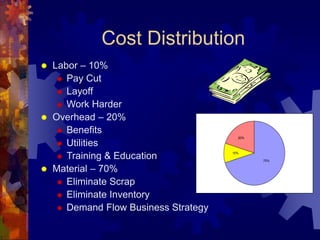
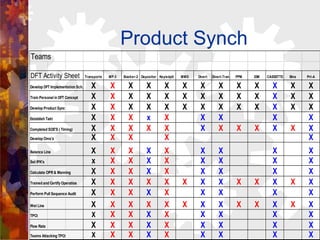
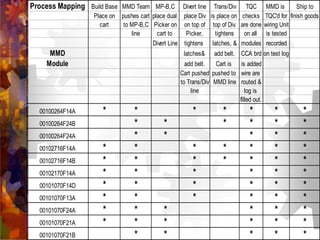
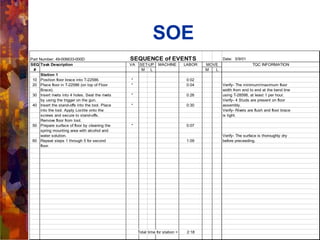
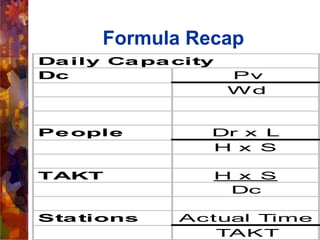
This document provides an overview and introduction to demand flow technology (DFT) principles and techniques for lean manufacturing. It discusses key DFT concepts like total product cycle time, takt time, line balancing, kanban systems, mixed model production, and measuring production linearity. The objectives are to develop knowledge of DFT philosophies and techniques, understand the total business strategy, and learn how to establish and perform the skills like setting operational standards and synchronizing production processes.