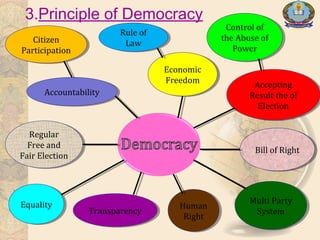
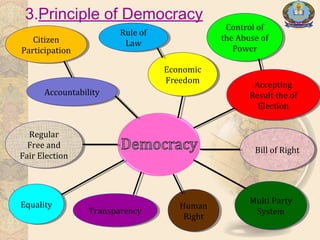
The document lists the members of a group and discusses democracy and elections. It defines democracy as a form of government where citizens have equal say in decisions. It outlines principles of democracy like rule of law, citizen participation, and free and fair elections. The benefits of democracy discussed are protection from oppression and laws that ensure citizen safety. Elections allow citizens to choose representatives and influence policies through voting. Key aspects covered are voting rights, voter registration, and primary vs general elections.