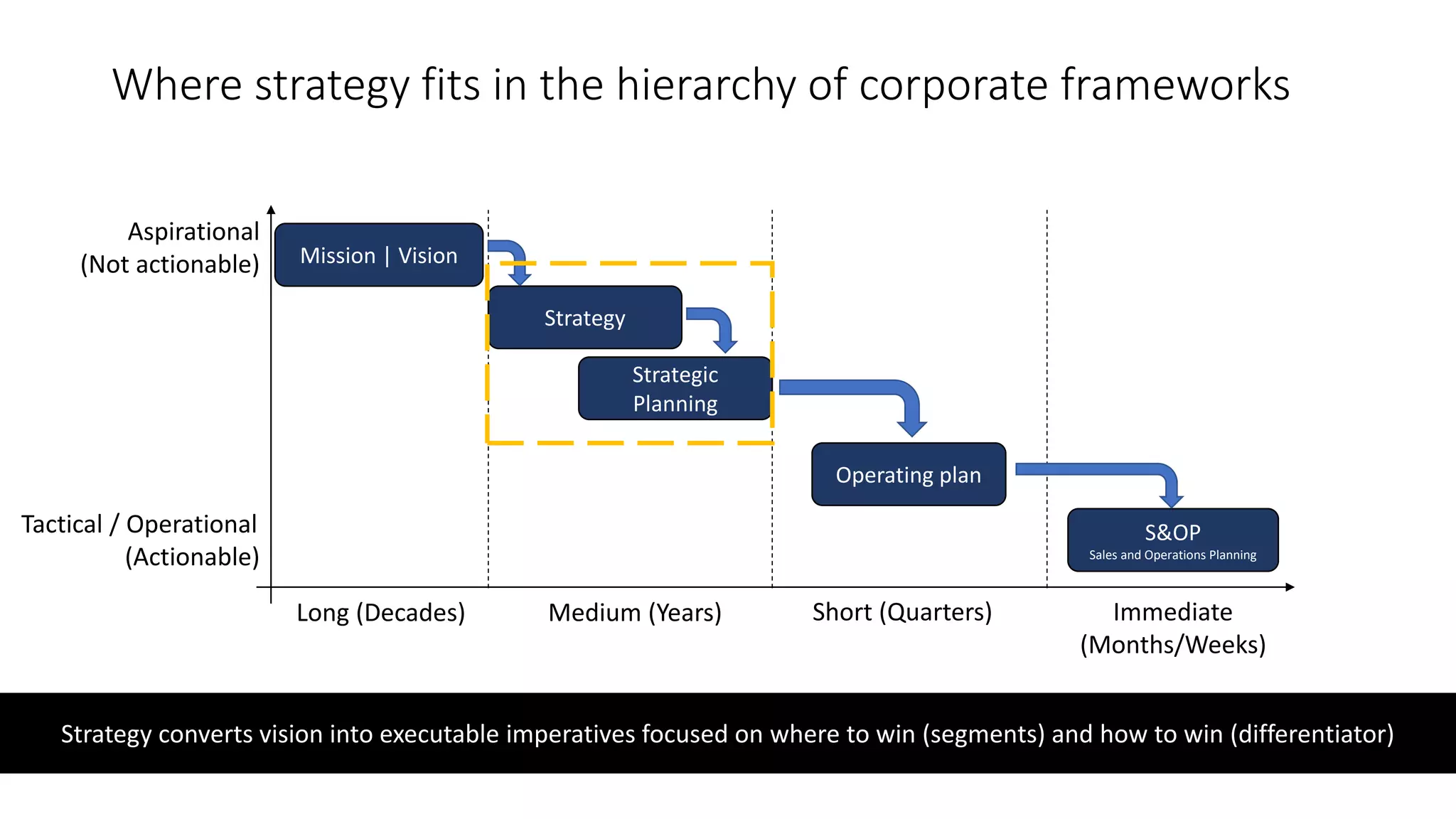
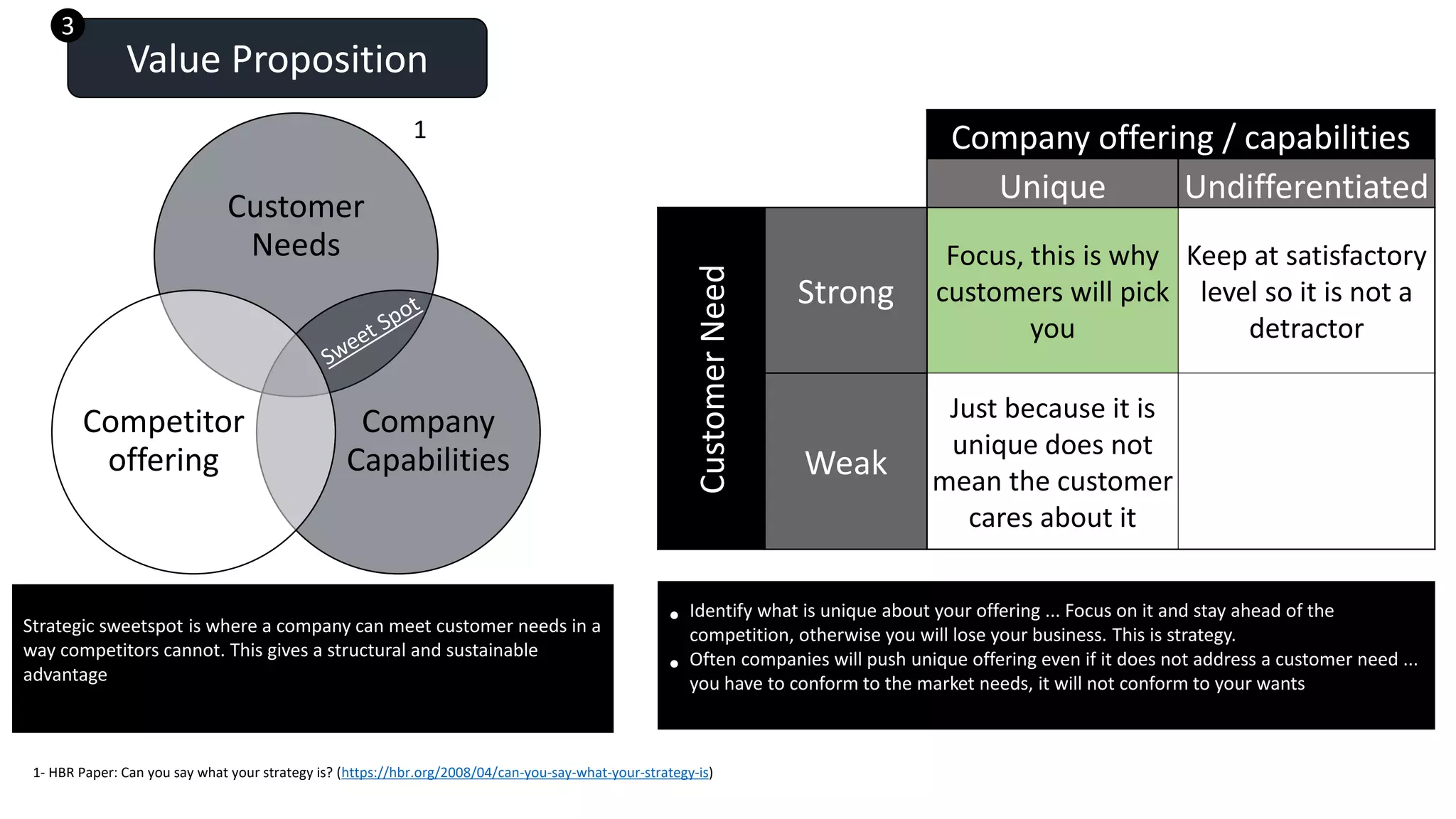
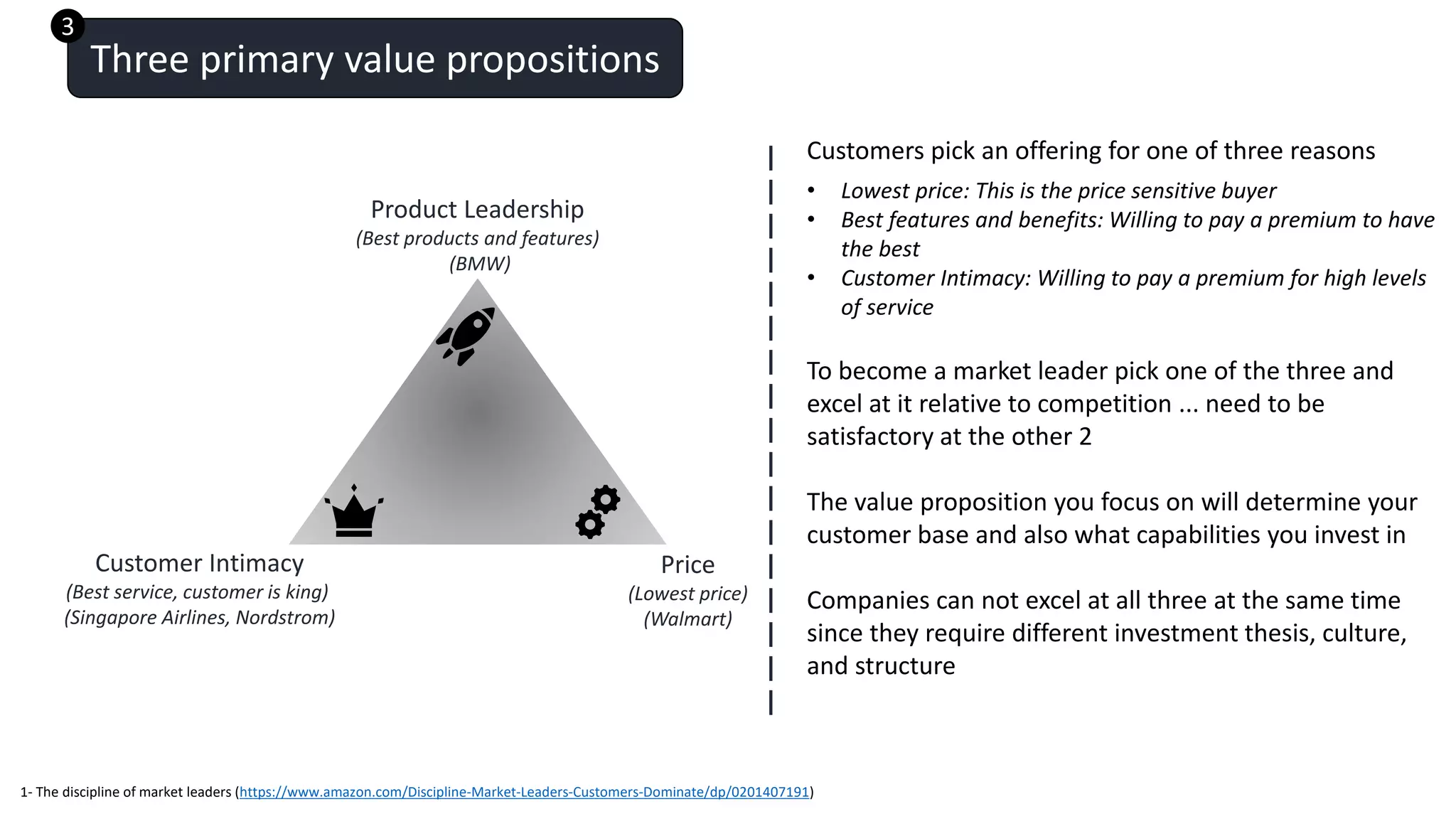
The document discusses developing an effective corporate strategy. It outlines where strategy fits within organizational frameworks and provides steps for strategy development. Strategy converts vision into executable imperatives that focus on winning key customer segments and differentiating from competitors. The steps include defining objectives, segmenting markets, crafting a value proposition, building necessary capabilities, and measuring performance. An effective strategy prioritizes goals, focuses resources, and guides investment decisions to protect the organization.