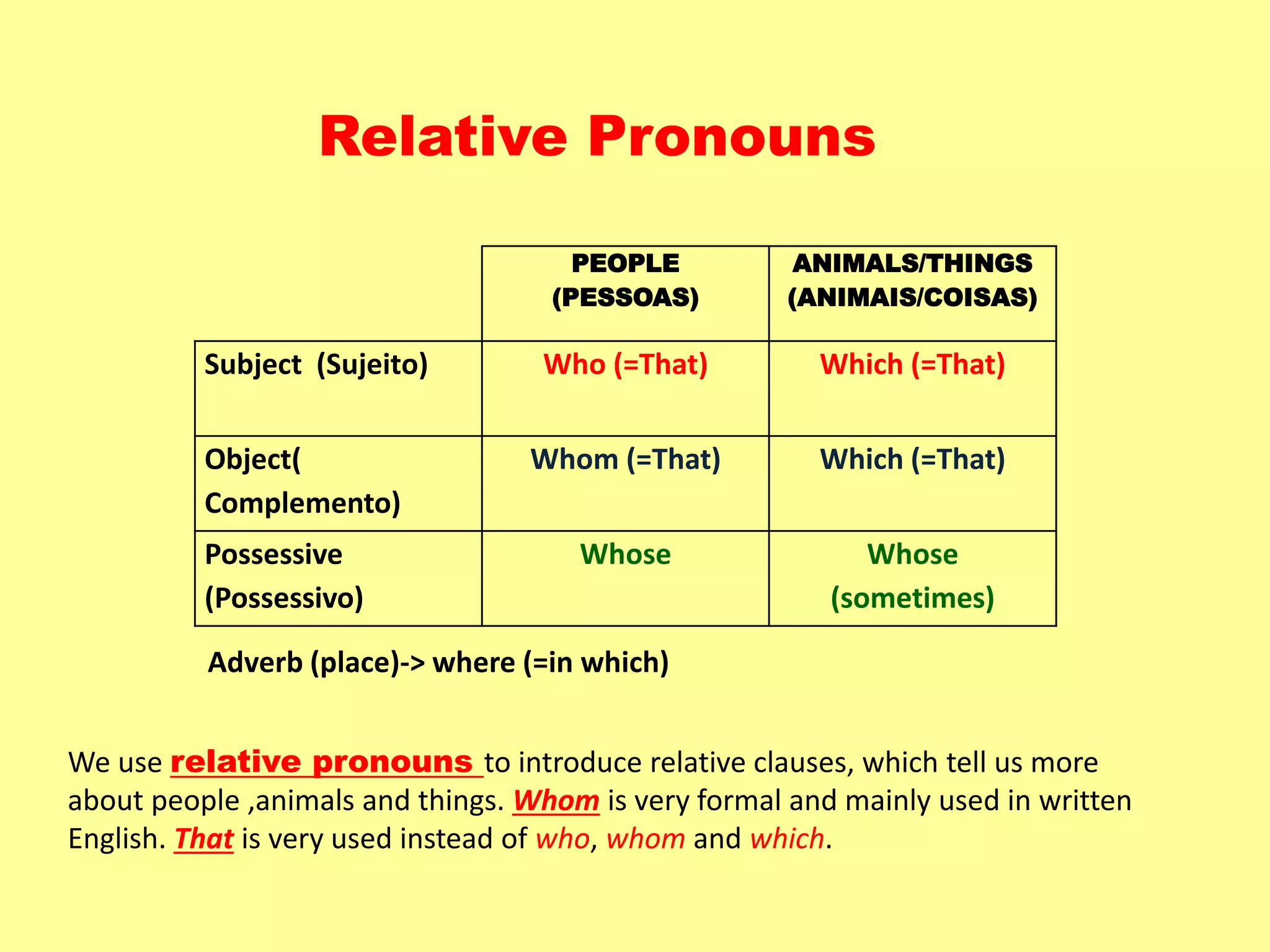
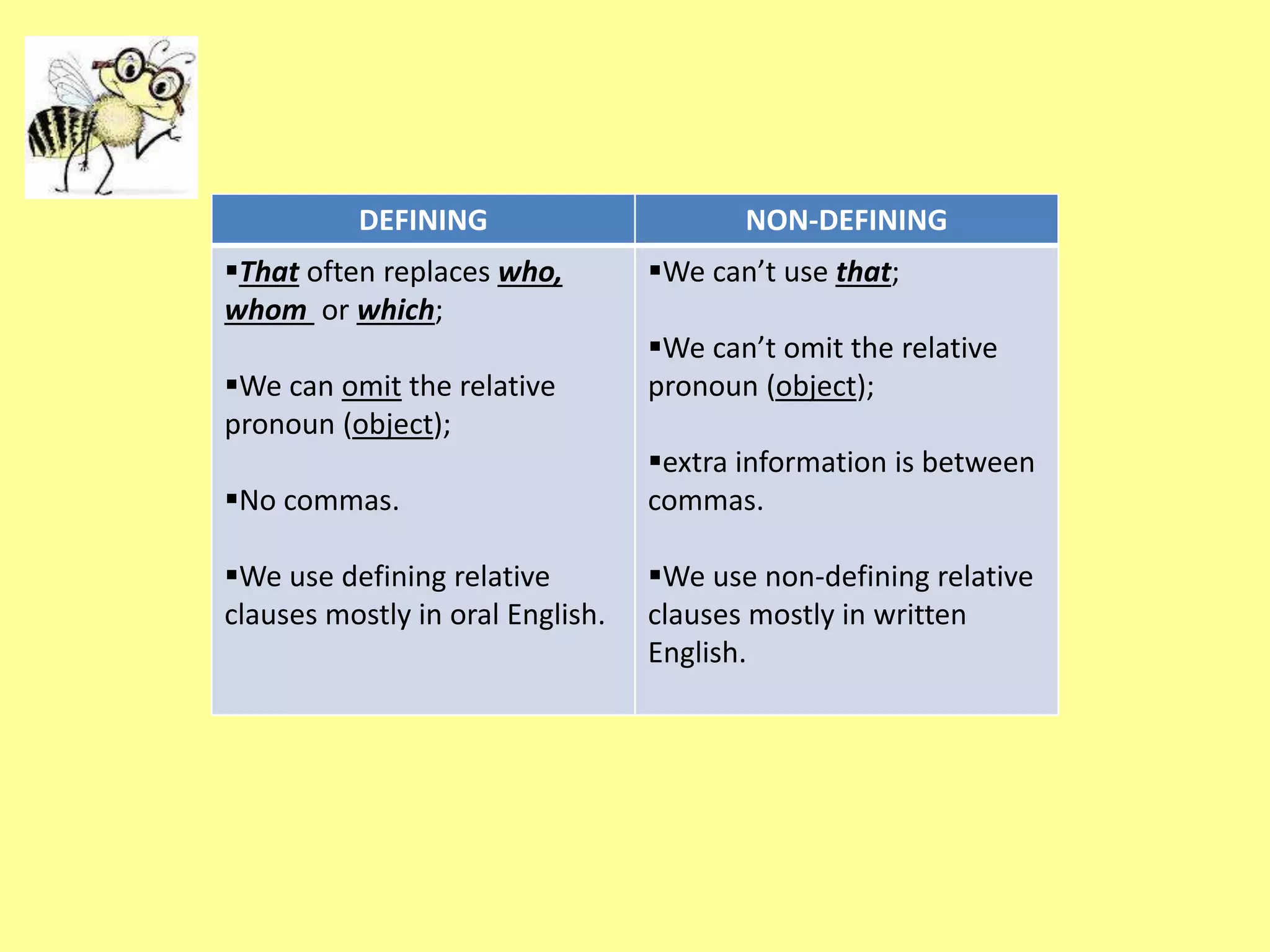
This document discusses relative clauses and relative pronouns. It provides examples of defining and non-defining relative clauses using who, whom, whose, which, that and where. Defining relative clauses identify a specific person or thing, while non-defining clauses provide extra information. Relative pronouns introduce the relative clause and the correct one to use depends on whether the antecedent is a person, animal or thing, and if it is the subject or object of the relative clause.