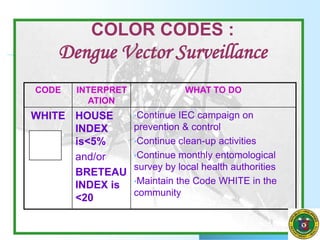
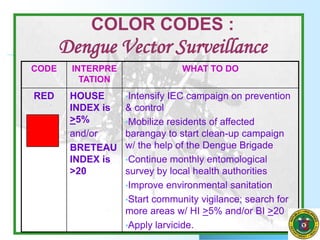
Vector surveillance involves the ongoing collection, analysis, and dissemination of mosquito data to inform appropriate public health actions. The key objectives are to monitor mosquito populations and breeding sites to determine infection risk levels and recommend prevention/control measures. Common surveillance methods include adult mosquito collection, pupal surveys, larval surveys, and ovitrapping. Larval surveys inspect water containers to calculate larval indices like House Index, Container Index, and Breteau Index. Analysis of findings considers vector characteristics, community factors, and prioritizes areas for intervention and monitoring based on mosquito density levels. The information benefits various stakeholders for public health decision-making and research.