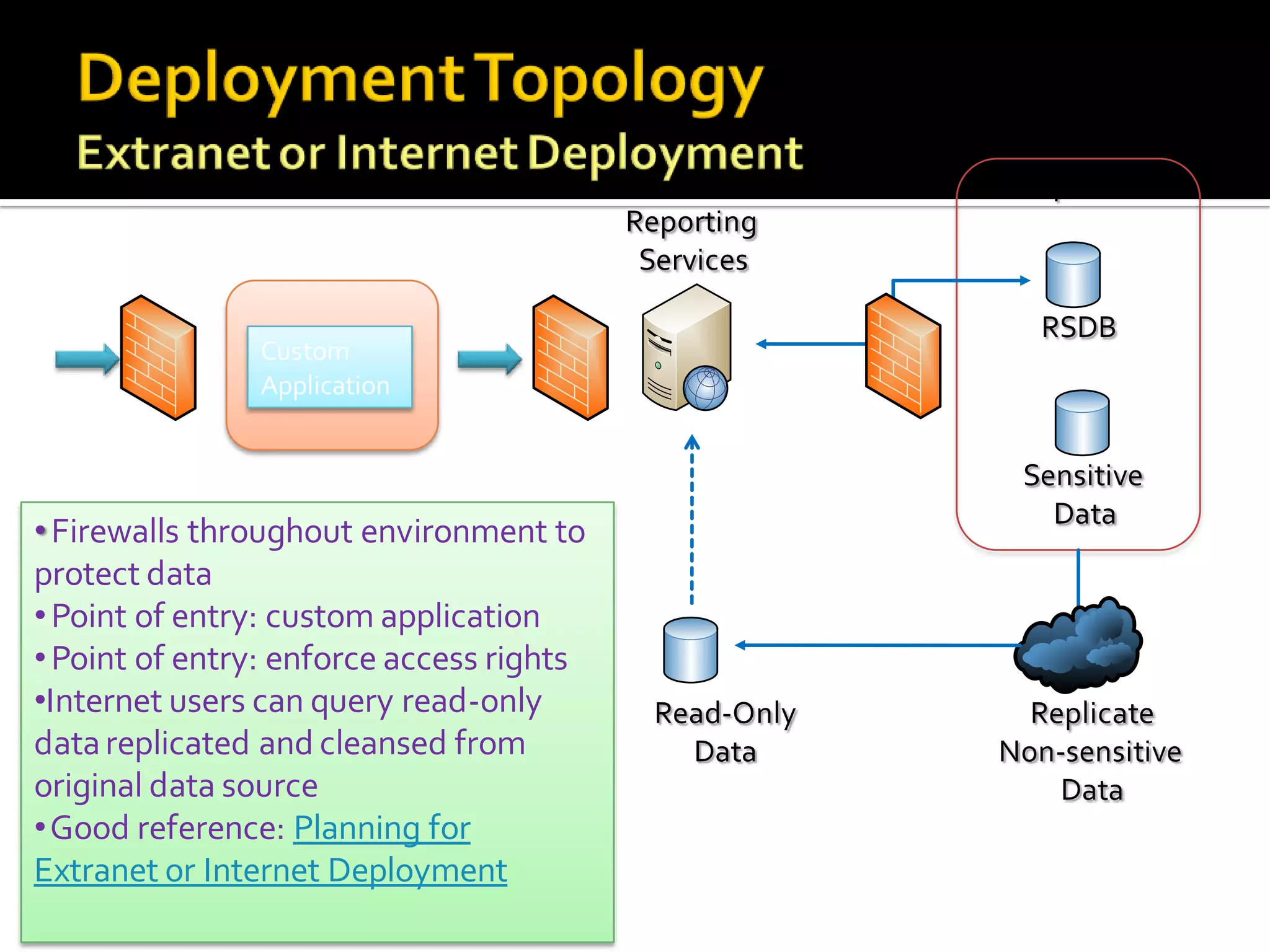
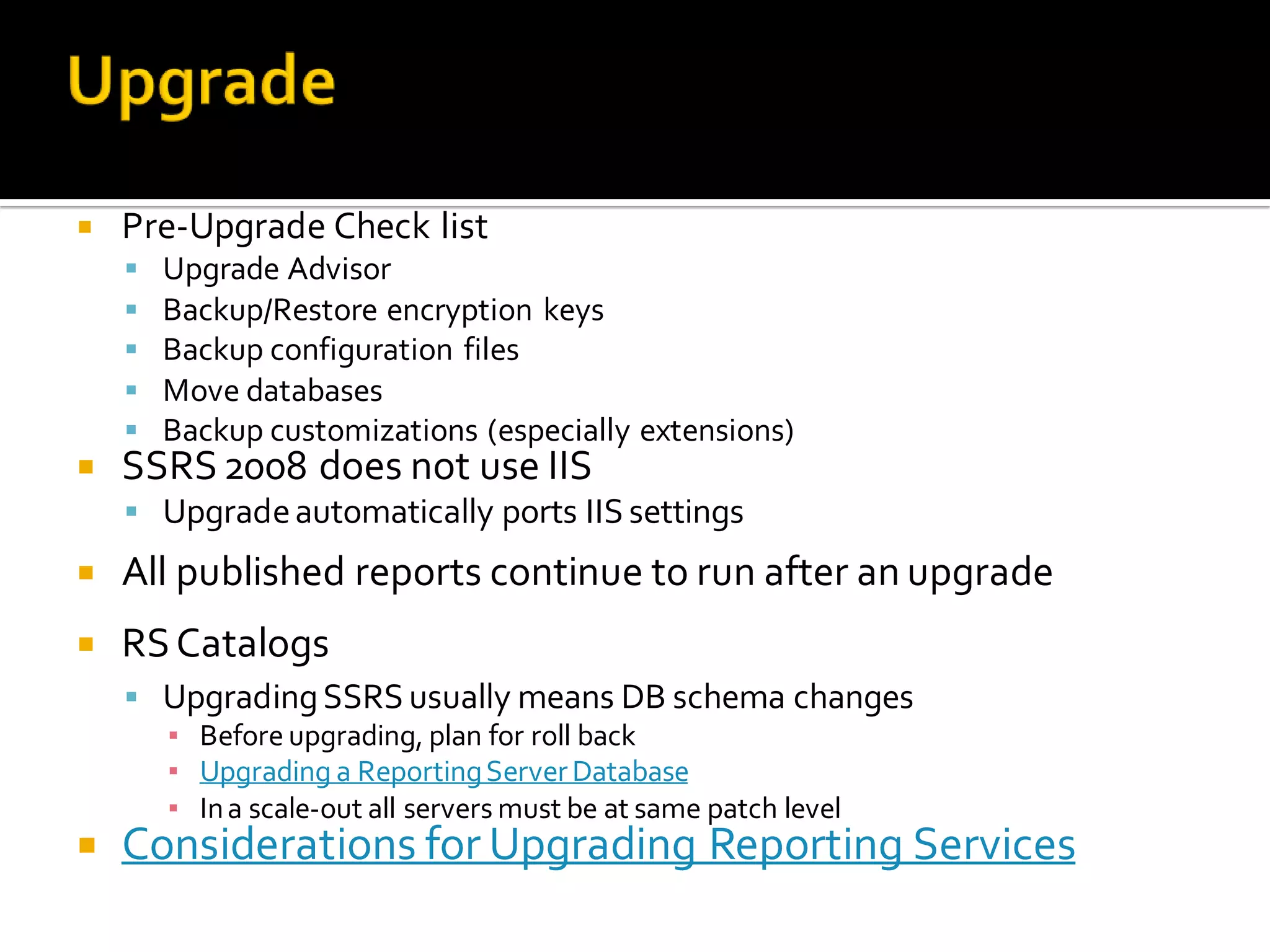
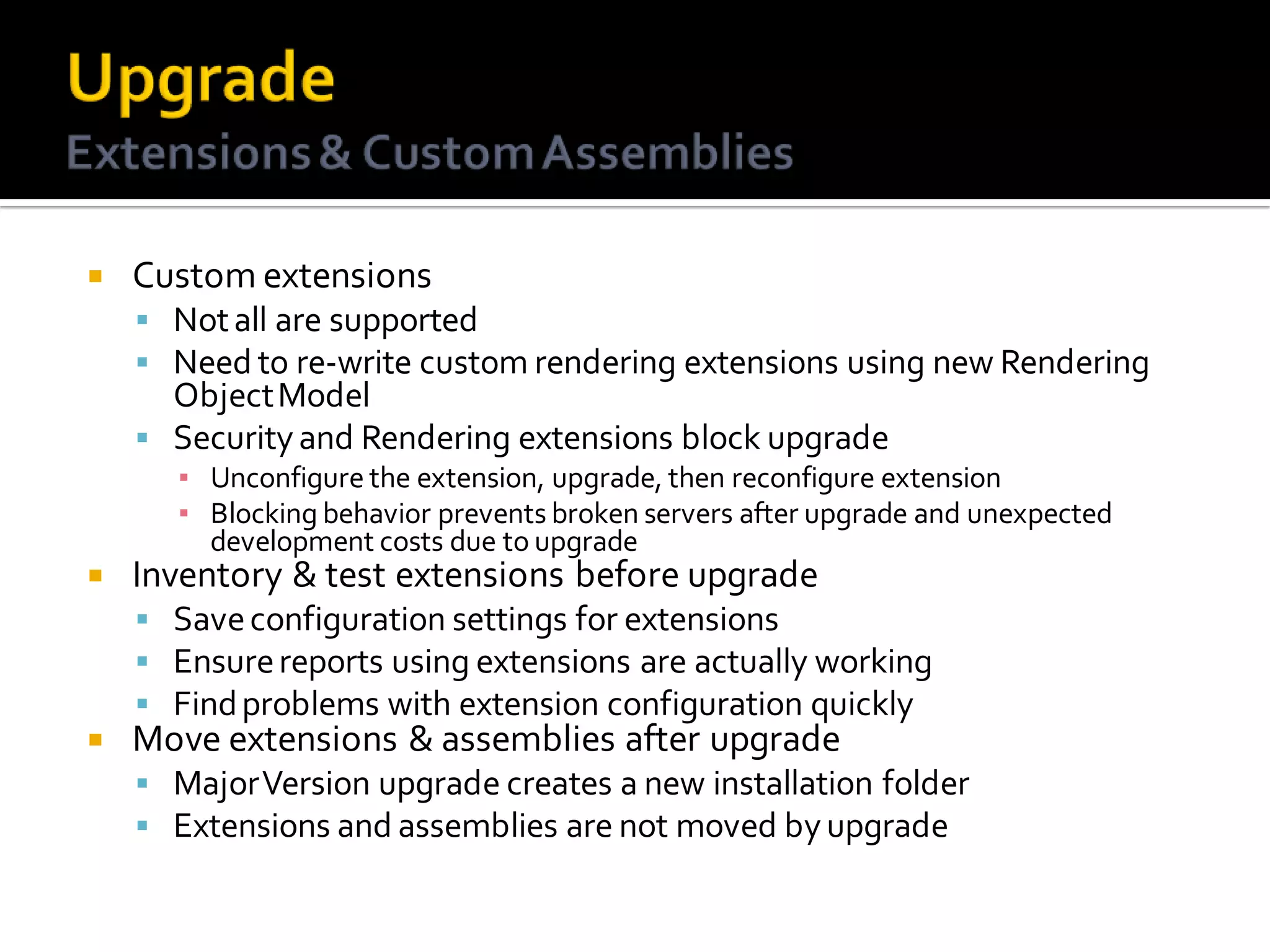
The document provides an in-depth overview of best practices and technical guidelines for deploying and managing SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS). It covers topics such as security, backup/restore processes, performance optimization, and infrastructure considerations for both new users and those with existing deployments. Additionally, the document includes resources for further learning and troubleshooting, emphasizing the importance of careful planning and configuration in SSRS implementations.