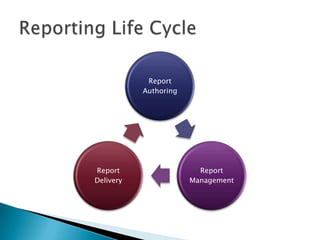
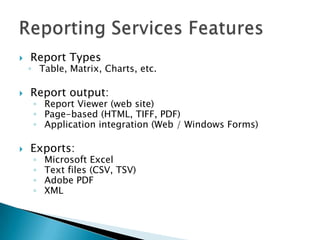
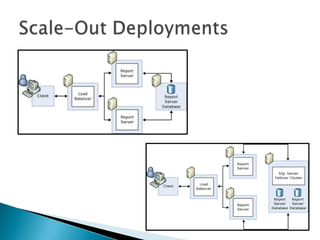
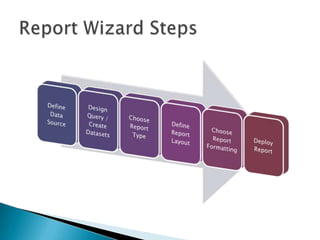
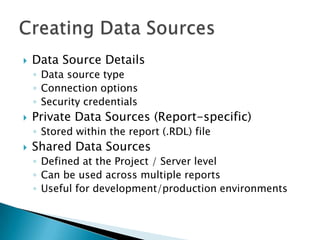
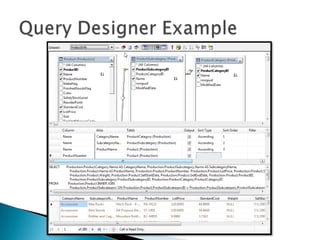
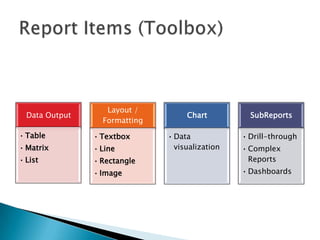
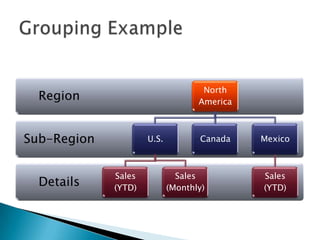
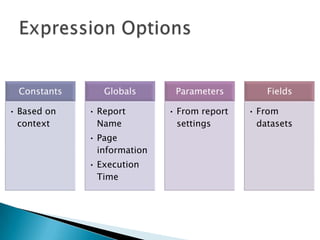
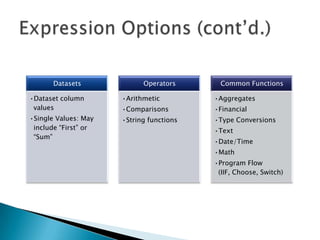
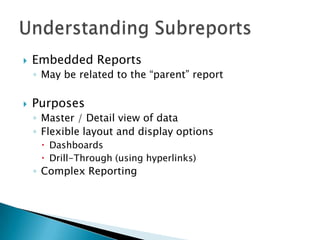
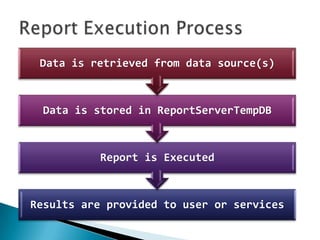
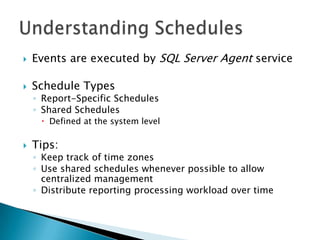
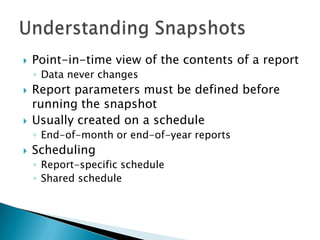
The document discusses features and components of SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS). It covers report authoring, delivery, and management. Key topics include developing reports with BIDS, supported report types and output formats, deployment options, and interacting with reports on the SSRS report server. The document also provides an overview of datasets, expressions, parameters, grouping and sorting to filter and organize reporting data.